Outline of cardiology
Overview of and topical guide to cardiology From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart.[1] The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.
What type of thing is cardiology?
Cardiology can be described as all of the following:
- An academic discipline
- Branch of science
- Branch of applied science
- Branch of medicine
- Branch of internal medicine
- Branch of medicine
- Branch of applied science
Branches of cardiology
- Adult cardiology –
- Cardiac electrophysiology – study of the electrical properties and conduction diseases of the heart.
- Clinical cardiac electrophysiology –Clinical cardiac electrophysiology, is a branch of the medical specialty of cardiology and is concerned with the study and treatment of rhythm disorders of the heart. Cardiologists with expertise in this area are usually referred to as electrophysiologists. Electrophysiologists are trained in the mechanism, function, and performance of the electrical activities of the heart.
- Cardiogeriatrics (geriatric cardiology) –Cardiogeriatrics, or geriatric cardiology, is the branch of cardiology and geriatric medicine that deals with the cardiovascular disorders in elderly people.
- Echocardiography – use of ultrasound to study the mechanical function/physics of the heart.
- Interventional cardiology – use of catheters for the treatment of structural and ischemic diseases of the heart.
- Nuclear cardiology – use of nuclear medicine to visualize the uptake of an isotope by the heart using radioactive sources.
- Cardiac electrophysiology – study of the electrical properties and conduction diseases of the heart.
- Pediatric cardiology – Pediatric cardiologists specialize in diagnosing and treating heart problems in children.
Anatomy of the heart
Heart –
Physical exam
The cardiac physical exam focuses on portions of the physical exam that elucidate information about diseases and disorders outlined below. Clinical judgment, of course, should guide the physical exam but the following are pertinent things related to a general / broad cardiac exam.
- Apex beat (point of maximum impulse)
- Bruits: carotid, renal
- Edema of the lower extremities and ascites that may indicate right heart failure
- Heart sounds, heart murmurs, pericardial rub, mechanical heart valve clicking
- Jugular venous distension
- Retina exam with ophthalmoscope for signs of hypertension (retinal hemorrhage) and diabetic retinopathy (cotton wool spots)
- Pulses: carotid, dorsalis pedis, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial, radial, temporal, ulnar
- Heart rate
- Pulse quality: pulsus paradoxus, pulsus parvus et tardus
- Respiratory sounds for crackles (edema) and other lung pathologies that can affect the heart
- Rheumatic diseases can have significant cardiac findings and is too lengthy to include here
- Arthritis is common amongst rheumatic diseases
- Skin exam for rashes (systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, vasculitis)
- Skin exam
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Endocarditis signs: Janeway lesions, Osler's nodes, splinter hemorrhages
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Scars indicating procedures: sternotomy, thoracotomy, pericardial window, carotid endarterectomy, thyroidectomy, etc.
- Skin bulges indicating implanted devices: pacemaker, ICD, implantable loop recorder, vagus nerve stimulation
- Vasculitis rashes
- Xanthomas & xanthelasmas
- Vital signs
- Blood pressure – hypertension, congenital heart disease manifestations
- Heart rate – bradycardia & tachycardia
- Respiratory rate – in distress, shortness of breath causes
Heart disorders
- Hypertension – elevated blood pressure above "normal." Long term high blood pressure is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, vision loss, and chronic kidney disease.[2][3] Lowering blood pressure is key for preventing these diseases.
- Types of hypertension
- Essential hypertension – Hypertension with no known cause, which is about 90–95% of people with hypertension. Often thought to be due to lifestyle. Management is through medications and blood pressure that does not respond is a red flag that it may be secondary hypertension. Due to the widespread nature of hypertension, cardiologists will end up managing or recommending treatments for essential hypertension.
- Secondary hypertension – Most causes of secondary hypertension are from kidney and endocrine disorders. Cardiovascular causes of hypertension include coarctation of aorta, atherosclerosis, and aortic stenosis.
- Complications of hypertension
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy – Increased pressure results in hypertrophy of the myocardium, particularly left ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary hypertension — which is separate from "hypertension" described above — can result in right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Hypertensive crisis – Generally considered to be a systolic blood pressure over 180. If there is no organ dysfunction it is called a hypertensive urgency, but if there is (e.g., confusion, breathlessness) then it is called hypertensive emergency.
- Pre-eclampsia (PreE) / Eclampsia – PreE is a disease of pregnancy that results in hypertension and proteinuria. PreE has negative consequences for both the mother and fetus/baby. Progression to eclampsia involves seizures. Currently, the only definitive treatment is delivery of the fetus.
- Hemorrhagic stroke – Infarction of the brain due to internal bleeding from Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms.
- Hypertensive encephalopathy, hypertensive nephropathy, hypertensive retinopathy – Damage to organs from chronic hypertension.
- Types of hypertension
- Cardiac arrhythmias – conditions in which the heartbeat is irregular, too fast, or too slow. Many types of arrhythmia have no symptoms. When symptoms are present these may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. More seriously there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, or chest pain.[4] While most types of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in cardiac arrest.
- Atrial fibrillation (afib or AF) – Fibrillation of the atria is fairly common and more common with increased age and overall disease of the heart. If the ventricular rate exceeds 100 then the afib is further classified as "afib with RVR" meaning rapid ventricular response.
- Atrial flutter (AFL) – A re-entrant tachycardia greater than 240 beats per minute and produces a characteristic saw-tooth pattern on ECG. It often degenerates to atrial fibrillation.
- Heart block – A decrease in the ability of the conduction system to transmit action pulses in the orderly manner. Blockage of the signal at different areas results in different types of heart block (e.g., first-degree AV block, left bundle branch block).
- Long QT syndrome – Lengthening of the QT interval can result in arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Specifically, it can lead to torsades de pointes than can then lead to ventricular fibrillation. It can be an inherited disorder or be acquired. Certain medications are associated with lengthening of the QT interval — drug-induced QT prolongation — and an EKG may be warranted before starting the medication to ensure a normal QT interval, but this practice is debated.
- Premature atrial contractions (PACs or APCs) – Normal beats originate in the SA node and extra beats originating from the atria are called PACs. They can be found in normal hearts and be asymptomatic; symptomatic PACs can be treated with beta blockers. PACs, like PVCs, can pair up with normal beats in a pattern called bigeminy.
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) – Normal beats are conducted through the AV node to the ventricles resulting in a narrow QRS complex. With PVCs, the extra beat originates within the ventricles and results in a wide QRS complex. Like PACs, they can be found in healthy hearts but are more likely to be found in bigeminy than PACs.
- Sick sinus syndrome, Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome (BTS) – Disease of the SA node that results in irregular changes in heart rate and in the case of BTS the arrhythmia alternates between bradycardia and tachycardia.
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) – A collection of tachycardia rhythms that originate before the ventricles and include the SA node, atria, and AV node. It is a broad, encompassing term that includes other rhythms in this list (e.g., afib with RVR) and others.
- Torsades de pointes – A type of ventricular tachycardia with a characteristic ECG appearance that can progress to ventricular fibrillation.
- Ventricular fibrillation (vfib) – Fibrillation of the ventricles is a life-threatening arrhythmia and should be treated by defibrillation and is a medical emergency. Vfib results from uncoordinated contraction of the ventricles and defibrillation acts as a 'reset' to synchronize contraction (i.e., a normal rhythm).
- Ventricular tachycardia (vtach) – Tachycardia that originates from within the ventricles. Typically, "vtach" implies monomorphology but it can be an umbrella term for both monomorphic and polymorphic (i.e., torsades de pointes). To classify a ventricular rhythm as vtach, at least 3 beats in a row must originate from the ventricles and have a rate over 100. If it lasts longer than 30 seconds, it can additionally be labelled as a sustained vtach.
- Coronary circulation disorders
- Atherosclerosis – Atherosclerosis is the condition in which an artery wall thickens as the result of a build-up of fatty materials (e.g., cholesterol) and white blood cells ("foam cells"). Atherosclerosis of a coronary artery leads to coronary artery disease (CAD). Atherosclerosis is a broad term referring to loss of elasticity of arteries and more specific terms exist — arteriosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis — to narrow which arteries are diseased and can easily be confused due to similar spelling. Overall, atherosclerosis tends to affect the arteries of highest pressure: aorta, coronary, renal, femoral, cerebral, and carotid.
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)– Coronary artery disease is a general term for any reduction in coronary circulation. One such cause is atherosclerosis. CAD can lead to ischemia (angina pectoris) or infarction (myocardial infarction). Treatment of CAD includes angioplasty, stenting, and coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
- Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) – ACS is a medical emergency and is a broad term encompassing many acute myocardial infarction symptoms. As a syndrome, it consists of a constellation of symptoms and can have many causes. The top three causes of ACS are ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 30%), non ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 25%), or unstable angina (38%). The first two are myocardial infarctions which are more commonly known as "heart attacks."
- Angina pectoris – Angina pectoris literally means "chest pain" that refers to pain caused by ischemia of the heart. The main cause of angina is coronary artery disease, but can result from other non-atherosclerotic causes such as anemia and heart failure. Stable angina results if the angina resolves with rest or nitroglycerin, but can progress to unstable angina which is a form of acute coronary syndrome.
- Myocardial infarction (also known as heart attack) – A myocardial infarction is the death of a part of the heart which is typically caused by a blockage of the coronary circulation but can be caused by other insufficiency such as cardiogenic shock.
- Restenosis – Recurrence of stenosis after being treated (e.g., stenting).
- Cardiac arrest – cessation of normal systemic circulation due to failure in proper contraction of the heart. There are several conditions that can cause cardiac arrest. Treatment of cardiac arrest includes cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), defibrillation, and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), and treatment of the underlying cause of arrest.
- Asystole ("flatline") – Asystole refers to the absence of electrical activity of the heart and is sometimes referred to as a "flatline" because the electrocardiogram shows a solid line due to the absence of electrical activity. This flatline is commonly used in television and movies to signal death. There are numerous causes of asystole that may be reversible if determined quickly enough, however, survival is very unlikely (~2% if not in a hospital). In contrast, asystole is desired and induced during cardiopulmonary bypass through a cardioplegia solution containing very high amounts of potassium. One additional example is the use of high potassium in lethal injection that results in asystole, cardiac arrest, and then death.
- Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) – Pulseless electrical activity is when the electrocardiogram shows a rhythm that should produce a pulse but it does not. PEA is commonly caused by the 6 H's and 6 T's (see PEA article) and results in decreased cardiac output and insufficient oxygen delivery to the body.
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia – Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) Is one classification of VT such that no pulse is felt because of an ineffective cardiac output which causes cardiac arrest, which also results in insufficient oxygen delivery to the body.
- Sudden cardiac death (SCD) – concept of natural death rather than a specific medical condition. There are several causes of sudden cardiac death and it is distinct from cardiac arrest. The leading cause of SCD in young athletes is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy but can also result from commotio cordis that is often sustained during athletic activity.
- Ventricular fibrillation – Ventricular fibrillation is fibrillation of the ventricles of the heart. Rhythmic contraction is necessary for efficient movement of blood, and fibrillation disrupts this rhythm sufficiently to cause cardiac arrest.
- Disorders of the myocardium
- Cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy is a deterioration of the myocardium. Several classifications have been used to categorize cardiomyopathies with the most common being primary vs. secondary, and dilated vs. restrictive vs. hypertrophic (presented below).
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy causing ischemia of the heart due to coronary artery disease.
- Nonischemic cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy caused by something other than ischemia.
- Amyloid cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy caused by amyloidosis.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) – Cardiomyopathy caused by hypertrophy of the heart and is the leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young adults.
- Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) (Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis (IHSS)) :
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) – Cardiomyopathy caused by dilation of the heart, typically caused by "drugs and bugs." It is the most common form of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy and the dilatation of the heart results in larger chamber volumes & thinner myocardial walls, both of which decrease the ability to pump. Specific kinds of dilated cardiomyopathy are listed below, and other causes include Chagas disease, chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., doxorubicin), tuberculosis, and pregnancy.
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy – A type of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by chronic abuse of alcohol and results from direct toxicity of ethanol on the myocardium.
- Tachycardia induced cardiomyopathy – A type of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by chronic tachycardia. A common arrhythmia that can lead to this form of cardiomyopathy is the common atrial fibrillation.
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (Transient apical ballooning, stress-induced cardiomyopathy) – A type of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by a sudden temporary weakening of the myocardium, which can include emotional stress (i.e. broken-heart syndrome). It presents as sudden heart failure with ECG changes similarly found in myocardial infarction and typically is found in post-menopausal women.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) – Cardiomyopathy caused by a genetic mutation of the desmosomes that connect myocytes.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) – Cardiomyopathy caused by excessive rigidity of the heart that prevents effective contraction and pumping. In comparison to DCM, RCM is often secondarily caused by other diseases such as amyloidosis, scleroderma, hemachromatosis (iron overload) and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. As such, the treatment for RCM is to treat the disease causing the RCM.
- Heart failure – Heart failure is failure of the heart to produce sufficient blood flow to meet metabolic demands of the body, or to do so at higher filling pressures. The hallmark signs of heart failure include shortness of breath (especially on exertion, at night, or while lying down) and leg swelling. Chest pain is rarely a feature of heart failure, which would point a diagnosis more toward angina pectoris or myocardial infarction. Perhaps confusingly, heart failure can be caused by coronary artery disease (CAD) and myocardial infarction (MI) that result in a deficiency in pumping that then leads to heart failure. Treatment of heart failure, like most secondary disorders, depends upon treatment of the primary cause which includes CAD & MI but also valvular problems like aortic stenosis and hypertension.
- Cor pulmonale – Untreated cor pulmonale can cause right heart failure from chronic pulmonary hypertrophy.
- Ventricular hypertrophy – Hypertrophy of the ventricle. Thickening of the myocardium (i.e., hypertrophy) can be physiological (a normal response) or pathological. An example of physiological hypertrophy is the result of significant athletic training (athletic heart syndrome).
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) – Hypertrophy of the left ventricle is more common than in the right and typically due to increased afterload on the heart such as from hypertension and aortic stenosis, but also from long standing mitral valve regurgitation. It can be diagnosed by echocardiography or ECG.
- Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) – Hypertrophy of the right ventricle and, it too, can be physiological from athletic training. Other causes include pulmonary hypertension and COPD as well as several congenital heart defects like ventricular septal defect, Tetralogy of Fallot and hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
- Heart cancer – Cancer of the heart is very rare and those cancers tend to be benign.
- Myxoma – Most common tumor of the heart. It is a benign tumor most commonly found in the left atrium and can be associated with Carney syndrome.
- Myocardial rupture and ventricular aneurysm – Rupture is a gross structural failure of the heart. Commonly a result of myocardial infarction that weakens the wall sufficiently to result in frank rupture and is typically seen 7–10 days after infarction. If not significant enough, the wall can develop into a ventricular aneurysm.
- Myocarditis – Infection and inflammation of the myocardium is myocarditis. Most causes are infectious (parvovirus B19, Lyme disease, Chagas disease), toxic (ethanol, anthracyclines, clozapine), or immunologic (systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and some of the vasculitides (see below)). Definitive diagnosis requires a biopsy.
- Uhl anomaly – A congenital heart defect in which the right ventricular myocardium is too thin or absent. It is a very rare disorder.
- Cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy is a deterioration of the myocardium. Several classifications have been used to categorize cardiomyopathies with the most common being primary vs. secondary, and dilated vs. restrictive vs. hypertrophic (presented below).
- Disorders of the pericardium
- Pericarditis – Inflammation of the pericardium that is typically idiopathic or infectious in nature. Treatment of viral & idiopathic pericarditis is NSAIDs or aspirin.
- Constrictive pericarditis – Pericarditis that constricts the expansion of the heart and inhibits heart function. Causes include infections (tuberculosis, fungus, parasites) and surgery. Definitive surgery is a pericardiectomy.
- Dressler syndrome – A form of pericarditis that develops 2–3 weeks after myocardial infarction and is accompanied by fever, pleuritic chest pain, and symptoms of pericarditis.
- Constrictive pericarditis – Pericarditis that constricts the expansion of the heart and inhibits heart function. Causes include infections (tuberculosis, fungus, parasites) and surgery. Definitive surgery is a pericardiectomy.
- Pericardial effusion – The serous pericardium normally contains fluid that reduces friction, but an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardium is called a pericardial effusion. The list of causes is lengthy but includes pericarditis, rheumatic diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), trauma, and blood from myocardial rupture. If an effusion worsens then the fluid can inhibit heart function and symptoms of cardiac tamponade appear. Treatment includes pericardiocentesis to drain the fluid, if necessary, and treatment of the underlying cause.
- Pericardial tamponade – Tamponade is a medical emergency resulting from accumulation of fluid in the pericardium that inhibits heart function. Tamponade is a consequence of the fibrous pericardium being too inelastic to permit adequate heart expansion during diastole. The classic finding is pulsus paradoxus as well as Beck's triad (low arterial blood pressure, distended neck veins, & soft heart sounds). Treatment is supportive until in a hospital where pericardiocentesis or a pericardial window can be performed to drain the fluid.
- Pericarditis – Inflammation of the pericardium that is typically idiopathic or infectious in nature. Treatment of viral & idiopathic pericarditis is NSAIDs or aspirin.
- Disorders of the heart valves
- Specific valvular problems – Specific problems of each valve.
- Aortic valve – Disorders and treatments of the aortic valve that separates the left ventricle and aorta.
- Aortic regurgitation / aortic insufficiency – Deficiency of the aortic valve that permits regurgitation from the aorta into the left ventricle.
- Aortic stenosis – Narrowing of the aortic valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve. Stenosis commonly occurs from calcification of the valve, which happens prematurely in those with a bicuspid aortic valve. Stenosis of the aortic valve produces a harsh systolic murmur that classically radiates in the carotid arteries as well as pulsus parvus et tardus.
- Aortic valve replacement – Replacement of the aortic valve due to aortic regurgitation, aortic stenosis, or other reasons. A special kind of replacement called percutaneous aortic valve replacement is done through catheters are does not require open-heart surgery.
- Aortic valve repair – Repair, instead of replacement, of the aortic valve.
- Aortic valvuloplasty – Repair of the valve by using a balloon catheter to force it open.
- Mitral valve – Disorders and treatments of the mitral valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle.
- Mitral valve prolapse – Prolapse of the mitral valve into the left atrium during ventricular systole.
- Mitral regurgitation / mitral insufficiency – Deficiency of the mitral valve that permits regurgitation from the left ventricle into the left atrium. Regurgitation produces a systolic murmur that radiates into the axilla.
- Mitral stenosis – Narrowing of the mitral valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve.
- Mitral valve replacement – Replacement of the mitral valve due to mitral regurgitation, mitral stenosis, or other reasons.
- Mitral valve repair – Repair, instead of replacement, of the mitral valve.
- Mitral valvuloplasty – Repair of the valve by using a balloon catheter to force it open.
- Pulmonary valve – Disorders of the pulmonary valve that separates the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Pulmonary regurgitation / pulmonary insufficiency – Deficiency of the pulmonary valve that permits regurgitation from the pulmonary artery into the right ventricle.
- Pulmonic stenosis – Narrowing of the pulmonary valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve.
- Tricuspid valve – Disorders of the tricuspid valve that separates the right atrium and right ventricle.
- Tricuspid regurgitation / tricuspid insufficiency – Deficiency of the tricuspid valve that permits regurgitation from the right ventricle into the right atrium.
- Tricuspid stenosis – Narrowing of the tricuspid valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve.
- Ebstein's anomaly – A congenital heart defect that results in the tricuspid valve leaflets being deeper in the heart (toward the apex) than normal. The annulus of the valve is in the correct position, however, and the portion of the ventricle affected becomes "atrialized" with thinner walls. The right atrium becomes hypertrophied and can result in conduction defects (e.g., Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome).
- Tricuspid atresia – A congenital heart defect that results in the absence of the tricuspid valve
- Aortic valve – Disorders and treatments of the aortic valve that separates the left ventricle and aorta.
- Endocarditis – The thin, inner lining of the heart is the endocardium and inflammation of this layer is called endocarditis. Endocarditis commonly affects the heart valves.
- Infective endocarditis – Commonly affects the valves due to absence of blood supply to the heart valve, which results in a decreased immune response to the valve leaflets. Typically, bacteria cause infective endocarditis of the mitral valve, but intravenous drug users (e.g., heroin, methamphetamine) have an increased risk of infection of the tricuspid valve. Common signs include Janeway lesions (non-tender), Osler's nodes (tender), and splinter hemorrhage of the nails.
- Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE) – Growths on the valves that are not from an infectious source and are composed of fibrin and platelets, and is associated with a history of rheumatic fever. The aortic valve is the most common valve affected (followed by mitral, tricuspid, & then pulmonary).
- Libman–Sacks endocarditis – A form of nonbacterial endocarditis specific to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and tends to affect the mitral valve (unlike NBTE which affects the aortic valve). It is the second most common heart finding in SLE after pericarditis
- Specific valvular problems – Specific problems of each valve.
- Congenital heart defects – defects in the structure of the heart which are present at birth and are often the result of aberrant embryological development. Defects can be syndromic or non-syndromic, with the later meaning defects that are isolated and not found in patterns (i.e., a syndrome). The top two syndromic causes of congenital heart defects are Noonan syndrome and Down syndrome. Down syndrome is more common than Noonan syndrome, but has a lower incidence of congenital heart defects, which makes Noonan syndrome the most common syndromic cause of congenital heart defects.
- Atrial septal defect (ASD) – Defect in the interatrial septum that permits blood flow between atria, including a patent foramen ovale (PFO).
- Bicuspid aortic valve – Formation of two valve leaflets in the aortic valve instead of three leaflets. This leads to aortic stenosis as the valve prematurely calcifies (as compared to calcification of a trileaflet valve).
- Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) – Narrowing of the aorta, typically of the aortic arch and is classically found in Turner syndrome. A "complete" coarction is called an interrupted aortic arch.
- Cor triatriatum – A membrane that divides one of the atria results in "three" atria (hence "triatriatum"). This tends to affect the left atrium more than the right atrium. The membrane may be present without complete division of the atrium. It presents similarly to stenosis of the respective semilunar valve (i.e., tricuspid stenosis for right atrium).
- Dextrocardia – Dextrocardia is a condition in which the apex of the heart is on the right side of the body, instead of the left. This can exist in isolation or as a part of situs inversus in which the entire body is mirrored not just the heart. Situs inversus can be a part of primary ciliary dyskinesia (aka Kartagener syndrome) that has recurrent respiratory infections and male infertility. A simple chest xray is sufficient to diagnose dextrocardia, provided care is taken in marking the correct side of the radiograph.
- Ebstein's anomaly – Malformation of the tricuspid valve (see above).
- Great artery defects – There are several conditions that affect the great arteries (e.g., double aortic arch, aberrant subclavian artery) that often result in problems with the trachea and breathing.
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome – Defect in the development of the left heart such that it is hypoplastic (under developed).
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) – Failure of the ductus arteriosus to close on birth.
- Patent foramen ovale (PFO) – An atrial septal defect in that the foramen ovale fails to close at birth.
- Persistent truncus arteriosus – Defect in that the truncus arteriosus fails to divide.
- Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) – Narrowing of the pulmonary valve that is the key finding in Noonan syndrome.
- Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) – Set of four anatomical abnormalities: pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, ventricular septal defect, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) – Abnormal spatial arrangement of the great vessels (superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and aorta).
- Uhl anomaly – Partial or total loss of the right ventricular wall.
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD) – Defect in the ventricular septum that permits blood flow between ventricles.
- Diseases of blood vessels – diseases of the blood vessels can be multidisciplinary in nature. For example, medical treatment of atherosclerosis tends to be managed by cardiologists while vascular surgery repairs aneurysms and stenotic arteries.
- Atherosclerosis – Thickening of an arterial wall due to increased cholesterol and macrophages (see above).
- Aneurysm – Balloon-like bulging of arteries (also possible of the heart: see ventricular aneurysm above).
- Aortic aneurysm – Aneurysm of the aorta, typically of the abdominal aorta (abdominal aortic aneurysm or AAA). They are associated with a smoking history and in connective tissue diseases (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome). Current USPSTF recommendations are for a single abdominal ultrasound screening for a AAA in anyone 65 or older who has smoked. Surgical repair of a AAA is advised after it is larger than 5.0–5.5 cm because of concern for rupture that leads to death from internal bleeding.
- Cerebral aneurysm – Aneurysms of the arteries in the brain most commonly affect the anterior cerebral artery. Rupture of the aneurysm results in a subarachnoid hemorrhage and a very severe headache.
- Aortic dissection – Dissection along the length of the aorta between the layers of the aortic wall. Dissection of the ascending aorta (type A) is a surgical emergency while dissection of the descending aorta (type B) can possibly be managed medically. Dissection of the ascending aorta is an emergency because dissection may interrupt coronary blood flow and blood flow to the brain, neither of which tolerate ischemia particularly well.
- Aortic rupture – Frank rupture of the aorta is often fatal from internal bleeding. Rupture of the aorta can occur at the sites of aneurysm, but is also due to trauma and results in a traumatic aortic rupture.
- Carotid artery – Diseases of the carotid arteries:
- Carotid artery stenosis / carotid artery disease – Narrowing of the carotid artery, typically due to atherosclerosis.
- Carotid artery dissection – Dissection along the length of the carotid artery between the layers of the carotid wall and filled with blood.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) – Formation of a thrombus in a deep vein, commonly in the legs that may break loose, travel to the lungs, and occlude blood flow (pulmonary embolism) sufficient to interrupt oxygenation to the body.
- Traveller's thrombosis / economy class syndrome: A DVT due to being sedentary during air travel.
- Microangiopathy – Disease of capillaries in which the walls become thick and weak, and result in bleeding and decreased blood flow. One very common cause is diabetes mellitus in which microangiopathy results in diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic neuropathy.
- Varicose veins – Veins that have become enlarged and tortuous with failed valves, commonly in the legs. Vericose veins have cosmetic concerns, but they may become painful. Surgery and sclerotherapy are two options for treating varicose veins.
- Vasculitis – Inflammation of blood vessels (veins & arteries) with a long list of causes.
- Aortitis – Inflammation of the aorta that can be seen in giant cell arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, syphilis and Takayasu's arteritis.
- Behçet's disease – Affects small-sized vessels that often initially presents with oral aphthous ulcers, genital ulcers and uveitis, and can be fatal from ruptured aneurysms. Pericarditis is commonly seen with Behçet's.
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA; formerly known as Churg–Strauss syndrome) – Affects small- & medium-sized vessels that often affects lungs, kidneys, & heart in those with a history of airway allergic hypersensitivity and p-ANCA antibodies.
- Giant-cell arteritis (GCA) / Temporal arteritis – Affects medium- & large-sized vessels of the head, typically branches of the external carotid artery and namely the temporal artery. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery results in blindness. Suspicion of GCA necessitates immediate treatment with glucocorticoids and temporal artery biopsy.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) – Affects small- & medium-sized vessels that often affects the lung & kidneys (RPGN) with classic saddle nose and c-ANCA antibodies.
- IgA vasculitis (IgAV; formerly known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura) – Affects small-sized vessels and produces palpable purpura and proteinuria from immunocomplex (IgA) deposition.
- Kawasaki disease – Affects medium-sized vessels mostly seen in young children with myocarditis, & pericarditis, and is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children (results in coronary artery aneurysms). Myocardial infarction from coronary thrombosis is the most common cause of death from Kawasaki disease.
- Thromboangiitis obliterans – Affects small- & medium-sized vessels that is strongly associated with tobacco products. Pain, diminished pulses, gangrene and eventual amputation of affected hands and feet.
Procedures to counter coronary artery disease
Summarize
Perspective
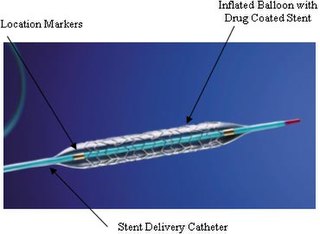
Coronary artery disease is not currently reversible and eventually requires surgical management if it progresses.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG): Grafting an artery or vein from elsewhere to bypass a stenotic coronary artery. Performed by cardiothoracic surgeons, a sternotomy is performed to open the chest and then grafts are performed. Cardiopulmonary bypass may be necessary. The internal mammary artery or saphenous vein can be used as grafts. The grafts are used to provide an alternate path for blood flow around a stenosis.
- Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP): Pneumatically assisting the heart to move blood using inflatable cuffs on the legs.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) – Procedures to treat stenotic coronary arteries by accessing through a blood vessel. Angioplasty in this manner is PTCA (described below) but may also involve the insertion of stents to keep vessels open.
- Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): Insertion of a catheter through the skin ("percutaneous") into a blood vessel ("transluminal") to enlarging the lumen of a coronary artery by forcibly expanding it with a balloon ("angioplasty"), hence the name. It is a form of PCI and generally what is implied when referring to "PCI."
- Atherectomy – Enlarging the lumen of an artery by removal of atherosclerotic plaque by means of catheterization. This is in contrast to angioplasty that does not remove the plaque but merely pushes it out of the way to increase the lumen size. This method is primarily used in peripheral disease, but has been used for coronary disease as well.
- Endarterectomy – Enlarging the lumen of an artery by removal of atherosclerotic plaque by means of open surgery. This is primarily done on the carotid arteries (Carotid endarterectomy or CEA) but was first performed on the superficial femoral artery. While not performed on coronary arteries, it is mentioned here for completeness.
- Stenting: Enlarging the lumen of an artery by forcibly expanding it with a metal wire tube by means of catheterization. Typically, the artery is expanded first through angioplasty (see PTCA above).
Devices used in cardiology
- Stethoscope – Acoustic device for hearing internal sounds including heart sounds. The stethoscope is the quintessential medical icon, regardless of specialty. Modern stethoscopes can have a diaphragm and a bell, and be sized for adults or children. In cardiology, it is primarily used to listen to heart sounds it can also be used to listen for bruits (carotid & renal for renal artery stenosis), bowel sounds, and lung sounds. Electronic stethoscopes can amplify and record sounds.
- EKG calipers – A type of divider caliper that can be used to measure intervals and compare intervals on EKGs. Special rulers can be used to measure the intervals as well.
- Devices used to maintain normal electrical rhythm:
- Pacemaker – An implanted electrical device that replaces the heart's natural pacemaker.
- Defibrillator – Electrical devices to alter the heart's rhythm with electrical energy. As the name implies, a defibrillator is used to stop fibrillation of the heart. It can be used to cardiovert atrial fibrillation if certain conditions are met, but is mainly used to cardiovert ventricular fibrillation which is life-threatening. Contrary to popular media's use, a defibrillator cannot and should not be used for asystole (a "flatline") as it has been shown to be ineffective in restoring a rhythm. If a person is in a rhythm not convertible by a defibrillator, then cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or more advanced care should be started.
- Automated external defibrillator (AED) – An external defibrillator that is commonly found outside of health care settings and is often designed for anyone to use through verbal instructions. AED's have increased in popularity and dispersal so that people with cardiac arrest in public can be cardioverted to a safer rhythm before help can arrive.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD): An implanted device to prevent life-threatening conditions (e.g., ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation) in people predisposed to these rhythms.
- Devices used to maintain blood pressure:
- Artificial heart – An internal pump that wholly replaces the pumping action of the heart.
- Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) / heart-lung machine: External pump to take over the function of both the heart and lungs. Commonly used in cardiothoracic surgery when the heart is being operated on for such surgeries like open valve replacement or CABG on the posterior side of the heart. The bypass machine is responsible for oxygenation of blood, removal of carbon dioxide, heating the blood (heat is lost from being outside the body) to maintain core body temperature or cooling blood for controlled hypothermia, and providing volatile anesthetics (e.g., isoflurane) if the lungs are not ventilated during bypass (the movement can be problematic while performing surgery). A cardioplegic solution is used to stop the heart from beating and combination with hypothermia reduces oxygen demand of the heart significantly (>97%) such that surgery is possible without causing damage.
- Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP): A balloon placed in the thoracic aorta to supplement cardiac output from the heart. It pulsates opposite to the heart such that it inflates during diastole and relaxes during systole. Deflation during systole decreases afterload (vacuum effect), thus decreasing myocardial oxygen demand, and inflates during diastole to increase diastolic pressure which increases coronary artery perfusion of the endocardium (the heart perfuses itself during diastole, not systole).
- Ventricular assist device (VAD) – Internal pump to supplement or replace the pumping action of a ventricle. Can be referred to RVAD or LVAD depending on if it's attached to the right or left ventricle.
Diagnostic tests and procedures
Summarize
Perspective

Various cardiology diagnostic tests and procedures.
- Blood tests
- Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood are associated with an increased risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
- Creatine kinase – When skeletal muscle injury is absent, CK-MB is fairly specific to myocardium injury.
- Troponin – The troponin complex is present in skeletal and cardiac muscle, but cardiac-specific forms of troponin I and troponin T are used as sensitive & specific indicators of heart damage if acute coronary syndrome is suspected. The presence of troponins are not exclusive to myocardial infarction, and so other conditions should be considered (e.g., heart failure, cardiomyopathies, trauma, defibrillation, cardioversion, ASD closure, radiofrequency ablation, toxicity from chemotherapy, snake venom, cyanide poisoning, ascending aortic dissection, stroke, seizure).
- Echocardiography ("echo"): Ultrasonography of the heart to inspect chambers, valves, and blood flow. Often utilizes the Doppler effect to determine blood flow through valves (stenosis & regurgitation) and through the septum (ASD & VSD). Agitated saline can be used as contrast for blood flow and microbubbles for capillary blood flow contrast.
- Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE): Echocardiogram of the heart through the thorax external to the body. Much easier to perform than TEE because it is non-invasive and takes less time, but has several disadvantages (namely clarity of images).
- Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE): Echocardiogram of the heart through the esophagus. TEE can require light sedation or general anesthesia and the patient must be NPO.
- Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR): Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart that utilizes the ECG for gating and to look at specific mechanical functions of the heart.
- Cardiac stress test – Testing of the cardiovascular system through controlled exercise or drugs.
- Auscultation – Listening to sounds (e.g., heart sounds) with a stethoscope.
- Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG): Measurement of the electrical activity of the heart, typically with 4 or 10 electrodes on the skin.
- Holter monitor – Portable ECG device for continuous monitoring.
- Electrophysiology study – Studying the electrical activity of the heart through the use of catheters placed in the heart via veins or arteries.
- Sphygmomanometer – Blood pressure cuff used to measure arterial blood pressure.
- Cardiac marker – Testing for biomarkers in the blood that may indicate various conditions.
- Coronary catheterization – Catheterization of the coronary arteries.
- Fractional flow reserve (FFR): Testing the blood flow through a stenosis of a coronary artery to determine the perfusion of the heart.
- Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS): Ultrasonography of a coronary artery.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): Testing through the use of optical scattering for coronary artery disease.
Drugs
Summarize
Perspective
There are several classes of pharmaceutical drugs used in cardiology to manage various diseases and many of them have cardiovascular side effects.
Drugs for the cardiovascular system
Drugs that manipulate the cardiovascular system do so through several ways. The first is ion channels, which are often manipulated to manage arrhythmias. The second is receptors of various types. The third is manipulation of enzymes.
Ion channels
Ion channels are responsible for cell membrane voltage, depolarization, and repolarization. These actions lead to conduction of signals down nerves and contraction of cardiomyocytes. Perhaps the most prominent manipulation of ion channels is through antiarrhythmic agents. These agents are commonly classified by the type of ion they manipulate and named the Vaughan Williams classification:
- Class I — Sodium channel blockers
- Class Ia — Fast sodium channels (quinidine, ajmaline, procainamide, disopyramide)
- Class Ib — Sodium channels (lidocaine, phenytoin, mexiletine, tocainide)
- Class Ic — Decrease conductivity (encainide, flecainide, propafenone, moricizine)
- Class II — Beta blockers (carvedilol, propranolol, esmolol, timolol, metoprolol, atenolol, bisoprolol)
- Class III — Potassium channel blockers (amiodarone, sotalol, ibutilide, dofetilide, dronedarone)
- Class IV — Calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem)
- Class V — Other (adenosine, digoxin, magnesium Sulfate)
Specifically, types I, III, & IV manipulate ion channels while the others are not.
Receptors
The adrenergic receptor is a set of receptors that are commonly manipulated. Four properties of the heart — chronotropy, dromotropy, inotropy, & lusitropy — are manipulated by adrenergic receptors. For example, the β1 receptor increases all four of these properties: chronotropy at the SA node, dromotropy through the AV node, inotropy of the cardiomyocytes through increased calcium, and lusitropy through phosphorylation of phospholamban. Catecholamines are a set of drugs and hormones that manipulate the adrenergic receptors. The natural catecholamines are norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine. There are numerous other drugs (e.g., dobutamine, ephedrine, isoproterenol) that manipulate the adrenergic receptors and have variable specificity for the receptors and are, thus, used for various reasons.
Angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs) block the angiotensin II receptors that are linked to hypertension and heart failure, mainly through vasodilation & heart remodeling inhibition.
Enzymes
ACE inhibitors works upstream from angiotensin II receptor antagonists and have similar effects on management of hypertension and heart failure.
Sodium nitroprusside and nitroglycerin function by causing vasodilation through nitric oxide, which manipulates cGMP levels through guanylate cyclase.
COX inhibitors (namely aspirin), warfarin, direct Xa inhibitors, direct thrombin inhibitors, heparin, low-molecular weight heparins, antibodies (e.g., abciximab), and a few others are used for anticoagulation therapy. This is important in those predisposed to blood clots (e.g., Factor V Leiden) but also for thrombus formation when an atherosclerotic plaque rupture that would, otherwise, lead to myocardial infarction.
Drugs with cardiovascular side effects
Numerous drug classes have well-known cardiovascular side effects.
- Anesthetics – As a general rule, all agents used in anesthesia have depressant effects on the cardiovascular system with the notable exception of ketamine.
- Chemotherapy – Doxorubicin is one agent known to have heart toxicity (leads to dilated cardiomyopathy). Another is trastuzumab. Immune checkpoint inhibitors can also lead to cardiotoxicity.
- Diuretics – The primary effect of diuretics is removal of intravascular volume, which then has secondary benefits to the cardiovascular system in diseases like heart failure.
- Lithium – Teratogenic effect of causing Ebstein's anomaly in mothers taking lithium.
- Opioids – Decreases blood pressure.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) – Toxicity causes arrhythmias including sinus tachycardia, junctional rhythms, and trigeminy. SSRI's also have interactions with anti-coagulation therapy and increases the risk of bleeding while on them.
- Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI) – Due to manipulation of norepinephrine, SNRI's can cause hypertension and so hypertension should be reduced before starting an SNRI.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) – TCAs behave like type Ia antiarrhythmics and could terminate ventricular fibrillation and decrease contractility. They can also cause tachycardia and hypotension.
Cardiology organizations
Cardiology publications
- Acta Cardiologica
- American Journal of Cardiology
- Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia
- Cardiology
- Cardiology in Review
- Circulation
- Circulation Research
- Clinical and Experimental Hypertension
- Clinical Cardiology
- EP – Europace
- European Heart Journal
- Experimental & Clinical Cardiology
- Heart
- Heart Rhythm
- International Journal of Cardiology
- Journal of the American College of Cardiology
- Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology
Persons influential in cardiology
- Robert Atkins (1930–2003) – known for the Atkins diet
- Eugene Braunwald (born 1929) – editor of Braunwald's Heart Disease and 1000+ publications
- Wallace Brigden (1916–2008) – identified cardiomyopathy
- Willem Einthoven (1860–1927) – a physiologist who built the first practical ECG and won the 1924 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine ("for the discovery of the mechanism of the electrocardiogram")
- Werner Forssmann (1904–1979) – who infamously performed the first human catheterization on himself that led to him being let go from Berliner Charité Hospital, quitting cardiology as a speciality, and then winning the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine ("for their discoveries concerning heart catheterization and pathological changes in the circulatory system")
- Andreas Gruentzig (1939–1985) – first developed balloon angioplasty
- Max Holzmann (1899–1994) – co-founder of the Swiss Society of Cardiology, president from 1952 to 1955
- Samuel A. Levine (1891–1966) – recognized the sign known as Levine's sign as well as the current grading of the intensity of heart murmurs, known as the Levine scale
- Bernard Lown (born 1921) known for being the original developer of the Defibrillator
- Henry Marriott (1917–2007) – ECG interpretation and Marriott's Practical Electrocardiography
- Jacqueline Noonan (born 1928) – discoverer of Noonan syndrome that is the top syndromic cause of congenital heart disease
- John Parkinson (1885–1976) – known for Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
- Helen B. Taussig (1898–1986) – founder of pediatric cardiology and extensively worked on blue baby syndrome
- Paul Dudley White (1886–1973) – known for Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
- Louis Wolff (1898–1972) – known for Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
- Stewart Wolf (1914–2005) – known for his research into the Roseto effect
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.