List of felids
Species in mammal family Felidae From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Felidae is a family of mammals in the order Carnivora, colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is called a felid.[1][2] The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to domestic cats. The characteristic features of cats have evolved to support a carnivorous lifestyle, with adaptations for ambush or stalking and short pursuit hunting. They have slender muscular bodies, strong flexible forelimbs and retractable claws for holding prey, dental and cranial adaptations for a strong bite, and often have characteristic striped or spotted coat patterns for camouflage.[3][4]

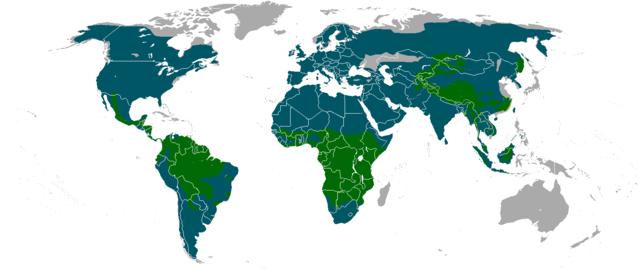
Felidae comprises two extant subfamilies, the Pantherinae and the Felinae. The former includes the five Panthera species tiger, lion, jaguar, leopard, and snow leopard, as well as the two Neofelis species clouded leopard and Sunda clouded leopard.[2] The subfamily Felinae includes 12 genera and 34 species, such as the bobcat, caracal, cheetah, cougar, ocelot, and common domestic cat.[5]
Traditionally, five subfamilies have been distinguished within the Felidae based on phenotypical features: the Felinae, the Pantherinae, the Acinonychinae (cheetahs), the extinct Machairodontinae, and the extinct Proailurinae.[6] Molecular phylogenetic analysis suggests that living (extant) felids fall into eight lineages (clades).[7][8] The placement of the cheetah within the Puma lineage invalidates the traditional subfamily Acinonychinae, and recent sources use only two subfamilies for extant genera.[5] The number of accepted species in Felidae has been around 40 since the 18th century, though research, especially modern molecular phylogenetic analysis, has over time adjusted the generally accepted genera as well as the divisions between recognized subspecies, species, and population groups.[9] In addition to the extant species listed here, over 30 fossil genera have been described; these are divided into the subfamilies Felinae, Pantherinae, Proailurinae, and Machairodontinae. This final subfamily includes the genus Smilodon, known as the saber-toothed cat, which went extinct around 10,000 years ago. The earliest known felid genus is Proailurus, part of Proailurinae, which lived approximately 25 million years ago in Eurasia.[10]
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (4 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (14 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (6 species) |
| LC | Least concern (15 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (0 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (2 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the cat's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
Classification
Summarize
Perspective
The family Felidae consists of 41 extant species belonging to 14 genera and divided into 92 subspecies. This does not include hybrid species (such as the liger) or extinct prehistoric species (such as Smilodon). Modern molecular studies indicate that the 14 genera can be grouped into 8 lineages.[9]
Subfamily Felinae: small and medium-sized cats
- Bay cat lineage
- Genus Catopuma: two species
- Genus Pardofelis: one species
- Caracal lineage
- Genus Caracal: two species
- Genus Leptailurus: one species
- Ocelot lineage
- Genus Leopardus: eight species
- Lynx lineage
- Genus Lynx: four species
- Puma lineage
- Genus Acinonyx: one species
- Genus Herpailurus: one species
- Genus Puma: one species
- Leopard cat lineage
- Genus Otocolobus: one species
- Genus Prionailurus: five species
- Domestic cat lineage
- Genus Felis: seven species
Subfamily Pantherinae: large cats
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Felids
Summarize
Perspective
The following classification is based on the most recent proposals, as codified in 2017 by the Cat Specialist Group of the IUCN.[9] Range maps are based on IUCN range data.
Subfamily Felinae
Bay cat lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian golden cat | C. temminckii (Vigors & Horsfield, 1827) Two subspecies
|
Scattered areas of Southeast Asia |
Size: 71–105 cm (28–41 in) long, 40–56 cm (16–22 in) tail[11] Habitat: Forest, savanna, grassland, and shrubland[12] Diet: Mostly unknown, with evidence of rodents, squirrels, and snakes[12] |
NT
|
| Bay cat | C. badia (Gray, 1874) |
The island of Borneo |
Size: 53–67 cm (21–26 in) long, 32–40 cm (13–16 in) tail[13] Habitat: Forest[14] Diet: Unknown[14] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marbled cat | P. marmorata (Martin, 1836) Two subspecies
|
Parts of Southeast Asia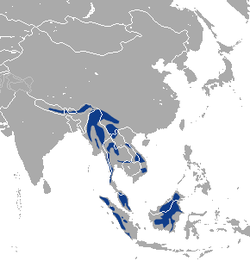 |
Size: 45–62 cm (18–24 in) long, 36–55 cm (14–22 in) tail[15] Habitat: Forest[16] Diet: Likely rodents, squirrels, and birds[16] |
NT
|
Caracal lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African golden cat | C. aurata (Temminck, 1827) Two subspecies
|
Central Africa |
Size: 65–90 cm (26–35 in) long, 28–35 cm (11–14 in) tail[17] Habitat: Forest[18] Diet: Rodents and squirrels, along with antelope and primates[18] |
VU
|
| Caracal | C. caracal (Schreber, 1776) Three subspecies
|
Most of non-desert Africa and Middle East |
Size: 80–100 cm (31–39 in) long, 20–34 cm (8–13 in) tail[19] Habitat: Forest, desert, grassland, shrubland, and savanna[20] Diet: Rodents, as well as antelope, birds, reptiles, and fish[20] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serval | L. serval (Schreber, 1776) Three subspecies
|
Non-rainforest sub-Saharan Africa |
Size: 59–100 cm (23–39 in) long, 20–38 cm (8–15 in) tail[21] Habitat: Grassland, inland wetlands, forest, and savanna[22] Diet: Small mammals and rodents, as well as birds, reptiles, and arthropods[22] |
LC
|
Ocelot lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andean mountain cat | L. jacobita (Cornalia, 1865) |
Andes mountains |
Size: 57–65 cm (22–26 in) long, 41–48 cm (16–19 in) tail[23] Habitat: Rocky areas, shrubland, and grassland[24] Diet: Rodents, as well as other small mammals[24] |
EN
|
| Geoffroy's cat | L. geoffroyi (d'Orbigny & Gervais, 1844) |
Southern and central regions of South America |
Size: 43–88 cm (17–35 in) long, 23–40 cm (9–16 in) tail[25] Habitat: Savanna, forest, shrubland, and grassland[26] Diet: Small rodents, birds, and rabbits[26] |
LC
|
| Kodkod | L. guigna (Molina, 1782) Two subspecies
|
Central and southern Chile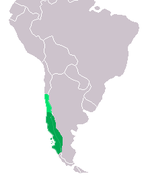 |
Size: 37–56 cm (15–22 in) long, 20–25 cm (8–10 in) tail[27] Habitat: Shrubland and forest[28] Diet: Small mammals, especially rodents, and also small marsupials, birds, reptiles, and carrion[28] |
VU
|
| Margay | L. wiedii (Schinz, 1821) Three subspecies
|
Most of South America and Central America |
Size: 46–69 cm (18–27 in) long, 23–52 cm (9–20 in) tail[29] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and savanna[30] Diet: Small mammals, as well as lizards and birds[30] |
NT
|
| Ocelot | L. pardalis (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
|
Most of South and Central America, Southwestern United States, Trinidad and Margarita in the Caribbean |
Size: 50–102 cm (20–40 in) long, 30–50 cm (12–20 in) tail[31] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and savanna[32] Diet: Small and medium mammals, birds and reptiles[32] |
LC
|
| Oncilla | L. tigrinus (Schreber, 1775) Three subspecies
|
Most of South America |
Size: 38–59 cm (15–23 in) long, 20–42 cm (8–17 in) tail[33] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[34] Diet: Small mammals, birds and reptiles[34] |
VU
|
| Pampas cat | L. colocola (Molina, 1782) Seven subspecies
|
West coast of South America and parts of Brazil |
Size: 42–79 cm (17–31 in) long, 22–33 cm (9–13 in) tail[35] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[36] Diet: Small mammals and ground-dwelling birds[36] |
NT
|
| Southern tigrina | L. guttulus (Hensel, 1872) |
Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay |
Size: 38–59 cm (15–23 in) long, 20–42 cm (8–17 in) tail[37] Habitat: Forest and savanna[38] Diet: Small mammals, birds and lizards[38] |
VU
|
Lynx lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bobcat | L. rufus (Schreber, 1777) Two subspecies
|
Most of the United States and parts of Canada and Mexico |
Size: 50–120 cm (20–47 in) long, 9–25 cm (4–10 in) tail[39] Habitat: Desert, shrubland, savanna, forest, and grassland[40] Diet: Rabbits, along with rodents and small or medium-sized mammals[40] |
LC
|
| Canada lynx | L. canadensis Kerr, 1792 |
Canada, Alaska, and parts of northern United States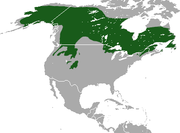 |
Size: 73–106 cm (29–42 in) long, 10–15 cm (4–6 in) tail[41] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[42] Diet: Almost exclusively hares, especially snowshoe hares[42] |
LC
|
| Eurasian lynx | L. lynx (Linnaeus, 1758) Six subspecies
|
Eastern Europe, Russia, and parts of China |
Size: 90–120 cm (35–47 in) long, 19–23 cm (7–9 in) tail[43] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, desert, rocky areas, and grassland[44] Diet: Deer, as well as other small or medium-sized mammals and birds[44] |
LC
|
| Iberian lynx | L. pardinus (Temminck, 1827) |
Scattered pockets of southern Spain | Size: 65–92 cm (26–36 in) long, 11–16 cm (4–6 in) tail[45] Habitat: Shrubland[46] Diet: Almost exclusively European rabbit[46] |
VU
|
Puma lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheetah | A. jubatus (Schreber, 1775) Four subspecies
|
Southern, eastern, and central Africa; Iran |
Size: 113–140 cm (44–55 in) long, 60–84 cm (24–33 in) tail[47] Habitat: Desert, grassland, savanna, and shrubland[48] Diet: Antelopes and gazelles[48] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaguarundi | H. yagouaroundi (Saint-Hilaire, 1803) |
Most of South and Central America |
Size: 49–78 cm (19–31 in) long, 28–59 cm (11–23 in) tail[49] Habitat: Grassland, shrubland, savanna, and forest[50] Diet: Small mammals, birds and reptiles[50] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cougar | P. concolor (Linnaeus, 1771) Two subspecies
|
South America and North America |
Size: 100–150 cm (39–59 in) long, 60–90 cm (24–35 in) tail[51] Habitat: Forest, desert, grassland, savanna, and shrubland[52] Diet: Deer, as well as smaller mammals such as feral pigs, raccoons and armadillos[52] |
LC
|
Leopard cat lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pallas's cat | O. manul (Pallas, 1776) Two subspecies
|
Central Asia |
Size: 46–65 cm (18–26 in) long, 21–31 cm (8–12 in) tail[53] Habitat: Rocky areas, grassland, shrubland, and desert[54] Diet: Small mammals, especially pikas, as well as rodents and birds[54] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fishing cat | P. viverrinus (Bennett, 1833) Two subspecies
|
South and Southeast Asia |
Size: 65–85 cm (26–33 in) long, 25–30 cm (10–12 in) tail[55] Habitat: Inland wetlands, shrubland, grassland, and forest[56] Diet: Rodents, birds and fish[56] |
VU
|
| Flat-headed cat | P. planiceps (Vigors & Horsfield, 1827) |
The Thai-Malay Peninsula, Borneo, and Sumatra |
Size: 45–52 cm (18–20 in) long, 13–17 cm (5–7 in) tail[57] Habitat: Inland wetlands and forest[58] Diet: Fish, as well as birds and small rodents[58] |
EN
|
| Leopard cat | P. bengalensis (Kerr, 1792) Two subspecies
|
Eastern Asia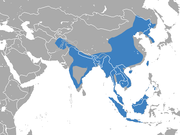 |
Size: 45–65 cm (18–26 in) long, 20–30 cm (8–12 in) tail[59] Habitat: Grassland, inland wetlands, shrubland, and forest[60] Diet: Rodents, particularly murids, as well as other small mammals, eels, and fish[60] |
LC
|
| Rusty-spotted cat | P. rubiginosus (Saint-Hilaire, 1834) Three subspecies
|
India, Sri Lanka, and Nepal |
Size: 35–48 cm (14–19 in) long, 20–25 cm (8–10 in) tail[61] Habitat: Desert, savanna, grassland, shrubland, and forest[62] Diet: Rodents[62] |
NT
|
| Sunda leopard cat | P. javanensis (Desmarest, 1816) Two subspecies
|
Sundaland islands of Java, Bali, Borneo, Sumatra, and the Philippines |
Size: 45–65 cm (18–26 in) long, 20–30 cm (8–12 in) tail[59] Habitat: Forest[63] Diet: Rodents, as well as amphibians, lizards, and birds[63][64] |
NE
|
Domestic cat lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African wildcat | F. lybica Forster, 1780 Three subspecies
|
Africa, West and Central Asia, northern India, and western China |
Size: 45–80 cm (18–31 in) long, 30 cm (12 in) tail[65] Habitat: Forest, desert, shrubland, savanna, and grassland[66] Diet: Rodents and rabbits, and to a lesser extent birds and other small animals[66] |
LC
|
| Black-footed cat | F. nigripes Burchell, 1824 |
Southern Africa |
Size: 37–52 cm (15–20 in) long, 14–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[67] Habitat: Savanna, grassland, and desert[68] Diet: Small mammals and birds[68] |
VU
|
| Chinese mountain cat | F. bieti Milne-Edwards, 1892 |
Northwest China |
Size: 60–85 cm (24–33 in) long, 29–35 cm (11–14 in) tail[69] Habitat: Grassland and forest[70] Diet: Unknown[70] |
VU
|
| Domestic cat | F. catus Linnaeus, 1758 |
Worldwide | Size: 46 cm (18 in) long, 30 cm (12 in) tail[71] Habitat: Domesticated; feral cats have a cosmopolitan distribution in forests, grasslands, tundra, coastal areas, agricultural land, scrublands, urban areas, and wetlands[72] Diet: Birds and small mammals in the wild[72] |
NE
|
| European wildcat | F. silvestris Schreber, 1777 Two subspecies
|
Spain, Scotland, the Balkans, and Central Europe |
Size: 45–80 cm (18–31 in) long, 30 cm (12 in) tail[74] Habitat: Shrubland and forest [75] Diet: Rodents and rabbits, and to a lesser extent birds[75] |
LC
|
| Jungle cat | F. chaus Schreber, 1777 Three subspecies
|
India and parts of the Middle East and Southeast Asia |
Size: 58–76 cm (23–30 in) long, 21–27 cm (8–11 in) tail[76] Habitat: Forest, inland wetlands, desert, grassland, shrubland, and savanna[77] Diet: Small mammals and rodents, as well as birds and other small animals[77] |
LC
|
| Sand cat | F. margarita Loche, 1858 Two subspecies
|
Scattered areas in Western Africa, Saudi Arabia, and near the Caspian Sea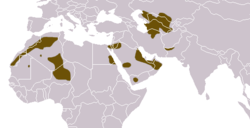 |
Size: 39–52 cm (15–20 in) long, 22–31 cm (9–12 in) tail[78] Habitat: Desert[79] Diet: Small rodents, as well as small birds and lizards[79] |
LC
|
Subfamily Pantherinae
Panthera lineage
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clouded leopard | N. nebulosa (Griffith, 1821) |
Scattered Southeast Asia and southern China (current in red, historical range in green) |
Size: 69–108 cm (27–43 in) long, 61–91 cm (24–36 in) tail[80] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[81] Diet: Medium-sized and small mammals on the ground and in trees, as well as birds[81] |
VU
|
| Sunda clouded leopard | N. diardi Cuvier, 1823 Two subspecies
|
Parts of Sumatra and Borneo |
Size: 69–108 cm (27–43 in) long, 61–91 cm (24–36 in) tail[82] Habitat: Forest[83] Diet: Medium-sized and small mammals[83] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaguar | P. onca (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Large swathes of South and Latin America, and Arizona in the United States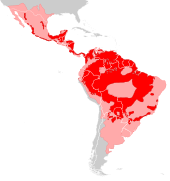 |
Size: 110–170 cm (43–67 in) long, 44–80 cm (17–31 in) tail[84] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, inland wetlands, savanna, and grassland[85] Diet: Variety of mammals, reptiles and birds, preferring ungulates[85] |
NT
|
| Leopard | P. pardus (Linnaeus, 1758) Eight subspecies
|
Much of Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, the Indian subcontinent, the Caucasus in Europe, Southeast Asia, and Siberia |
Size: 91–191 cm (36–75 in) long, 51–101 cm (20–40 in) tail[86] Habitat: Forest, desert, rocky areas, grassland, savanna, and shrubland[87] Diet: Ungulates, as well as other mammals, insects, reptiles, and birds[87] |
VU
|
| Lion | P. leo (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies |
Sub-Saharan Africa and India |
Size: 137–250 cm (54–98 in) long, 60–100 cm (24–39 in) tail[88] Habitat: Forest, grassland, shrubland, savanna, and desert[89] Diet: Ungulates such as antelopes, zebra, and wildebeest, as well as other small to large mammals[89] |
VU
|
| Snow leopard | P. uncia (Schreber, 1775) |
Himalayas reaching north to Mongolia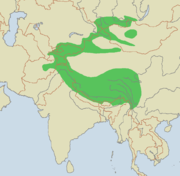 |
Size: 90–120 cm (35–47 in) long, 80–100 cm (31–39 in) tail[90] Habitat: Shrubland, rocky areas, forest, and grassland[91] Diet: Caprids such as sheep and goats, as well as small mammals and birds[91] |
VU
|
| Tiger | P. tigris (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
|
Scattered sections of Southeast Asia, Indian subcontinent, and Siberia |
Size: 150–230 cm (59–91 in) long, 90–110 cm (35–43 in) tail[92] Habitat: Shrubland, forest, and grassland[93] Diet: Deer and wild pigs, as well as a wide variety of other animals[93] |
EN
|
Notes
- Population figures rounded to the nearest hundred. Population trends as described by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.









































