List of islands of Japan
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Japan is an island country of 14,125 islands, of which approximately 260 are inhabited.[1][2] Japan is the third-largest island country in the world, behind Indonesia and Madagascar.[3] Japan is also the second-most-populous island country in the world, only behind Indonesia.

According to a survey conducted by the Japan Coast Guard in 1987, the number of islands in Japan was 6,852. At that time, the survey only counted islands with coastlines of 100 meters or more that were shown on paper maps. On February 28, 2023, the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan announced that the number of islands had been updated to 14,125 through a recount using digital maps. Since there is no international standard for counting islands, only islands with a coastline of 100 meters or more were counted, as in the past. According to the GSI, advances in surveying technology and the detailed representation of topographic features through digital mapping contributed to this announcement.[4][1]
Japanese archipelago
Summarize
Perspective
Main islands
The four main islands of Japan are:[5][6]
- Hokkaido – the northernmost and second largest main island, third most populous.
- Honshu – the largest and most populous island, with the capital Tokyo. Honshu is connected to the other three main islands by bridges and tunnels.
- Kyushu – the third largest main island, second most populous and the nearest to the Asian continent.
- Shikoku – the smallest and least populous main island, located between Honshu and Kyushu.
Hokkaido prefecture
Islands of Honshu in the Sea of Japan
Islands in Tokyo Bay
- Dream Island (Yume No Shima)
- Odaiba (artificial island)
- Sarushima (natural)
- Jonan Island
- Heiwa Island
- Showa Island
- Keihin Island
- Tokyo International Airport (artificial island)
- Katsushima
- Hakkeijima
- Higashi Ogijima
- Wakasu
- Oogishima
- Ukishima
Islands in Osaka Bay
- Maishima
- Yumeshima
- Sakishima
- Kansai International Airport (artificial island)
- Kobe Airport (artificial island)
- Port Island
- Rokkō Island
- Minami Ashiyahama
- Wakayama Marina City
- Nishinomiyahama
Islands in Ise Bay
- Chūbu Centrair International Airport (artificial island)
- Kami-shima
- Kashiko Island
- Kozukumi Island
- Mikimoto Pearl Island
Islands in Mutsu Bay
Nanpō Islands (Nanpō Shotō)
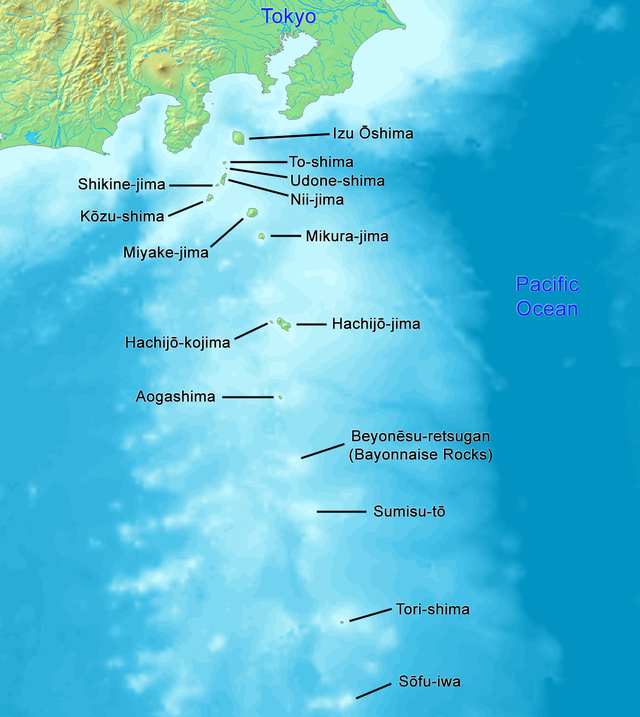

- Kazan Rettō (Volcano Islands)
- Nishinoshima
- Kita Iwo Jima (North Iwo Jima)
- Iwo Jima[15]
- Minami Iwo Jima (South Iwo Jima)
Other Japanese islands
- Minami Torishima (Marcus Island)
- Enoshima
- Okino Torishima (Parece Vela)
Islands around Kyushu
Most of these are located in the East China Sea.
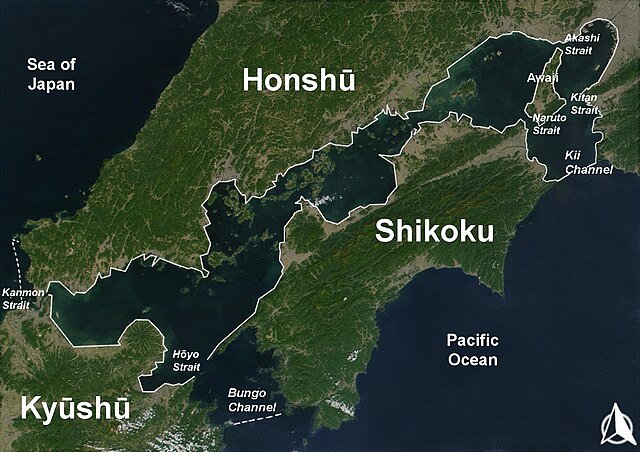
Islands around Shikoku
Ryukyu Islands (Nansei-shotō)

Satsunan Islands
The northern half is administratively part of Kagoshima Prefecture and Kyushu.
Ōsumi Islands
The North-Eastern Group:
The North-Western Group:
Tokara Islands
The Shichi-tō:
Amami Islands
Ryukyu Islands (Ryūkyū-shotō)
The Southern Half, Okinawa Prefecture
Okinawa Islands
The Central Group or Ryukyu proper:
Sakishima Islands
Also known as the Further Isles:
- Miyako Islands
- Yaeyama Islands
- Senkaku Islands - controlled by Japan, disputed by China and Taiwan.
Seto Inland Sea islands
- Kasaoka Islands
- Takashima Island (Okayama) 高島 (岡山県笠岡市)
- Shiraishi Island
- Kitagi Island, 北木島
- Obishi Island, 大飛島
- Kobi Island, 小飛島
- Manabeshima, 真鍋島
- Mushima Island (Okayama), 六島 (岡山県)
- Shiwaku Islands
- Awaji[9]
- Etajima
- Kurahashi-jima
- Inujima
- Itsukushima (popularly known as "Miyajima")
- Shōdoshima
- Naoshima Islands
- Suō-Ōshima, Yamaguchi
- Himeshima, Ōita
- Aoshima, Ehime
- Hashira Island
- Okamura Island
- Ōshima (Ehime)
- Mukaishima Island, Hiroshima
- Ōmishima Island, Ehime
- Ōkunoshima (often called "Rabbit Island")
Islands in lakes
- Daikon-island
- Bentenjima in Lake Tōya
- Bentenjima in Lake Hamana
Other artificial islands
- Chūbu Centrair International Airport
- Dejima[8]
- New Kitakyushu Airport
- Midori No Shima, off Hakodate (artificial)
- Malimpia Okinosu (artificial)
- Wakaejima (artificial)
- Island City, Fukuoka (artificial)
Claims but does not control

The Northern Territories
There are four disputed Kuril Islands that are controlled by Russia and claimed by Japan. These islands are called the Chishima Islands.[18]
- Iturup - Etorofu (択捉島, Etorofu-tō)
- Kunashir - Kunashiri (国後島, Kunashiri-tō)
- Shikotan - Shikotan (色丹島, Shikotan-tō)
- Habomai Islands - Habomai (歯舞群島, Habomai-guntō)

Others
- Liancourt Rocks (Dokdo/Takeshima) - controlled by South Korea, disputed by Japan. North Korea also claims Dokdo belongs to North Korea, and blasts Japan for its claim over Dokdo.[19]
Former
- South Seas Mandate (1919–1947) - part of the Japanese colonial empire until its defeat in 1945. Formally revoked by the United Nations in 1947. The Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands later became a U.S. territory.
- Taiwan and Penghu (1895–1952) - part of the Japanese colonial empire until its defeat in 1945. Returned to the Republic of China in 1945 but unrecognized by the Allies. All claims relinquished by the Treaty of San Francisco signed in 1951.
- Karafuto (1905–1949) - the southern half of the island of Sakhalin, controlled by Japan after the Russo-Japanese War. Japan lost control of Karafuto after its invasion by the Soviet Union during World War II. Formally abolished as a legal entity by Japan in 1949. Japan in addition controlled the northern half of Sakhalin between 1920 and 1925, during and after the Russian Civil War.
- Jeju Island (1910–1945) - part of Korea, annexed by Japanese colonial empire until its defeat in 1945.
Largest islands of Japan
Summarize
Perspective
These are the 50 largest islands of Japan. It excludes the disputed Kuril islands known as the northern territories.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

