Menthofuran
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Menthofuran is an organic compound found in a variety of essential oils including that of pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium). It is highly toxic and believed to be the primary toxin in pennyroyal responsible for its potentially fatal effects.[1] After ingestion of menthofuran, it is metabolically activated to chemically reactive intermediates that are hepatotoxic.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
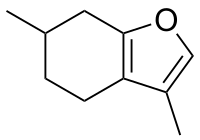
3,6-Dimethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzofuran | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.087 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O | |
| Molar mass | 150.221 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 208 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 86 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Biosynthesis
Menthofuran is produced biosynthetically from pulegone by the enzyme menthofuran synthase.
Chemistry
Synthesis
Menthofuran can be synthesized from 5-methylcyclohexane-1,3-dione and allenyldimethylsulfonium bromide in two steps via a furannulation strategy consisting of enolate addition and rearrangement.[3]
Pharmacology
Menthofuran is a metabolite of pulegone. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have found the pulegone metabolite menthofuran to be an inhibitor of CYP2A6.[4][5][6][7]
Menthofuran may deplete glutathione levels, leaving hepatocytes vulnerable to free radical damage.[5]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

