List of cingulates
Species in mammal order Cingulata From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Cingulata is an order of armored placental mammals. Members of this order are called cingulates, or colloquially, armadillos. They are primarily found in South America, though the northern naked-tailed armadillo is found mainly in Central America and the nine-banded armadillo has a range extending into North America. They are generally found in forests, but also savannas, shrublands, and grasslands. They all follow a similar body plan, and range in size from the pink fairy armadillo, at 11 cm (4 in) plus a 2 cm (1 in) tail, to the giant armadillo, at 100 cm (39 in) plus a 50 cm (20 in) tail. No population estimates have been made for any cingulate species, though the giant armadillo and the Brazilian three-banded armadillo are categorized as vulnerable species.

The twenty-two extant species of Cingulata are divided into two families: Dasypodidae, containing a single genus of nine species in the subfamily Dasypodinae, and Chlamyphoridae, containing thirteen species split between the two genera in the subfamily Chlamyphorinae, three in the subfamily Euphractinae, and three in the subfamily Tolypeutinae. Prior to 2016, all four subfamilies were included in Dasypodidae, with Chlamyphoridae containing only extinct species of glyptodonts.[1][2] Over one hundred extinct Cingulata species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.[3]
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (0 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (2 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (5 species) |
| LC | Least concern (8 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (5 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (2 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the cingulate's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
Classification
Summarize
Perspective
The order Cingulata consists of two families, Dasypodidae and Chlamyphoridae. Dasypodidae contains nine species in a single genus, while Chlamyphoridae contains thirteen species in eight genera, divided into three subfamilies. Many of these species are further subdivided into subspecies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species.
Family Dasypodidae
- Subfamily Dasypodinae
- Genus Dasypus (long-nosed armadillos): nine species
Family Chlamyphoridae
- Subfamily Chlamyphorinae
- Genus Calyptophractus (greater fairy armadillo): one species
- Genus Chlamyphorus (pink fairy armadillo): one species
- Subfamily Euphractinae
- Genus Chaetophractus (hairy armadillos): two species
- Genus Euphractus (six-banded armadillo): one species
- Genus Zaedyus (pichi): one species
- Subfamily Tolypeutinae
- Genus Cabassous (naked-tailed armadillos): four species
- Genus Priodontes (giant armadillo): one species
- Genus Tolypeutes (three-banded armadillos): two species
Cingulates
Summarize
Perspective
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by the reference work Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis.[4]
Dasypodidae
Subfamily Dasypodinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| East Amazonian long-nosed armadillo
|
D. beniensis Lönnberg, 1942 |
North-central South America | Size: 51–58 cm (20–23 in) long, plus 33–48 cm (13–19 in) tail[5] Habitat: Forest[6] Diet: Insects[5] |
NE
|
| Greater long-nosed armadillo | D. kappleri Krauss, 1862 |
Northeastern South America | Size: 51–58 cm (20–23 in) long, plus 33–48 cm (13–19 in) tail[7] Habitat: Forest[6] Diet: Insects[7] |
LC
|
| Hairy long-nosed armadillo | D. pilosus (Fitzinger, 1856) |
Western South America |
Size: 32–44 cm (13–17 in) long, plus 23–31 cm (9–12 in) tail[8] Habitat: Forest[9] Diet: Insects[8] |
NE
|
| Llanos long-nosed armadillo | D. sabanicola Mondolfi, 1968 |
Northern South America |
Size: 25–31 cm (10–12 in) long, plus 17–21 cm (7–8 in) tail[10] Habitat: Forest[11] Diet: Termites, as well as ants, beetles, and worms[10] |
NT
|
| Nine-banded armadillo | D. novemcinctus Linnaeus, 1758 Six subspecies
|
Central and northern South America, and central, southern, and eastern North America |
Size: 35–57 cm (14–22 in) long, plus 24–45 cm (9–18 in) tail[12] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[13] Diet: Omnivorous, including invertebrates, birds, fruit, and roots[12] |
LC
|
| Seven-banded armadillo | D. septemcinctus Linnaeus, 1758 |
Eastern South America |
Size: 24–31 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 12–17 cm (5–7 in) tail[14] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[15] Diet: Insects, seeds, and other plant material[14] |
LC
|
| Southern long-nosed armadillo | D. hybridus Desmarest, 1804 |
Southeastern South America |
Size: 26–31 cm (10–12 in) long, plus 15–19 cm (6–7 in) tail[16] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[17] Diet: Ants, termites, and beetles, as well as plant material and small vertebrates[16] |
NT
|
| West Amazonian long-nosed armadillo
|
D. pastasae (Thomas, 1901) |
Northwestern South America | Size: 51–58 cm (20–23 in) long, plus 33–48 cm (13–19 in) tail[18] Habitat: Forest[6] Diet: Insects[18] |
DD
|
| Yepes's mulita | D. mazzai Yepes, 1933 |
South-central South America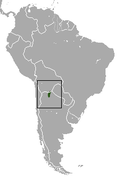 |
Size: About 31 cm (12 in) long, plus 18–23 cm (7–9 in) tail[19] Habitat: Forest[20] Diet: Believed to be omnivorous with a preference for insects[19] |
DD
|
Chlamyphoridae
Subfamily Chlamyphorinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greater fairy armadillo | C. retusus (Burmeister, 1863) |
Central South America |
Size: 14–18 cm (6–7 in) long, plus 4 cm (2 in) tail[21] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and desert[22] Diet: Insects, worms, snails, roots, and small seeds[21] |
DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink fairy armadillo | C. truncatus Harlan, 1825 |
Southern South America |
Size: 11–15 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in)tail[23][24] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[25] Diet: insects, worms and snails, as well as possibly plants[23] |
DD
|
Subfamily Euphractinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big hairy armadillo | C. villosus (Desmarest, 1804) |
Southern South America |
Size: 22–40 cm (9–16 in) long, plus 9–17 cm (4–7 in) tail[12] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[26] Diet: Omnivorous, including insects, invertebrates, small vertebrates, plants, and carrion[27] |
LC
|
| Screaming hairy armadillo | C. vellerosus (Gray, 1865) Two subspecies
|
Southern South America |
Size: 20–30 cm (8–12 in) long, plus tail[28] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[29] Diet: Beetles, butterfly larvae, plants, and small vertebrates[29] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six-banded armadillo | E. sexcinctus (Linnaeus, 1758) Five subspecies
|
Central and eastern South America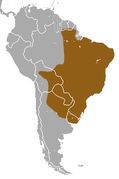 |
Size: 40–50 cm (16–20 in) long, plus 20–25 cm (8–10 in) tail[30] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[31] Diet: Carrion, small vertebrates, insects, spiders, bird eggs, and plants[30] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pichi | Z. pichiy (Desmarest, 1804) Two subspecies
|
Southern South America |
Size: 26–34 cm (10–13 in) long, plus 10–12 cm (4–5 in) tail[12] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert[32] Diet: Insects, worms, and other invertebrates, as well as carrion[12] |
NT
|
Subfamily Tolypeutinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chacoan naked-tailed armadillo | C. chacoensis Wetzel, 1980 |
South-central South America |
Size: 30–35 cm (12–14 in) long, plus 9–10 cm (4–4 in) tail[33] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[34] Diet: Ants and termites, as well as seeds and fruit[33] |
NT
|
| Greater naked-tailed armadillo | C. tatouay (Desmarest, 1804) |
Eastern South America |
Size: 36–49 cm (14–19 in) long, plus 15–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[35] Habitat: Forest and grassland[36] Diet: Ants and termites[37] |
LC
|
| Northern naked-tailed armadillo | C. centralis (Miller, 1899) |
Northern South America and Central America |
Size: 30–40 cm (12–16 in) long, plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail[12] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[38] Diet: Termites and ants[12] |
DD
|
| Southern naked-tailed armadillo | C. unicinctus (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
|
Northern and central South America |
Size: 35–44 cm (14–17 in) long, plus 16–20 cm (6–8 in) tail[39] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[40] Diet: Ants and termites[39] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giant armadillo | P. maximus (Kerr, 1792) |
Northern and central South America |
Size: 75–100 cm (30–39 in) long, plus 50 cm (20 in) tail[41] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[42] Diet: Termites and certain ant species[43] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazilian three-banded armadillo | T. tricinctus (Linnaeus, 1758) |
Eastern South America |
Size: 23–25 cm (9–10 in) long, plus tail[44] Habitat: Savanna and shrubland[45] Diet: Ants, termites, beetles, and other insects, as well as plants[44] |
VU
|
| Southern three-banded armadillo | T. matacus (Desmarest, 1804) |
South-central South America |
Size: 20–25 cm (8–10 in) long, plus tail[46] Habitat: Savanna and shrubland[47] Diet: Insects, as well as fruit and seeds[46] |
NT
|
References
Sources
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.




















