List of German inventions and discoveries
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
German inventions and discoveries are ideas, objects, processes or techniques invented, innovated or discovered, partially or entirely, by Germans. Often, things discovered for the first time are also called inventions and in many cases, there is no clear line between the two.
"What the world is today, good and bad, it owes to Gutenberg. Everything can be traced to this source, but we are bound to bring him homage, … for the bad that his colossal invention has brought about is overshadowed a thousand times by the good with which mankind has been favored."
American writer Mark Twain (1835−1910)[1]
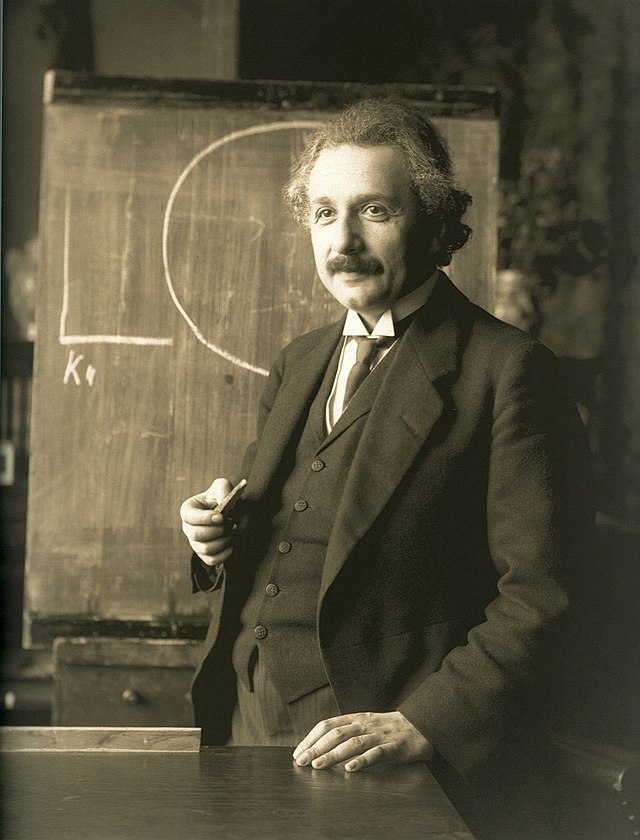
Germany has been the home of many famous inventors, discoverers and engineers, including Carl von Linde, who developed the modern refrigerator.[2] Ottomar Anschütz and the Skladanowsky brothers were early pioneers of film technology, while Paul Nipkow and Karl Ferdinand Braun laid the foundation of the television with their Nipkow disk and cathode-ray tube (or Braun tube) respectively.[3][4] Hans Geiger was the creator of the Geiger counter and Konrad Zuse built the first fully automatic digital computer (Z3) and the first commercial computer (Z4).[5][6] Such German inventors, engineers and industrialists as Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin,[7] Otto Lilienthal, Werner von Siemens, Hans von Ohain, Henrich Focke, Gottlieb Daimler, Rudolf Diesel, Hugo Junkers and Karl Benz helped shape modern automotive and air transportation technology, while Karl Drais invented the bicycle.[8] Aerospace engineer Wernher von Braun developed the first space rocket at Peenemünde and later on was a prominent member of NASA and developed the Saturn V Moon rocket. Heinrich Rudolf Hertz's work in the domain of electromagnetic radiation was pivotal to the development of modern telecommunication.[9] Karl Ferdinand Braun invented the phased array antenna in 1905,[10] which led to the development of radar, smart antennas and MIMO, and he shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Guglielmo Marconi "for their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy".[11] Philipp Reis constructed the first device to transmit a voice via electronic signals and for that the first modern telephone,[12][13] while he also coined the term.[14]
Georgius Agricola gave chemistry its modern name. He is generally referred to as the father of mineralogy and as the founder of geology as a scientific discipline, while Justus von Liebig is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry.[15] Otto Hahn is the father of radiochemistry and discovered nuclear fission, the scientific and technological basis for the utilization of atomic energy. Emil Behring, Ferdinand Cohn, Paul Ehrlich, Robert Koch, Friedrich Loeffler and Rudolph Virchow were among the key figures in the creation of modern medicine, while Koch and Cohn were also founders of microbiology.[16]
Johannes Kepler was one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, natural and modern science.[17][18][19] Wilhelm Röntgen discovered X-rays.[20] Albert Einstein introduced the special relativity and general relativity theories for light and gravity in 1905 and 1915 respectively. Along with Max Planck, he was instrumental in the creation of modern physics with the introduction of quantum mechanics, in which Werner Heisenberg and Max Born later made major contributions.[21] Einstein, Planck, Heisenberg and Born all received a Nobel Prize for their scientific contributions; from the award's inauguration in 1901 until 1956, Germany led the total Nobel Prize count.[22] Today the country is third with 115 winners.
The movable-type printing press was invented by German blacksmith Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. In 1997, Time Life magazine picked Gutenberg's invention as the most important of the second millennium.[23] In 1998, the A&E Network ranked Gutenberg as the most influential person of the second millennium on their "Biographies of the Millennium" countdown.[23]
The following is a list of inventions, innovations or discoveries known or generally recognised to be German.
Anatomy
- 17th century: First description of duct of Wirsung by Johann Georg Wirsung[24]
- 1720: Discovery of the ampulla of Vater by Abraham Vater[25]
- 1745: First description of crypts of Lieberkühn by Johann Nathanael Lieberkühn[26]
- 19th century: First description of Auerbach's plexus by Leopold Auerbach[27]
- 19th century: First description of Meissner's plexus by Georg Meissner[28]
- 19th century: Discovery of Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system by Theodor Schwann[29]
- 1836: Discovery and study of pepsin by Theodor Schwann[30]
- 1840: First medical report on poliomyelitis (Heine-Medin disease), and the first to recognize the illness as a clinical entity, by Jakob Heine[31]
- 1852: First description of tactile corpuscle by Georg Meissner and Rudolf Wagner[32]
- 1868: Discovery of Langerhans cell by Paul Langerhans[33]
- 1869: Discovery of islets of Langerhans by Paul Langerhans[34]
- 1875: First description of Merkel cell by Friedrich Sigmund Merkel[35]
- 1882: First successful cholecystectomy by Carl Langenbuch in Berlin[36]
- 1906: Discovery of the Alzheimer's disease by Alois Alzheimer[37]
- 1909: First description of Brodmann area by Korbinian Brodmann[38]
- 1977: Plastination by Gunther von Hagens[39]
Animals

- 1907: Modern zoo (Tierpark Hagenbeck) by Carl Hagenbeck in Hamburg[40]
- 1916: Guide dog; the world's first training school, established by Dr. Gerhard Stalling in Oldenburg[41]
Archaeology and paleontology

- Early 18th century: Founding of modern archaeology by Johann Joachim Winckelmann[42]
- 1825: Rhamphorhynchus by Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring[43]
- 1834: Plateosaurus by Johann Friedrich Engelhardt near Nuremberg, described in 1837 by Hermann von Meyer[44]
- 1856: Neanderthal 1 near Düsseldorf[45]
- 1856–1857: First description of the Neanderthal by Johann Carl Fuhlrott and Hermann Schaaffhausen[46]
- 1860: Teratosaurus by Sixt Friedrich Jakob von Kapff near Stuttgart, described in 1861 by Hermann von Meyer[47]
- 1861: Archaeopteryx by Hermann von Meyer near Solnhofen[48]
- 1868–1879: Troy by Heinrich Schliemann[49]
- c. 1900: Gordium by Alfred and Gustav Körte[50]
- 1906–1913: Hattusa by Hugo Winckler[51]
- 1908: Homo heidelbergensis by Daniel Hartmann and Otto Schoetensack near Heidelberg[52]
- 1912: The Nefertiti Bust by Ludwig Borchardt[53]
- 1915: Description of Spinosaurus, the largest known theropod, by Ernst Stromer[54]
- 1925: Stomatosuchus by Ernst Stromer[55]
- 1931: Description of Carcharodontosaurus by Ernst Stromer[56]
- 1932: Aegyptosaurus by Ernst Stromer[57]
- 1934: Bahariasaurus by Ernst Stromer[58]
- 1991: Ötzi by Helmut and Erika Simon from Nuremberg[59]
Arts


- 40.000 BC: The oldest confirmed sculptures in the world, the 41,000 to 39,000-year-old Lion Man[60] and the 42,000 to 41,000-year-old Venus of Hohle Fels[61][62]
- 15th century: Drypoint by the Housebook Master, a south German artist[63]
- 1525: Ray tracing by Albrecht Dürer[64]
- 1642: Mezzotint by Ludwig von Siegen
- 1708: Meissen porcelain, the first European hard-paste porcelain, by Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus in Meissen[65]
- 1810: Theory of Colours by Johann Wolfgang Goethe[66]
- 1864: Wothlytype uranium-based photographic printing process[67][68]
- Early 1900s: The modernist movement Expressionism[69]
- 1919: Bauhaus by Walter Gropius[70]
Astronomy


- 1450–1550: Copernican heliocentrism, developed by Regiomontanus and Nicolaus Copernicus[71]
- 1609–1619: Kepler's laws of planetary motion by Johannes Kepler[72]
- 1781: Discovery of Uranus, with two of its major moons (Titania and Oberon), by William Herschel[73]
- 1846: Discovery of Neptune by Johann Galle[74]
- 1902: Discovery of the stratosphere by Richard Assmann[75]
- 1909: Discovery of cosmic ray by Theodor Wulf[76]
- 1916: Schwarzschild metric[77] and Schwarzschild radius[78] by Karl Schwarzschild
Biology and genetics


- 1759: Description of mesonephros by Caspar Friedrich Wolff[79]
- 1790s: Recapitulation theory by Johann Friedrich Meckel and Carl Friedrich Kielmeyer[80]
- Late 1790s/early 1800s: Humboldtian science by Alexander von Humboldt[81]
- 1834: Humboldt penguin by Franz Meyen, after its initial discovery by Alexander von Humboldt[82]
- 1835: Cell division by Hugo von Mohl[83]
- 1835: Discovery and description of mitosis by Hugo von Mohl[84]
- 1839: Cell theory by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden (with contributions from Rudolf Virchow)[85]
- 1840: Discovery of hemoglobin by Friedrich Ludwig Hünefeld[86]
- 1845: Odic force by Carl Reichenbach[87]
- 1851: Discovery of alternation of generations as a general principle in plant life by Wilhelm Hofmeister[88]
- 1876: Discovery and description of meiosis by Oscar Hertwig[89]
- 1877: Description of dyslexia by Adolf Kussmaul[90]
- 1880s: Bacteriology by Robert Koch[91]
- Late 19th century: Isolated the non-protein component of "nuclein", determining the chemical composition of nucleic acids, and later isolated its five primary nucleobases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine and uracil) by Albrecht Kossel[92]
- 1885: Forgetting curve and learning curve by Hermann Ebbinghaus[93]
- 1888: Description and naming of the centrosome by Theodor Boveri[94]
- 1890: Description of mitochondrion by Richard Altmann[95]
- 1892: Weismann barrier and germ plasm by August Weismann[96]
- 1908: Hardy–Weinberg principle by Wilhelm Weinberg[97]
- 1928: First reliable pregnancy test by Selmar Aschheim and Bernhard Zondek[98]
- 1928: Artificial cloning of organisms by Hans Spemann and Hilde Mangold[99]
- 1932: Urea cycle by Kurt Henseleit and Hans Adolf Krebs[100]
- 1937: Citric acid cycle by Hans Adolf Krebs[101]
- 1974: First genetically modified animal (a mouse) by Rudolf Jaenisch[102]
- 2014: CityTree, a large-scale urban air purifier intended to filter smog in cities, by Green City Solutions[103]
Chemistry





- 1625: Glauber's salt by Johann Rudolf Glauber[104]
- 1669: Discovery of phosphorus by Hennig Brand in Hamburg[105]
- 1706: Prussian blue by Heinrich Diesbach in Berlin[106]
- 1717: Johann Heinrich Schulze used a light-sensitive slurry to capture images of cut-out letters on a bottle, sometimes seen as the start of photography[107][108]
- 1724: Temperature scale Fahrenheit by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit[109]
- 1746: Basic theory of isolating zinc by Andreas Sigismund Marggraf[110]
- c. 1770 – c. 1785: Identification of molybdenum, tungsten, barium and chlorine by Carl Wilhelm Scheele[111]
- 1773 or earlier: discovery of oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first) by Carl Wilhelm Scheele[112]
- 1789: Discovery of the elements uranium[113] and zirconium[114] by Martin Heinrich Klaproth
- 1799: Production of sugar from sugar beets, the beginning of the modern sugar industry,[115] by Franz Karl Achard, after foundations were laid by Andreas Sigismund Marggraf[116]
- 19th century: Eupione by Carl Reichenbach[117]
- 1817: Discovery of cadmium by Karl Samuel Leberecht Hermann and Friedrich Stromeyer[118]
- 1820s: Oechsle scale by Ferdinand Oechsle[119]
- 1823: Döbereiner's lamp, often hailed as the first lighter,[120] by Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner
- 1828: Discovery of creosote by Carl Reichenbach[121]
- 1828, 1893: Isolation (1828) of nicotine by Wilhelm Heinrich Posselt and Karl Ludwig Reimann.[122] The structure (1893) of nicotine was later discovered by Adolf Pinner and Richard Wolffenstein[123]
- 1828: Synthesis of urea by Friedrich Wöhler (Wöhler synthesis)[124]
- 1830: Creation of paraffin wax by Carl Reichenbach[125]
- 1832: Discovery of pittacal by Carl Reichenbach[126]
- 1834: Melamine by Justus von Liebig[127]
- 1834: Discovery of phenol by Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge[128]
- 1836 (or 1837): Discovery of diatomaceous earth (Kieselgur in German) by Peter Kasten on the northern slopes of the Haußelberg hill, in the Lüneburg Heath in North Germany[129]
- 1838: Fuel cell by Christian Friedrich Schönbein[130]
- 1839: Discovery of ozone by Christian Friedrich Schönbein[131]
- 1839, 1930: Discovery of polystyrene by Eduard Simon, was made a commercial product by IG Farben in 1930[132]
- c. 1840: Nitrogen-based fertiliser by Justus von Liebig,[133] important innovations were later made by Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch (Haber process) in the 1900s[134]
- 1846: Discovery of guncotton by Christian Friedrich Schönbein[135]
- 1850s: Siemens-Martin process by Carl Wilhelm Siemens[136]
- c. 1855: Bunsen burner by Robert Bunsen and Peter Desaga[137]
- 1857: Siemens cycle by Carl Wilhelm Siemens[138]
- 1859: Pinacol coupling reaction by Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig[139]
- 1860–61: Discovery of caesium and rubidium by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff[140]
- 1860: Erlenmeyer flask by Emil Erlenmeyer[141]
- 1863–64: Discovery of indium by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter[142][143][144]
- 1863: First synthesis of trinitrotoluene (TNT) by Julius Wilbrand[145]
- 1864: First synthesis of barbiturate by Adolf von Baeyer, first marketed by Bayer under the name "Veronal" in 1903[146]
- 1864: Wothlytype uranium-based photographic printing process patented[67][68]
- 1865: Synthetic indigo dye by Adolf von Baeyer, first marketed by BASF in 1897[147]
- c. 1870: Brix unit by Adolf Brix[148]
- 1872: Synthesis of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) by Eugen Baumann[149]
- 1877: Poly(methyl methacrylate) by Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig, was made a commercial product (Plexiglas) by Otto Röhm in 1933[150]
- 1882: Tollens' reagent by Bernhard Tollens[151]
- 1883: Claus process by Carl Friedrich Claus[152]
- 1884: Paal–Knorr synthesis by Carl Paal and Ludwig Knorr[153]
- 1885–1886: Discovery of germanium by Clemens Winkler[154]
- 1887: Petri dish by Julius Richard Petri[155]
- 1888: Büchner flask and Büchner funnel by Ernst Büchner[156]
- 1895: Hampson–Linde cycle by Carl von Linde[157]
- 1897: Galalith by Wilhelm Krische[158]
- 1898: Polycarbonate by Alfred Einhorn, was made an commercial product by Hermann Schnell at Bayer in 1953 in Uerdingen[159]
- 1898: Synthesis of polyethylene, the most common plastic, by Hans von Pechmann[160]
- 1898: First synthesis of purine by Emil Fischer. He had also coined the word in 1884.[161]
- Early 20th century: Schlenk flask by Wilhelm Schlenk[162]
- 1900s: Haber process by Carl Bosch and Fritz Haber[134]
- 1902: Ostwald process by Wilhelm Ostwald[163]
- 1903: First commercially decaffeination process by Ludwig Roselius[164]
- 1907: Thiele tube by Johannes Thiele[165]
- 1913: Coal liquefaction (Bergius process) by Friedrich Bergius[166][167]
- 1913: Identification of protactinium by Oswald Helmuth Göhring[168]
- 1925: Discovery of rhenium by Otto Berg, Ida Noddack and Walter Noddack[169]
- 1928: Diels–Alder reaction by Kurt Alder and Otto Diels[170]
- 1929: Discovery of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by Karl Lohmann[171]
- 1929: Styrene-butadiene (synthetic rubber) by Walter Bock[172]
- 1935: Karl Fischer titration by Karl Fischer[173]
- 1937: Creation of polyurethane by Otto Bayer at IG Farben in Leverkusen[174]
- 1953: Ziegler–Natta catalyst by Karl Ziegler[175]
- 1954: Wittig reaction by Georg Wittig[176]
- 1981–1996: Discovery and creation of bohrium by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Münzenberg at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt[177]
- 1982: Discovery and creation of meitnerium at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research[178]
- 1984: Discovery and creation of hassium at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research[177]
- 1994: Discovery and creation of darmstadtium at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research[179]
- 1994: Discovery and creation of roentgenium at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research[180]
- 1996: Discovery and creation of copernicium at the GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research[181]
Clothing and cosmetics

- 13th century: Functional buttons with buttonholes for fastening or closing clothes[182]
- 1709: Eau de Cologne by Johann Maria Farina (Giovanni Maria Farina) in Cologne[183]
- 1905: Permanent wave that was suitable for use on people, by Karl Nessler[184]
- 1911: Nivea, the first modern cream,[185] by Beiersdorf AG[186]
- 1960s: BB cream by Christine Schrammek[187]
Computing


- Late 17th century: Modern binary numeral system by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz[188]
- 1918–1923: Enigma machine by Arthur Scherbius[189]
- 1920s: Hellschreiber (precursor of the impact dot matrix printers and faxes) by Rudolf Hell[190][191]
- 1941: First programmable, fully automatic digital computer (Z3) by Konrad Zuse[192]
- 1942–1945: Programming language Plankalkül, the first high-level programming language to be designed for a computer,[193] by Konrad Zuse
- 1945: The world's first commercial digital computer (Z4) by Konrad Zuse[6]
- 1957: Stack (abstract data type) by Klaus Samelson and Friedrich L. Bauer of Technical University Munich[194]
- 1960s: Smart card by Jürgen Dethloff and Helmut Gröttrup[195]
Construction, architecture and shops


- 1831–1834: Wire rope by Wilhelm Albert[196][197]
- 1858: Hoffmann kiln by Friedrich Hoffmann[198]
- 1880: The world's first electric elevator by Werner von Siemens[199]
- 1895: Electrically driven hand drill by Carl and Wilhelm Fein in Stuttgart[200]
- 1895: Exothermic welding process by Hans Goldschmidt[201]
- 1926–1927: Portable electric (by Andreas Stihl in 1926 in Cannstatt) and the first petrol chainsaw (by Emil Lerp in 1927).[202] A precursor of chainsaws was made around 1830 by Bernhard Heine (osteotome)[203]
- 1927: Concrete pump by Max Giese and Fritz Hull[204]
- 1930s: Particle board by Max Himmelheber[205]
- 1954: Angle grinder by Ackermann + Schmitt (FLEX-Elektrowerkzeuge) in Steinheim an der Murr[206][207]
- 1958: Modern (plastic) wall plug (Fischer Wall Plug) by Artur Fischer[208][209][210]
- 1962: The world's first sex shop by Beate Uhse AG in Flensburg[211]
- 1963–1967: First hydraulic breaker by Krupp in Essen[212]
- 1988–1990: The concept of the passive house by Wolfgang Feist in Darmstadt[213]
Cuisine








- Altbier
- Angostura bitters by Johann Gottlieb Benjamin Siegert in Venezuela, 1824[214]
- First automat restaurant (Quisisana) in Berlin, 1895[215]
- Baumkuchen
- Berliner (doughnut)
- Bethmännchen
- Berliner Weisse
- Bienenstich
- Black Forest cake
- Bock
- Bratwurst
- Braunschweiger
- Currywurst by Herta Heuwer[216]
- Dominostein by Herbert Wendler[217]
- Donauwelle
- Modern doner kebab sandwich in Berlin, 1972[218]
- Dortmunder Export
- Fanta
- Frankfurter Kranz
- Frankfurter Würstchen
- Gummy bear
- Hamburger (the "founder" is unknown, but it has German origins)[219][220]
- Hamburg steak
- Hedgehog slice (Kalter Hund)
- Helles
- Hot Dog[221][222]
- Jägermeister
- Kölsch
- Lager[223]
- Lebkuchen
- Marmite by Justus von Liebig[224][225]
- Märzen
- Meat extract by Justus von Liebig[226]
- Obatzda
- Parboiled rice (Huzenlaub Process) by Erich Huzenlaub[227]
- Pilsener by Josef Groll[228][229]
- Pinkel
- Pretzel (the origin is disputed, but the earliest recorded evidence of pretzels appeared in Germany)[230]
- Prinzregententorte
- Pumpernickel
- Radler
- Riesling wine[231]
- Rye beer
- Saumagen
- Schwarzbier
- Sprite[232]
- Strammer Max
- Stollen
- Streuselkuchen
- Teewurst
- Thuringian sausage
- Toast Hawaii
- Vienna sausage by Johann Georg Lahner in 1805[233]
- Welf pudding
- Wheat beer
- Zwieback
- Zwiebelkuchen
Education, language and printing


- 12th century: Lingua Ignota, the first entirely artificial language, by St. Hildegard of Bingen, OSB[234]
- c. 1440: Printing press with movable type by Johannes Gutenberg,[23] starting the global spread of the printing press
- 1605: First newspaper (Relation aller Fürnemmen und gedenckwürdigen Historien) by Johann Carolus in Strasbourg (then part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation)[235]
- 1774: The process of deinking by Justus Claproth[236]
- 1796: Lithography by Alois Senefelder[237]
- Early 19th century: Humboldtian model of higher education by Wilhelm von Humboldt,[238] which led to the creation of the first modern university (University of Berlin) in 1810,[239] although the University of Halle is also regarded as "the first truly modern university"[240]
- 1812–1858: Grimms' Fairy Tales by Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm[241]
- 1830s: Kindergarten concept by Friedrich Fröbel[242]
- 1844: Wood pulp process for use in papermaking by Friedrich Gottlob Keller[243]
- 1879: The constructed language Volapük by Johann Martin Schleyer[244]
- 1884–1886: Linotype machine by Ottmar Mergenthaler[245]
- 1905: The Morse code distress signal SOS ( ▄ ▄ ▄ ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ ▄ ▄ ▄ )[246][247]
- 1919: Waldorf education by Emil Molt and Rudolf Steiner in Stuttgart[248]
Entertainment, electronics and media



- c. 1150: The earliest known morality play (Ordo Virtutum) by St. Hildegard of Bingen, OSB[249]
- c. 1505: The world's first (pocket) watch (Watch 1505) by Peter Henlein[250]
- 1663: First magazine (Erbauliche Monaths Unterredungen)[251]
- 1885: Nipkow disk (fundamental component in the earliest televisions) by Paul Gottlieb Nipkow[3]
- 1897: Cathode-ray tube (CRT) and the oscilloscope by Ferdinand Braun[252]
- 1903: Printed circuit board by Albert Hanson of Berlin[253]
- 1907: Earplug by Max Negwer (Ohropax)[254]
- 1907: Pigeon photography by Julius Neubronner[255]
- 1920s: Small format camera (35mm format) by Oskar Barnack[256]
- 1928: Magnetic tape in Dresden, later developed and commercialized by AEG[257]
- 1930s: (Modern) tape recorder by BASF (then part of the chemical giant IG Farben) and AEG in cooperation with the state radio RRG[258][259]
- 1934: Fernsehsender Paul Nipkow (TV Station Paul Nipkow) in Berlin, first public television station in the world[260][261]
- 1949: Integrated circuit by Werner Jacobi (Siemens AG)[262]
- 1961: Phase Alternating Line (PAL), a colour encoding system for analogue television, by Walter Bruch of Telefunken in Hanover[263]
- 1970: Twisted nematic field effect by Wolfgang Helfrich (with Swiss physicist Martin Schadt)[264]
- 1983: Controller Area Network (CAN bus) by Robert Bosch GmbH[265]
- 1984: Short Message Service (SMS) concept by Friedhelm Hillebrand[266][267]
- 1990s: MP3 format by Karlheinz Brandenburg and others at the Fraunhofer Society[268]
- 1990–1991: Junghans Mega: first radio-controlled digital wristwatch and later first radio-controlled wristwatch with hands by Junghans[269]
- 1991: SIM card by Giesecke & Devrient in Munich[270]
- 2005: YouTube, co-founded by Jawed Karim[271]
- c. 2011: Li-Fi by Harald Haas[272]
Geography, geology and mining

- 1507: Martin Waldseemüller and his collaborator Matthias Ringmann have been credited with the first recorded usage of the word America, to name a portion of the New World in honour of Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci.[273][274]
- 1812: Mohs scale of mineral hardness by Friedrich Mohs[275]
- 1855: Stauroscope by Wolfgang Franz von Kobell[276]
- 1884: Köppen climate classification by Wladimir Köppen.[277] Changes were later made by Rudolf Geiger (it is thus sometimes hailed as the "Köppen–Geiger climate classification system").[278]
- 1912: Theory of continental drift and the postulation of the existence of Pangaea by Alfred Wegener[279]
- 1933: Central place theory by Walter Christaller[280]
- 1935: Richter magnitude scale by Beno Gutenberg (together with Charles Francis Richter)[281]
Household and office appliance


- 1835: Modern (silvered-glass) mirror by Justus von Liebig[282][283]
- 1864: Ingrain wallpaper by Hugo Erfurt[284]
- 1870–1895: Modern refrigerator and modern refrigeration by Carl von Linde[2][285][286][287]
- 1871: Modern mattress (the innerspring mattress) by Heinrich Westphal in Berlin[288][289]
- 1886: Hole punch and ring binder by Friedrich Soennecken in Bonn[290]
- 1886: Folding ruler by Anton Ullrich in Maikammer[291]
- 1901: Adhesive tape by company Beiersdorf AG[292]
- 1907: (Modern) Laundry detergent (Persil) by Henkel[293]
- 1908: Paper coffee filter by Melitta Bentz[294]
- 1909: Egg slicer by Willy Abel in Berlin[295]
- 1929, 1949: First tea bag packing machine (1929)[296] and the modern tea bag (1949)[297] by Adolf Rambold of Teekanne
- 1941: Chemex Coffeemaker by Peter Schlumbohm[298]
- 1954: Wigomat, the first electric drip coffee maker[299]
- 1969: Glue stick by Henkel[300]
Mathematics
- 1489: The + and - symbols first appeared in print in Johannes Widmann's book Behende und hüpsche Rechenung auff allen Kauffmanschafft, published in Leipzig in 1489, in reference to surpluses and deficits in business problems[301]
- 1490: Prosthaphaeresis, invented by Johannes Werner[302]
- 1525: The "√" symbol, first published by Christoph Rudolff[303]
- 1611: Kepler conjecture by Johannes Kepler[304]
- 1623: Mechanical calculator by Wilhelm Schickard[305][306]
- Late 17th century: Calculus[307] and Leibniz's notation[308] by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
- 1673–1676: Leibniz formula for π by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz[309]
- 1675: Integral symbol by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz[310]
- 1795: Least squares by Carl Friedrich Gauss[311]
- c. 1810: Gaussian elimination by Carl Friedrich Gauss[312]
- 1824: Generalization of the Bessel function by Friedrich Bessel[313]
- 1827: Gauss map[314] and Gaussian curvature[315] by Carl Friedrich Gauss
- 1837: Analytic number theory by Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet[316]
- c. 1850: Riemann geometry by Bernhard Riemann[317]
- 1859: Riemann hypothesis by Bernhard Riemann[318]
- 1874: Cantor's first uncountability proof and set theory by Georg Cantor[319]
- 1882: Klein bottle by Felix Klein[320]
- 1891: Cantor's diagonal argument and Cantor's theorem by Georg Cantor[321]
- 1897: Cantor–Bernstein–Schroeder theorem by Felix Bernstein and Ernst Schröder[322]
- c. 1900: Runge–Kutta methods by Wilhelm Kutta and Carl Runge[323][324]
- 1900s: Hilbert space by David Hilbert[325]
- Early 20th century: Weyl tensor by Hermann Weyl[326]
Medicine and drugs






- 1796: Homeopathy by Samuel Hahnemann[327]
- 1803–1827: First isolation of morphine by Friedrich Sertürner in Paderborn; first marketed to the general public by Sertürner and Company in 1817 as a pain medication; and the first commercial production began in 1827 in Darmstadt by Merck.[328]
- 1832: First synthesis of chloral hydrate, the first hypnotic drug,[329] by Justus von Liebig at the University of Giessen;[330] Oscar Liebreich introduced the drug into medicine in 1869 and discovered its hypnotic and sedative qualities.[331]
- 1840: Discovery and description of Graves-Basedow disease by Karl Adolph von Basedow[332]
- 1847: Kymograph by Carl Ludwig[333]
- 1850s: Microscopic pathology by Rudolf Virchow[334]
- 1850–51: Ophthalmoscope by Hermann von Helmholtz[335][336]
- 1852: First complete blood count by Karl von Vierordt[337]
- 1854: Sphygmograph by Karl von Vierordt[338]
- 1855: First synthesis of the cocaine alkaloid by Friedrich Gaedcke;[339] development of an improved purification process by Albert Niemann in 1859–1860, who also coined the name "cocaine".[340] First commercial production of cocaine began in 1862 in Darmstadt by Merck.[341]
- 1881: First modern caesarean section performed by Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer (introduction of the transverse incision technique)[342]
- 1882: Adhesive bandage (Guttaperchapflastermulle) by Paul Carl Beiersdorf[343]
- 1882: Discovery of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria which causes tuberculosis, by Robert Koch[344]
- 1884: Discovery of the pathogenic bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae which causes diphtheria, by Edwin Klebs and Friedrich Löffler[345]
- 1884: Koch's postulates by Robert Koch and Friedrich Loeffler, based on earlier concepts described by Jakob Henle[346]
- 1884: Discovery of the vibrio cholerae bacteria which causes cholera, by Robert Koch[347]
- 1887: Amphetamine by Romanian-born Lazăr Edeleanu in Berlin[348]
- 1887: Löffler's medium by Friedrich Loeffler[349]
- 1888: First successful afocal scleral glass contact lenses by Adolf Gaston Eugen Fick[350]
- 1890: Diphtheria antitoxin by Emil von Behring[351]
- 1890s-1910s: modern scientific psychiatry, psychopharmacology and psychiatric genetics by Emil Kraepelin
- 1897–1899: Aspirin by Felix Hoffmann or Arthur Eichengrün at Bayer in Elberfeld[352]
- 1897: Heroin by Felix Hoffmann at Bayer in Elberfeld[353]
- 1897: Protargol by Arthur Eichengrün.[354]
- 1897: Discovery of the cause of foot-and-mouth disease (Aphthovirus) by Friedrich Loeffler[355]
- 1907–1910: First synthesis of arsphenamine, the first antibiotic,[356] by Paul Ehrlich and Alfred Bertheim.[357] In 1910 marketed by Hoechst under the name Salvarsan.[358]
- 1908–1911: Creation of dihydrocodeine[359]
- 1909, 1929: First intrauterine device (IUD) by Richard Richter (of Waldenburg, in 1909), and the first ring (Gräfenberg's ring, 1929) used by a significant number of women by Ernst Gräfenberg.[360]
- 1912: MDMA by Merck chemist Anton Köllisch[361][362]
- 1914: Creation of oxymorphone[363]
- 1916: Creation of oxycodone by Martin Freund and Edmund Speyer at the University of Frankfurt[364]
- 1920–1924: First synthesis of hydrocodone by Carl Mannich and Helene Löwenheim in 1920,[365] first marketed by former German drug development company Knoll as Dicodid in 1924.[366]
- 1922: Discovery and creation of desomorphine by Knoll[367]
- 1923: Creation of hydromorphone (Dilaudid) by Knoll[368]
- 1924: Electroencephalography (EEG) by Hans Berger. He also invented the electroencephalogram and discovered alpha waves.[369]
- 1929: Cardiac catheterization by Werner Forssmann[370]
- 1932: Prontosil by Josef Klarer and Fritz Mietzsch at Bayer[371]
- 1934: Synthesis of Chloroquine by Italian-born Hans Andersag working for Bayer AG[372]
- 1937–1939: Creation of methadone by Max Bockmühl and Gustav Ehrhart of IG Farben[373]
- 1939: Intramedullary rod by Gerhard Küntscher[374]
- 1943: Luria–Delbrück experiment by Max Delbrück[375]
- 1953: Echocardiography by Carl Hellmuth Hertz (with Swedish physician Inge Edler)[376]
- 1969: Articaine (Ultracain), a dental local anesthetic first synthesized by pharmacologist Roman Muschaweck and chemist Robert Rippel (former Hoechst AG)[377][378]
- 1997: C-Leg by Ottobock[379]
- 2007: Small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) by Walter Sekundo and Marcus Blum[380]
- 2020: mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) based on research by Uğur Şahin and Özlem Türeci[381][382]
Military and weapons




- 1498: Barrel rifling in Augsburg[383]
- 1836: Dreyse needle gun by Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse[384]
- 1901: Modern flamethrower by Richard Fiedler[385]
- 1916: First anti-tank grenade[386]
- 1918: First anti-tank rifle (Mauser Tankgewehr M1918) by Mauser[387]
- 1918: First practical submachine gun (MP 18) by Theodor Bergmann[388]
- 1920s: Creation of Zyklon B by Walter Heerdt and Bruno Tesch at Degesch[389]
- 1935: Flecktarn by Johann Georg Otto Schick[390]
- 1936: The first ever nerve agent, tabun, by Gerhard Schrader (IG Farben) in Leverkusen[391]
- 1937: Jerrycan by Eisenwerke Müller & Co. in Schwelm[392]
- 1938: The nerve agent sarin by IG Farben in Wuppertal-Elberfeld[393]
- 1939: Warfare method of blitzkrieg by i.a. Heinz Guderian[394][395]
- 1941: The only rocket-powered fighter aircraft ever to have been operational and the first piloted aircraft of any type to exceed 1000 km/h (621 mph) in level flight, the Messerschmitt Me 163, by Alexander Lippisch.[396]
- 1942: First modern assault rifle (StG 44) by Hugo Schmeisser[397]
- 1943: First aviation unit (Kampfgeschwader 100) to use precision-guided munition[398]
- 1944: First operational cruise missile (V-1 flying bomb) by Robert Lusser at Fieseler[399]
- 1944: The world's first long-range guided ballistic missile (V-2 rocket), created under the direction of Wernher von Braun[400][401]
- 1944: The nerve agent soman by Konrad Henkel in Heidelberg[402]
Musical instruments


- c. 1690: Clarinet by Johann Christoph Denner in Nuremberg[403]
- 1805: Panharmonicon by Johann Nepomuk Mälzel[404]
- 1814–1816: Metronome by Johann Nepomuk Mälzel and Dietrich Nikolaus Winkel[405]
- c. 1815: (Modern) French horn by Heinrich Stölzel and Friedrich Blühmel[406]
- 1821: Harmonica by Christian Friedrich Ludwig Buschmann in Berlin[407]
- 1828: Flugelhorn by Heinrich Stölzel in Berlin[408]
- c. 1815: Oldest found accordion, from Nuremberg[409]
- 1835: Tuba by Wilhelm Friedrich Wieprecht and Johann Gottfried Moritz in Berlin[410]
- 1850s: Wagner tuba by Richard Wagner[411]
- 1854: Bandoneon by Heinrich Band[412]
- 1877: Microphone by Emile Berliner[413]
- 1887: Gramophone record by Emile Berliner[413][414]
- 1914: Hornbostel–Sachs, the most used system in musical instrument classification, by Curt Sachs (together with Erich Moritz von Hornbostel)[415]
Physics and scientific instruments







- 1512, 1576: Theodolite by Gregorius Reisch and Martin Waldseemüller (1512),[416] although the first "true" version was created by Erasmus Habermehl (1576)[417]
- 1650: First vacuum pump by Otto von Guericke[418]
- 1654: Magdeburg hemispheres by Otto von Guericke[419]
- 1663: First electrostatic generator by Otto von Guericke[420]
- 1745: Leyden jar (Kleistian jar) by Ewald Georg von Kleist[421]
- 1777: Discovery of Lichtenberg figures by Georg Christoph Lichtenberg[422]
- 1801: Discovery of ultraviolet by Johann Wilhelm Ritter[423]
- 1813: Gauss's law by Carl Friedrich Gauss[424]
- 1814: Discovery of Fraunhofer lines by Joseph von Fraunhofer[425]
- 1817: Ackermann steering geometry by Georg Lankensperger in Munich[426]
- 1817 or earlier: Gyroscope by Johann Gottlieb Friedrich von Bohnenberger in Tübingen[427]
- 1820: Galvanometer by Johann Schweigger in Halle[428]
- 1827: Ohm's law by Georg Ohm[429]
- 1833: Magnetometer by Carl Friedrich Gauss[430]
- 1845: Kirchhoff's circuit laws by Gustav Kirchhoff[431]
- 1850: Formulation of the first and second law of thermodynamics by Rudolf Clausius[432][433]
- 1852: First experimental investigation of the Magnus effect by Heinrich Gustav Magnus[434]
- 1857: Geissler tube by Heinrich Geißler[435]
- 1857: Helmholtz resonance by Hermann von Helmholtz[436]
- 1859: Spectrometer by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff[437]
- 1861: First telephone transmitter by Johann Philipp Reis;[438][13] he also coined the term "telephone"[13]
- 1864–1875: Centrifuge by brothers Alexander and Antonin Prandtl from Munich[439]
- 1865: Concept of entropy by Rudolf Clausius[440]
- 1869: First observation of cathode rays by Johann Wilhelm Hittorf and Julius Plücker[441]
- 1870: Virial theorem by Rudolf Clausius[442]
- 1874: Refractometer by Ernst Abbe[443]
- 1883: First accurate electricity meter (Pendelzähler) by Hermann Aron[444]
- 1886: Discovery of anode rays by Eugen Goldstein[445]
- 1887: Discoveries of electromagnetic radiation, photoelectric effect and radio waves by Heinrich Hertz[446]
- 1887: First parabolic antenna by Heinrich Hertz[447]
- 1893–1896: Wien approximation (1896)[448] and Wien's displacement law (1893)[449] by Wilhelm Wien
- 1895: Discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Röntgen in Würzburg[450]
- 1897: Nernst lamp by Walther Nernst[451]
- 1900: Drude model by Paul Drude[452]
- 1900: Planck constant and Planck's law by Max Planck[453]
- 1900–1930: Quantum mechanics by i.a. Max Planck and Werner Heisenberg[454]
- 1901: Modern pyrometer by Ludwig Holborn and Ferdinand Kurlbaum[455]
- 1904: Boundary layer theory by Ludwig Prandtl[456]
- 1904: First radar system by Christian Hülsmeyer (Telemobiloscope)[457]
- 1905: Mass–energy equivalence (E = mc2)[458] and special relativity[459] by Albert Einstein
- 1905: Rubens tube by Heinrich Rubens[460]
- 1906–1912: Third law of thermodynamics (Nernst's theorem) by Walther Nernst[461]
- 1913: Echo sounding by Alexander Behm[462][463]
- 1913: Discovery of the Stark effect by Johannes Stark[464]
- 1915: Noether's theorem by Emmy Noether[465]
- 1916: General relativity by Albert Einstein[466]
- 1917: Laser's theoretical foundation by Albert Einstein[467]
- 1919: Discovery of the Barkhausen effect by Heinrich Barkhausen[468]
- 1919: Betz's law by Albert Betz[469]
- 1920s: (Modern) hand-held metal detector by Gerhard Fischer[470]
- 1921: Discovery of nuclear isomerism by Otto Hahn[471]
- 1921–22: Stern–Gerlach experiment by Otto Stern and Walther Gerlach[472]
- 1924: Description of coincidence method by Walther Bothe[473]
- 1924–25: Bose–Einstein statistics, Bose–Einstein condensate and Boson by Albert Einstein[474]
- 1927: Free electron model by Arnold Sommerfeld[475]
- 1927: Uncertainty principle by Werner Heisenberg[476]
- 1928: Geiger–Müller counter by Hans Geiger and Walther Müller[477]
- 1931: Electron microscope by Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll[478]
- 1933: Discovery of the Meissner effect by Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld[479]
- 1937–39: CNO cycle (Bethe–Weizsäcker process) by Carl von Weizsäcker and Hans Bethe[480]
- 1937: Scanning electron microscope (SEM) by Manfred von Ardenne[481]
- 1938: Discovery of nuclear fission by Otto Hahn and Fritz Straßmann in Berlin[482][483]
- 1949: Development of the nuclear shell model by Maria Goeppert-Mayer and J. Hans D. Jensen[484]
- 1950s: Quadrupole ion trap by Wolfgang Paul[485]
- 1958: Discovery of the Mössbauer effect by Rudolf Mössbauer[486]
- 1959: Penning trap by Hans Georg Dehmelt[487]
- 1961: Bark scale by Eberhard Zwicker[488]
- 1963: Proposition of heterojunction by Herbert Kroemer[489]
- 1980: Quantum Hall effect by Klaus von Klitzing[490]
- 1980s: Atomic force microscope and the scanning tunneling microscope by Gerd Binnig[491][492]
- 1988: Discovery of giant magnetoresistance by Peter Grünberg[493]
- 1994: STED microscopy by Stefan Hell and Jan Wichmann[494]
- 1998: Frequency comb by Theodor W. Hänsch[495]
Sociology, philosophy and politics


- Late 18th century: German idealism by Immanuel Kant[496]
- Mid-19th century: Marxism by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels[497]
- 1852: Credit union by Franz Hermann Schulze-Delitzsch in Saxony, later further developed by Friedrich Wilhelm Raiffeisen[498]
- 1879: Psychology by Wilhelm Wundt in Leipzig[499][500]
- 1880s: The German Empire (1871–1918) became the first modern welfare state in the world under statesman Otto von Bismarck,[501] when he e.g. innovatively implemented the following:
- Health insurance (Krankenversicherung) in 1883[502]
- Accident insurance (Unfallversicherung) in 1884[502]
- Pension insurance (Gesetzliche Rentenversicherung) in 1889[502]
- 1897: Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, the first LGBT rights organization in history,[503][504] founded by Magnus Hirschfeld in Berlin
- 1916: The German Empire became the first country in the world to implement daylight saving time (DST)[505]
- 1930s: Critical theory by the Frankfurt School[506]
- 1966: Private copying levy (also known as blank media tax or levy)[507]
- 1978: Blue Angel certification, the world's first ecolabel[508]
Religion, ethics and festivities


- 1434: The world's first genuine christmas market (Striezelmarkt) in Dresden[509]
- 1517: Protestantism and Lutheranism by Martin Luther[510][511]
- 16th century: Modern Christmas tree[512][513]
- 17th century: Easter Bunny[514]
- c. 1610: Tinsel in Nuremberg[515]
- 1776: Illuminati by Adam Weishaupt[516]
- 1810: Oktoberfest, the world's largest Volksfest,[517] in Munich
- 1839: Advent wreath by Johann Hinrich Wichern[518]
- c. 1850: Advent calendar by German Lutherans;[519] the modern version was created by Gerhard Lang (1881–1974) from Munich[520]
Sport


- c. 1790: Balance beam by Johann Christoph Friedrich GutsMuths[522]
- c. 1810: Horizontal bar, parallel bars, rings and the vault apparatus by Friedrich Ludwig Jahn, who is often hailed as the "father of modern gymnastics"[523][524]
- 1901: Modern bodybuilding by Eugen Sandow[525]
- 1906: Schutzhund, a dog sport that tests a dog's tracking[526]
- c. 1910: Loop jump in figure skating by Werner Rittberger[527]
- 1917–1919: Handball by Max Heiser and Karl Schelenz[528][529]
- 1920: Gliding by Oskar Ursinus[530]
- 1925: Wheel gymnastics by Otto Feick in Schönau an der Brend[531]
- 1936: The tradition of the Olympic torch relay by Carl Diem and Alfred Schiff in Berlin[532]
- 1946: Goalball by Sepp Reindle[533]
- 1948: Paralympic Games by German-born Ludwig Guttmann[534][535]
- 1954: Modern football boots with screw-in studs by Adolf (Adidas) or Rudolf Dassler (Puma)[536]
- 1963: Grass skiing by Josef Kaiser[537][538]
- 1964: Underwater rugby in Mülheim[539]
- 1989: International Paralympic Committee in Düsseldorf[540]
- 1993: Jugger in Heidelberg[541]
- 2001: Speed badminton by Bill Brandes in Berlin[542]
Tourism and recreation

- 1505: The first version of a carabiner[543]
- 1882: Strandkorb by Wilhelm Bartelmann in Rostock[544][545]
- 1891–1900: First purpose-built cruise ship (Prinzessin Victoria Luise) by Albert Ballin[546]
- Early 20th century: Pilates by Joseph Pilates[547]
- 1915 or earlier: Modern parachute (the first collapsible parachute) by Katharina Paulus[548][549]
- 1920s: Autogenic training by Johannes Heinrich Schultz[550]
Toys and games


- c. 1780: Schafkopf card game[551]
- c. 1810: Skat card game in Altenburg[552]
- 1890: Plastilin by Franz Kolb[553]
- 1892: Chinese checkers by Ravensburger[554]
- 1902: Teddy bear by Richard Steiff[555]
- 1907–08: Mensch ärgere Dich nicht board game by Josef Friedrich Schmidt[556]
- 1964: fischertechnik by Artur Fischer[557]
- 1972: First home video console (Magnavox Odyssey) by German-born Ralph H. Baer[558]
- 1974: Playmobil by Hans Beck[559]
- 1995: Catan by Klaus Teuber[560]
Transportation





- 1655: First self-propelled wheelchair by Stephan Farffler[561]
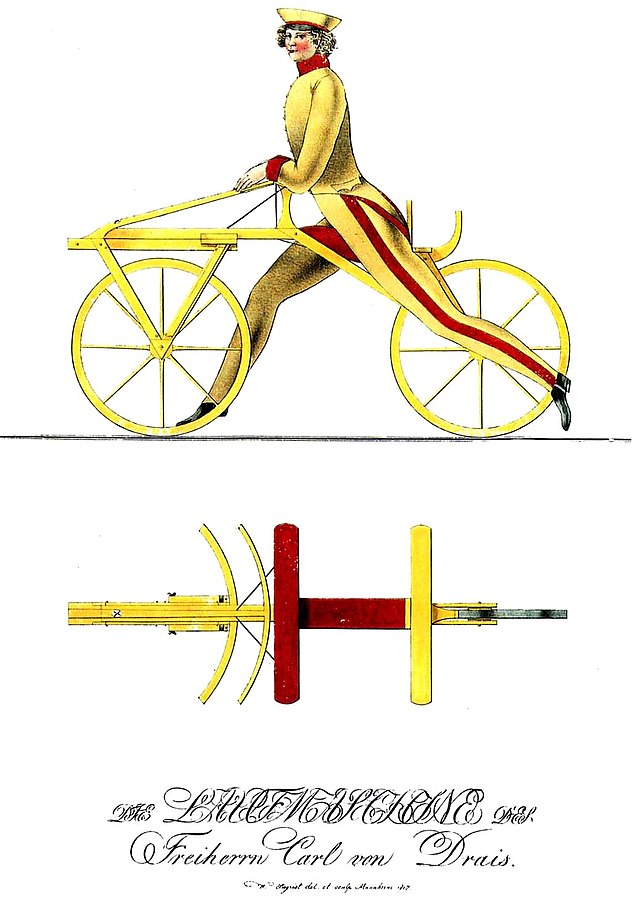
- 1817: The first bicycle (dandy horse) by Baron Karl von Drais[562]
- 1817: Tachometer by Diedrich Uhlhorn[563]
- 1834: First practical rotary electric motor by Moritz von Jacobi[564]
- 1839: First electric boat by Moritz von Jacobi[565]
- 1876: Otto engine by Nicolaus Otto[566]
- 1879–1881: First electric locomotive[567] and electric tramway (Gross-Lichterfelde Tramway) by Siemens & Halske[568][569]
- 1882: Trolleybus (Electromote) by Werner von Siemens[570]
- 1885: First automobile (Benz Patent-Motorwagen) by Karl Benz in Mannheim[571][572]
- 1885, 1894: First motorcycle (Daimler Reitwagen) by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach.[573] The motorcycle of Hildebrand & Wolfmüller from 1894 (created by Heinrich and Wilhelm Hildebrand, and Alois Wolfmüller) was the first machine to be called a "motorcycle" and the world's first production motorcycle.[574]
- 1885: First modern internal combustion engine by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach[575]
- 1886: First automobile on four wheels, by Gottlieb Daimler[576]
- 1886: Motorboat by Lürssen, in commission of Gottlieb Daimler[577]
- 1888: Driver's license by Karl Benz[578]
- 1888: The world's first filling station was the city pharmacy in Wiesloch[579]
- 1888: Flocken Elektrowagen, regarded by some as the first real electric car,[580] by Andreas Flocken in Coburg
- 1889: V engine by Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach[581]
- 1891: Taximeter by Friedrich Wilhelm Gustav Bruhn[582]
- 1893: Diesel engine, diesel fuel and biodiesel by Rudolf Diesel in Augsburg[583]
- 1893: Zeppelin, the first rigid airship,[584] by Ferdinand von Zeppelin[585]
- 1894: Lilienthal Normalsegelapparat, the first aeroplane to be serially produced, by Otto Lilienthal[586][587]
- 1895: Internal combustion engine bus by Daimler[588]
- 1896: First truck (Daimler Motor Lastwagen) by Gottlieb Daimler[589]
- 1897: Flat engine by Karl Benz[590]
- 1897: Internal combustion engine taxicab by Gottlieb Daimler[591]
- 1901: Mercedes 35 hp, regarded by some as the first real modern automobile,[592] by Paul Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach. The car also had the world's first drum brakes.[593]
- 1902, 1934: Concept of maglev by Alfred Zehden (1902) and Hermann Kemper (1934).[594]
- 1902: First high voltage spark plug by Gottlob Honold[595]
- 1902: First practical speedometer by Otto Schultze[596][597]
- 1906: Gyrocompass by Hermann Anschütz-Kaempfe[598]
- 1909: The world's first airline; DELAG.[599] The company also employed the first flight attendant, Heinrich Kubis, in 1912.[600]
- 1912: The world's first diesel locomotive by Gesellschaft für Thermo-Lokomotiven Diesel-Klose-Sulzer GmbH from Munich[601] and Borsig from Berlin[602]
- 1915: The world's first all-metal aircraft (Junkers J 1) by Junkers[603]
- 1916: Gasoline direct injection (GDI) by Junkers[604]
- 1928: First rocket-powered aircraft (Lippisch Ente) by Alexander Lippisch[605]
- 1935: Swept wing by Adolf Busemann[606]
- 1936: The first successful and practical helicopter (Focke-Wulf Fw 61), by Focke-Achgelis[607][608]
- 1939: First jet-powered aircraft (Heinkel He 178), by Hans von Ohain[609]
- 1943: Krueger flap by Werner Krüger[610]
- 1951: Airbag by Walter Linderer[611]
- 1957: Wankel engine by Felix Wankel[612]
- 1960s: Defogger by Heinz Kunert[613]
- Late 1960s: Oxygen sensor by Robert Bosch[614]
- 1995: Electronic stability control (ESC) by Robert Bosch and Mercedes-Benz[615]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
