List of organisms by chromosome count
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The list of organisms by chromosome count describes ploidy or numbers of chromosomes in the cells of various plants, animals, protists, and other living organisms. This number, along with the visual appearance of the chromosome, is known as the karyotype,[1][2][3] and can be found by looking at the chromosomes through a microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics.[4] The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics.
| Organism (B SULLAR) |
Chromosome number | Picture | Karyotype | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jack jumper ant (Myrmecia pilosula) |
2/1 |  | 2 for females, males are haploid and thus have 1; smallest number possible. Other ant species have more chromosomes.[5] | [5] | |
| Myrmecia croslandi | 2/1 | 2 for females, males are haploid and thus have 1; smallest number possible.[6] | [6] | ||
| Spider mite (Tetranychidae) |
4–14 |  | Spider mites (family Tetranychidae) are typically haplodiploid (males are haploid, while females are diploid)[7] | [7] | |
| Cricotopus sylvestris | 4 |  | [8] | ||
| Oikopleura dioica | 6 |  | [9] | ||
| Yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) |
6 |  |  |
The 2n=6 chromosome number is conserved in the entire family Culicidae, except in Chagasia bathana, which has 2n=8.[10] | [10] |
| Indian muntjac (Muntiacus muntjak) |
6/7 |  |  |
2n = 6 for females and 7 for males. The lowest diploid chromosomal number in mammals.[11] | [12] |
| Hieracium | 8 |  | |||
| Fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) |
8 |  |  |
6 autosomal and 2 allosomic (sex) | [13] |
| Macrostomum lignano | 8 |  |
[14] | ||
| Marchantia polymorpha | 9 |  |  |
Typically haploid with dominant gametophyte stage. 8 autosomes and 1 allosome (sex chromosome). The sex-determination system used by this species and most other bryophytes is called UV. Spores can carry either the U chromosome, which results in female gametophytes, or the V chromosome, which results in males. The chromosome number n = 9 is the basic number in many species of Marchantiales. In some species of Marchantiales, plants with various ploidy levels (having 18 or 27 chromosomes) were reported, but this is rare in nature. | [15] |
| Thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana) |
10 |  |  |
||
| Swamp wallaby (Wallabia bicolor) |
10/11 |  |  |
11 for male, 10 for female | [16] |
| Australian daisy (Brachyscome dichromosomatica) |
12 |  | This species can have more B chromosomes than A chromosomes at times, but 2n=4. | [17] | |
| Nematode (Caenorhabditis elegans) |
12/11 |  |
12 for hermaphrodites, 11 for males | ||
| Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) |
12 |  |  |
[18] | |
| Broad bean (Vicia faba) |
12 |  |  |
[19] | |
| Yellow dung fly (Scathophaga stercoraria) |
12 |  |  |
10 autosomal and 2 allosomic (sex) chromosomes. Males have XY sex chromosomes and females have XX sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are the largest chromosomes and constitute 30% of the total length of the diploid set in females and about 25% in males.[20] | [20] |
| Slime mold (Dictyostelium discoideum) |
12 |  | [21] | ||
| Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) |
14 |  | [22] | ||
| Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii) |
14 |  |  |
||
| Rye (Secale cereale) |
14 |  | [23] : 108 | ||
| Pea (Pisum sativum) |
14 |  |  |
[23] : 172 | |
| Barley (Hordeum vulgare) |
14 |  |  |
[24] | |
| Aloe vera | 14 |  |  |
The diploid chromosome number is 2n = 14 with four pair of long acrocentric chromosomes ranging from 14.4 μm to 17.9 μm and three pair of short sub metacentric chromosomes ranging from 4.6 μm to 5.4 μm.[25] | [25] |
| Koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) |
16 |  | |||
| Kangaroo | 16 |  | This includes several members of genus Macropus, but not the red kangaroo (M. rufus, 20) | [26] | |
| Botryllus schlosseri | 16 |  | [27] | ||
| Schistosoma mansoni | 16 |  |  |
2n=16. 7 autosomal pairs and ZW sex-determination pair.[28] | [28] |
| Welsh onion (Allium fistulosum) |
16 |  |  |
[29] | |
| Garlic (Allium sativum) |
16 |  |  |
[29] | |
| Itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei) |
17/18 |  |  |
According to the observation of embryonic cells of egg, chromosome number of the itch mite is either 17 or 18. While the cause for the disparate numbers is unknown, it may arise because of an XO sex determination mechanism, where males (2n=17) lack the sex chromosome and therefore have one less chromosome than the female (2n=18).[30] | [30] |
| Radish (Raphanus sativus) |
18 |  | [23] : 60 | ||
| Carrot (Daucus carota) |
18 |  |  |
The genus Daucus includes around 25 species. D. carota has nine chromosome pairs (2n = 2x = 18). D. capillifolius, D. sahariensis and D. syrticus are the other members of the genus with 2n = 18, whereas D. muricatus (2n = 20) and D. pusillus (2n = 22) have a slightly higher chromosome number. A few polyploid species as for example D. glochidiatus (2n = 4x = 44) and D. montanus (2n = 6x = 66) also exist.[31] | [31] |
| Cabbage (Brassica oleracea) |
18 |  |  |
Broccoli, cabbage, kale, kohlrabi, brussels sprouts, and cauliflower are all the same species and have the same chromosome number.[23]: 49 | [23] : 49 |
| Citrus (Citrus) |
18 |  | Chromosome number of the genus Citrus, which including lemons, oranges, grapefruit, pomelo and limes, is 2n = 18.[32] | [33] | |
| Passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) |
18 | [34] | |||
| Setaria viridis (Setaria viridis) |
18 |  | [35] | ||
| Maize (Zea mays) |
20 |  | [23] : 128 | ||
| Cannabis (Cannabis sativa) |
20 |  | |||
| Western clawed frog (Xenopus tropicalis) |
20 |  |  |
[36] | |
| Australian pitcher plant (Cephalotus follicularis) |
20 |  | [37] | ||
| Cacao (Theobroma cacao) |
20 |  |  |
[38] | |
| Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus) |
22 |  | Although some contradictory cases have been reported, the large homogeneity of the chromosome number 2n = 22 is now known for 135 (33.5%) distinct species among genus Eucalyptus.[39] | [40] | |
| Virginia opossum (Didelphis virginiana) |
22 |  |
[41] | ||
| Bean (Phaseolus sp.) |
22 |  |  |
All species in the genus Phaseolus have the same chromosome number, including common bean (P. vulgaris), runner bean (P. coccineus), tepary bean (P. acutifolius) and lima bean (P. lunatus).[23]: 168 | [23] : 168 |
| Snail | 24 |  | |||
| Melon (Cucumis melo) |
24 |  |  |
[42] | |
| Rice (Oryza sativa) |
24 |  |  |
[23] : 98 | |
| Silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium) |
24 |  | [43] | ||
| Sweet chestnut (Castanea sativa) |
24 |  |  |
[44] | |
| Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) |
24 |  |  |
[45] | |
| European beech (Fagus sylvatica) |
24 |  |  |
[46] | |
| Bittersweet nightshade (Solanum dulcamara) |
24 |  | [47][48] | ||
| Cork oak (Quercus suber) |
24 |  |  |
[49] | |
| Edible frog (Pelophylax kl. esculentus) |
26 |  |  |
Edible frog is the fertile hybrid of the pool frog and the marsh frog.[50] | [51] |
| Axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) |
28 |  |  |
[52] | |
| Bed bug (Cimex lectularius) |
29–47 |  | 26 autosomes and varying number of the sex chromosomes from three (X1X2Y) to 21 (X1X2Y+18 extra Xs).[53] | [53] | |
| Pill millipede (Arthrosphaera magna attems) |
30 |  | [54] | ||
| Giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) |
30 |  |  |
[55] | |
| American mink (Neogale vison) |
30 |  | |||
| Pistachio (Pistacia vera) |
30 |  | [56] | ||
| Japanese oak silkmoth (Antheraea yamamai) | 31 |  |
 |
[57] | |
| Baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) |
32 |  | |||
| European honey bee (Apis mellifera) |
32/16 |  |  |
32 for females (2n = 32), males are haploid and thus have 16 (1n =16).[58] | [58] |
| American badger (Taxidea taxus) |
32 |  | |||
| Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) |
32 |  |  |
Cultivated alfalfa is tetraploid, with 2n=4x=32. Wild relatives have 2n=16.[23]: 165 | [23]: 165 |
| Red fox (Vulpes vulpes) |
34 |  | Plus 0-8 B chromosomes. | [59] | |
| Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) |
34 |  |  |
[60] | |
| Porcupine (Erethizon dorsatum) |
34 |  | [61] | ||
| Globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus) |
34 |  |  |
[62] | |
| Yellow mongoose (Cynictis penicillata) |
36 |  | |||
| Tibetan sand fox (Vulpes ferrilata) |
36 |  | |||
| Starfish (Asteroidea) |
36 |  | |||
| Red panda (Ailurus fulgens) |
36 |  | |||
| Meerkat (Suricata suricatta) |
36 |  | |||
| Cassava (Manihot esculenta) |
36 |  |
[63] | ||
| Long-nosed cusimanse (Crossarchus obscurus) |
36 |  | |||
| Earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) |
36 |  | |||
| African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) |
36 |  |  |
[36] | |
| Waterwheel plant (Aldrovanda vesiculosa) |
38 |  | [37] | ||
| Tiger (Panthera tigris) |
38 |  |  |
||
| Sea otter (Enhydra lutris) |
38 |  | |||
| Sable (Martes zibellina) |
38 | ||||
| Raccoon (Procyon lotor) |
38 |  | [64] | ||
| Pine marten (Martes martes) |
38 |  | |||
| Pig (Sus) |
38 |  |  |
||
| Oriental small-clawed otter (Aonyx cinerea) |
38 |  | |||
| Lion (Panthera leo) |
38 |  | |||
| Fisher (Pekania pennanti) |
38 |  | a type of marten | ||
| European mink (Mustela lutreola) |
38 |  | |||
| Coatimundi | 38 |  | |||
| Cat (Felis catus) |
38 |  |  |
||
| Beech marten (Martes foina) |
38 |  | |||
| Baja California rat snake (Bogertophis rosaliae) |
38 |  | [65] | ||
| American marten (Martes americana) |
38 |  | |||
| Trans-Pecos ratsnake (Bogertophis subocularis) |
40 |  | [66] | ||
| Mouse (Mus musculus) |
40 |  |  |
[67] | |
| Mango (Mangifera indica) |
40 |  | [23] : 7 | ||
| Hyena (Hyaenidae) |
40 |  | |||
| Ferret (Mustela furo) |
40 |  | |||
| European polecat (Mustela putorius) |
40 |  | |||
| American beaver (Castor canadensis) |
40 |  | |||
| Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) |
40 |  |  |
Cultivated peanut is an allotetraploid (2n = 4x = 40). Its closest relatives are the diploid (2n = 2x = 20).[68] | [68] |
| Wolverine (Gulo gulo) |
42 |  | |||
| Wheat (Triticum aestivum) |
42 |  |  |
This is a hexaploid with 2n=6x=42. Durum wheat is Triticum turgidum var. durum, and is a tetraploid with 2n=4x=28.[23]: 120 | [23] : 120 |
| Rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) |
42 |  |  |
[69] | |
| Rat (Rattus norvegicus) |
42 |  |  |
[70] | |
| Oats (Avena sativa) |
42 |  |  |
This is a hexaploid with 2n=6x=42. Diploid and tetraploid cultivated species also exist.[23]: 87 | [23] : 87 |
| Giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) |
42 |  | |||
| Fossa (Cryptoprocta ferox) |
42 |  | |||
| European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) |
44 |  |  |
||
| Eurasian badger (Meles meles) |
44 |  | |||
| Moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) |
44 |  | [71] | ||
| Dolphin (Delphinidae) |
44 |  | |||
| Arabian coffee (Coffea arabica) |
44 |  |  |
Out of the 103 species in the genus Coffea, arabica coffee is the only tetraploid species (2n = 4x = 44), the remaining species being diploid with 2n = 2x = 22.[72] | |
| Reeves's muntjac (Muntiacus reevesi) |
46 |  | |||
| Human (Homo sapiens) |
46 |  |  |
44 autosomal. and 2 allosomic (sex) | [73] |
| Olive
(Olea Europaea) |
46 |  |
|||
| Nilgai (Boselaphus tragocamelus) |
46 |  |
[74] | ||
| Parhyale hawaiensis | 46 |  |  |
[75] | |
| Water buffalo (swamp type) (Bubalus bubalis) |
48 |  | |||
| Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) |
48 |  |  |
Cultivated species N. tabacum is an amphidiploid (2n=4x=48) evolved through the interspecific hybridization of the ancestors of N. sylvestris (2n=2x=24, maternal donor) and N. tomentosiformis (2n=2x=24, paternal donor) about 200,000 years ago.[76] | [76] |
| Potato (Solanum tuberosum) |
48 |  |  |
This is for common potato Solanum tuberosum (tetraploid, 2n = 4x = 48). Other cultivated potato species may be diploid (2n = 2x = 24), triploid (2n = 3x = 36), tetraploid (2n = 4x = 48), or pentaploid (2n = 5x = 60).[77] Wild relatives mostly have 2n=24.[23]: 279 | [77] |
| Orangutan (Pongo) |
48 |  |  |
||
| Hare (Lepus) |
48 |  | [78][79] | ||
| Gorilla (Gorilla) |
48 |  | |||
| Deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) |
48 |  | |||
| Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) |
48 |  |  |
[80] | |
| Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber) |
48 |  | |||
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) |
50 |  |
[81] | ||
| Woodland hedgehogs Erinaceus |
48 |  | [82] | ||
| African hedgehogs Atelerix |
48 |  | [83] | ||
| Water buffalo (Riverine type) (Bubalus bubalis) |
50 |  |  |
||
| Striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis) |
50 |  | |||
| Pineapple (Ananas comosus) |
50 |  | [23] : 15 | ||
| Kit fox (Vulpes macrotis) |
50 |  | |||
| Spectacled bear (Tremarctos ornatus) |
52 |  | |||
| Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) |
52 |  |  |
Ten sex chromosomes. Males have X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5Y5, females have X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5.[84] | [85] |
| Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) |
52 |  |  |
This is for the cultivated species G. hirsutum (allotetraploid, 2n=4x=52). This species accounts for 90% of the world cotton production. Among 50 species in the genus Gossypium, 45 are diploid (2n = 2x = 26) and 5 are allotetraploid (2n = 4x = 52).[86] | [86] |
| Sheep (Ovis aries) |
54 |  |  |
||
| Hyrax (Hyracoidea) |
54 |  |  |
Hyraxes were considered to be the closest living relatives of elephants,[87] but sirenians have been found to be more closely related to elephants. | [88] |
| Raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides procyonoides) |
54 |  |  |
This number is for common raccoon dog (N. p. procyonoides), 2n=54+B(0–4). On the other hand, Japanese raccoon dog (N. p. viverrinus) with 2n=38+B(0–8). Here, B represents B chromosome and its variation in the number between individuals.[89][90] | [89] |
| Capuchin monkey (Cebinae) |
54 |  | [91] | ||
| Silkworm (Bombyx mori) |
56 |  | 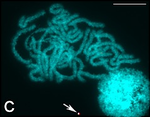 |
This is for the species mulberry silkworm, B. mori (2n=56). Probably more than 99% of the world's commercial silk today come from this species.[92] Other silk producing moths, called non-mulberry silkworms, have various chromosome numbers. (e.g. Samia cynthia with 2n=25–28,[93] Antheraea pernyi with 2n=98.[94]) | [95] |
| Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) |
56 |  |  |
This number is octoploid, main cultivated species Fragaria × ananassa (2n = 8x = 56). In genus Fragaria, basic chromosome number is seven (x = 7) and multiple levels of ploidy, ranging from diploid (2n = 2x = 14) to decaploid (F. iturupensis, 2n = 10x = 70), are known.[96] | [96] |
| Gaur (Bos gaurus) |
56 |  | |||
| Elephant (Elephantidae) |
56 |  | |||
| †Woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius) |
58 |  | extinct; tissue from a frozen carcass | ||
| Domestic yak (Bos grunniens) |
60 |  | |||
| Goat (Capra hircus) |
60 |  |  |
||
| Cattle (Bos taurus) |
60 |  |  |
||
| American bison (Bison bison) |
60 |  | |||
| Sable antelope (Hippotragus niger) |
60 |  | [97] | ||
| Bengal fox (Vulpes bengalensis) |
60 |  | |||
| Gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar dispar) |
62 |  | |||
| Donkey (Equus asinus) |
62 |  | |||
| Scarlet macaw (Ara macao) |
62–64 |  |  |
[98] | |
| Mule | 63 |  | semi-infertile (odd number of chromosomes – between donkey (62) and horse (64) makes meiosis much more difficult) | ||
| Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus) |
64 |  |  |
||
| Spotted skunk (Spilogale x) |
64 |  | |||
| Horse (Equus caballus) |
64 |  |  |
||
| Fennec fox (Vulpes zerda) |
64 |  | [99] | ||
| Echidna (Tachyglossidae) |
63/64 |  | 63 (X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5, male) and 64 (X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5, female)[100] | ||
| Chinchilla (Chinchilla lanigera) |
64 |  | [61] | ||
| Nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) |
64 |  |  |
[101] | |
| Gray fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus) |
66 |  | [99] | ||
| Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
68 |  | |||
| Elk (wapiti) (Cervus canadensis) |
68 |  | |||
| Roadside hawk (Rupornis magnirostris) |
68 |  | [102] | ||
| White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) |
70 |  | |||
| Black nightshade (Solanum nigrum) |
72 |  | [103] | ||
| Tropical blue bamboo (Bambusa chungii) |
64–72 |  | [104] | ||
| Bat-eared fox (Otocyon megalotis) |
72 |  | [99] | ||
| Sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) |
74 |  | |||
| Sloth bear (Melursus ursinus) |
74 |  | |||
| Polar bear (Ursus maritimus) |
74 |  | |||
| Brown bear (Ursus arctos) |
74 |  | |||
| Asian black bear (Ursus thibetanus) |
74 |  | |||
| American black bear (Ursus americanus) |
74 |  | |||
| Bush dog (Speothos venaticus) |
74 |  | |||
| Maned wolf (Chrysocyon brachyurus) |
76 |  | |||
| Gray wolf (Canis lupus) |
78 |  | |||
| Golden jackal (Canis aureus) |
78 |  | [99] | ||
| Dove (Columbidae) |
78 |  | Based on African collared dove | [105] | |
| Dog (Canis familiaris) |
78 |  |  |
Normal dog karyotype is composed of 38 pairs of acrocentric autosomes and two metacentric sex chromosomes.[106][107] | [108] |
| Dingo (Canis familiaris) |
78 |  | [99] | ||
| Dhole (Cuon alpinus) |
78 |  | |||
| Coyote (Canis latrans) |
78 |  | [99] | ||
| Chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) |
78 |  | |||
| African wild dog (Lycaon pictus) |
78 |  | [99] | ||
| Tropical pitcher plant (Nepenthes rafflesiana) |
78 |  | [37] | ||
| Turkey (Meleagris) |
80 |  | [109] | ||
| Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) |
80 |  |  |
This is for S. officinarum (octoploid, 2n = 8× = 80).[110] About 70% of the world's sugar comes from this species.[111] Other species in the genus Saccharum, collectively known as sugarcane, have chromosome numbers in the range 2n=40–128.[112] | [110] |
| Pigeon (Columbidae) |
80 |  | [113] | ||
| Azure-winged magpie (Cyanopica cyanus) |
80 |  |
[114] | ||
| Great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) |
82 |  | [115] | ||
| Bloody crane's-bill (Geranium sanguineum) |
84 |  | [116] | ||
| Moonworts (Botrychium) |
90 |  | |||
| Grape fern (Sceptridium) |
90 |  | |||
| Pittier's crab-eating rat (Ichthyomys pittieri) |
92 |  | Previously thought to be the highest number in mammals, tied with Anotomys leander. | [117] | |
| Prawn (Penaeus semisulcatus) |
86–92 |  | [118] | ||
| Aquatic rat (Anotomys leander) |
92 |  | Previously thought to be the highest number in mammals, tied with Ichthyomys pittieri. | [117] | |
| Kamraj (fern) (Helminthostachys zeylanica) |
94 |  | |||
| Crucian carp (Carassius carassius) |
100 |  |  |
[119] | |
| Red viscacha rat (Tympanoctomys barrerae) |
102 |  |  |
Highest number known in mammals, thought to be a tetraploid[120] or allotetraploid.[121] | [122] |
| Walking catfish (Clarias batrachus) |
104 |  |  |
[123] | |
| American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) |
120 |  | [124] | ||
| Limestone fern (Gymnocarpium robertianum) |
160 |  | Tetraploid (2n = 4x = 160) | [125] | |
| African baobab (Adansonia digitata) |
168 |  | Also known as the "tree of life". 2n = 4x = 168 | [126] | |
| Northern lampreys (Petromyzontidae) |
174 |  | [127] | ||
| Rattlesnake fern (Botrypus virginianus) |
184 |  | [128] | ||
| Red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) |
208 |  | |||
| Field horsetail (Equisetum arvense) |
216 |  | |||
| Agrodiaetus butterfly (Agrodiaetus shahrami) |
268 |  | This insect has one of the highest chromosome numbers among all animals. | [129] | |
| Black mulberry (Morus nigra) |
308 |  | Highest ploidy among plants, 22-ploid (2n = 22x = 308)[130] | [131] | |
| Atlas blue (Polyommatus atlantica) |
448–452 |  |  |
2n = c. 448–452. Highest number of chromosomes in the non-polyploid eukaryotic organisms.[132] | [132] |
| Adders-tongue (Ophioglossum reticulatum) |
1260 |  | n=120–720 with a high degree of polyploidization.[133] Ophioglossum reticulatum n=720 in hexaploid species, 2n=1260 in decaploid species.[134] | ||
| Ciliated protozoa (Tetrahymena thermophila) |
10 (in micronucleus) |  | 50x = 12,500 (in macronucleus, except minichromosomes) 10,000x = 10,000 (macronuclear minichromosomes)[135] |
||
| Ciliated protozoa (Sterkiella histriomuscorum) |
16000[136] |  | Macronuclear "nanochromosomes"; ampliploid. MAC chromosomes × 1900 ploidy level = 2.964 × 107 chromosomes | [137][138][139] |
- Karyotype of a human being. It shows 22 homologous autosomal chromosome pairs, both the female (XX) and male (XY) versions of the two sex chromosomes, as well as the mitochondrial genome (at bottom left).
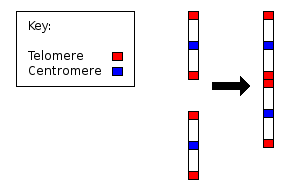
- Fusion of ancestral chromosomes left distinctive remnants of telomeres, and a vestigial centromere. As other non-human extant hominidae have 48 chromosomes it is believed that the human chromosome 2 is the result of the merging of two chromosomes.[140]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.