Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Median aperture
Structure within the human brain From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
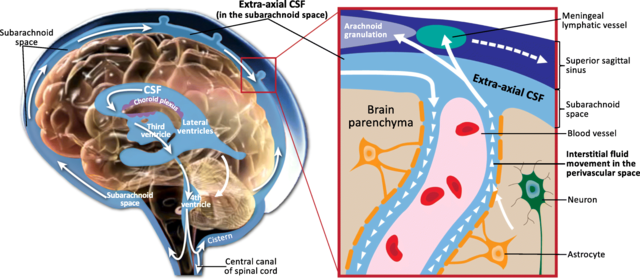
The median aperture (median aperture of fourth ventricle or foramen of Magendie) is an opening at the caudal portion of the roof of the fourth ventricle.[1] It allows the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna.[2][3] The other openings of the fourth ventricle are the lateral apertures - one on either side.[4] The median aperture varies in size but accounts for most of the outflow of CSF from the fourth ventricle. [1]
Remove ads
Structure
Relations
The median foramen on axial images is posterior to the pons and anterior to the caudal cerebellum. It is surrounded by the obex and gracile tubercles of the medulla, tela choroidea of the fourth ventricle and its choroid plexus, which is attached to the cerebellar vermis.[4][5]
Eponym
The foramen of Magendie is named for François Magendie, who first described it.[6] The term "foramen of Magendie" is commonly used, and this opening is frequently described and illustrated as a foramen in the inferior roof of the fourth ventricle. However, the opening is an aperture, rather than a foramen.[5]
Additional images
- Median aperture
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads


