Lenapehoking
Lands traditionally inhabited by the Lenape people From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
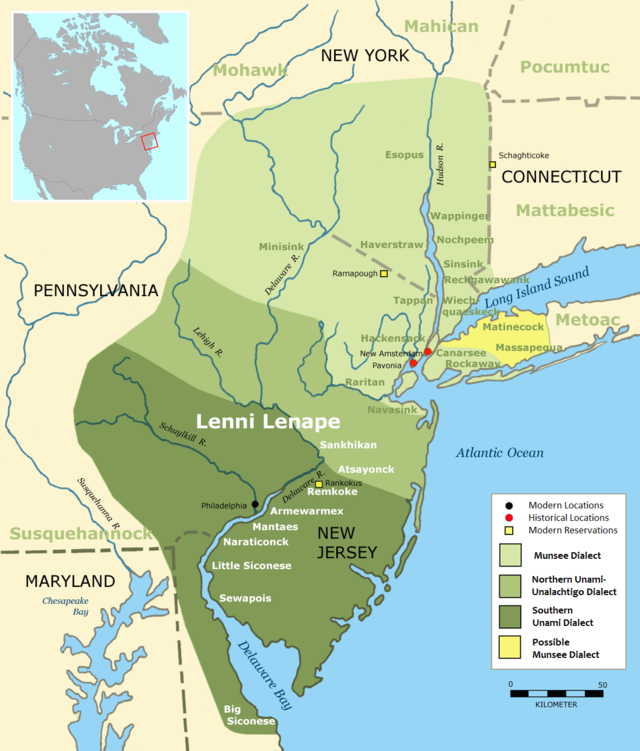
Lenapehoking (Unami: Lënapehòkink[1]) is widely translated as 'homelands of the Lenape', which in the 16th and 17th centuries, ranged along the Eastern seaboard from western Connecticut to Delaware, and encompassed the territory adjacent to the Delaware and lower Hudson river valleys, and the territory between them.
| Person | Lënape (Monsi / Wënami) |
|---|---|
| People | Lënapeyok (Monsiyok / Wënamiyok) |
| Language | Lënapei èlixsuwakàn (Monsii èlixsuwakàn / Wënami èlixsuwakàn) |
| Country | Lënapehòkink (Monsihòkink / Wënamihòkink) |
Beginning in the 17th century, European colonists started settling on traditional Lenape lands. Combined with the concurrent introduction of Eurasian infectious diseases and encroachment from the colonists, the Lenape were severely depopulated and lost control over large portions of Lenapehoking. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the United States government forcibly removed the Lenape to the American Midwest, including the state of Oklahoma.[2]
Lenape nations today control lands within Oklahoma (Delaware Nation and Delaware Tribe of Indians), Wisconsin (Stockbridge-Munsee Community), and Ontario (Munsee-Delaware Nation, Moravian of the Thames First Nation, and Delaware of Six Nations).
Meaning
Lenape speakers in Oklahoma called their northeastern homelands Lenapehoking translating to: in the land of the Lenape. It was popularized when Nora Thompson Dean shared the term with conservationist Theodore Cornu in 1970, and later with archaeologist Herbert C. Kraft.[3] This term has gained widespread acceptance and is found widely in recent literature on the Lenape and in New York institutions today as part of land acknowledgement.
Another historical Lenape term for much of the same region is Scheyischbi or Scheyichbi, although this is also often cited as referring specifically to New Jersey.
Range and bounds
Summarize
Perspective
At the time of the arrival of the Europeans in the 16th and 17th centuries, the Lenape homeland ranged along the Atlantic's coast from western Connecticut to Delaware, which generally encompassed the territory adjacent to the Delaware and lower Hudson river valleys, as well the hill-and-ridge dominated territory between them. Relatives of the Algonquian Amerindians whose territories ranged along the entire coast from beyond the Saint Lawrence River in today's Canada, and the tribes throughout all of New England,[2] down into northern South Carolina,[2] the Delaware Confederation[a] stretched from the southern shores of modern-day Delaware along the Atlantic seaboard into western Long Island and Connecticut, then extended westwards across the Hudson water gap into the eastern Catskills part of the Appalachians range around the headwaters of the Delaware River and along both banks of its basin down to the mouth of the Lehigh River.
Inland, the tribe had to deal with the fierce and territorial Susquehannocks; the Delawares' territory has generally been plotted with boundaries[b] along mountain ridges[c] topped by the drainage divides between the right bank tributaries of the Delaware River on the east—and on the west and south—the left bank tributaries of the Susquehanna and Lehigh Rivers; bounds which included the Catskills, parts of Northeastern Pennsylvania through the entire Pocono Mountains along the left bank of the Lehigh River. The Schuylkill River and its mouth in the present-day Philadelphia area or right bank of the Lehigh River were contested hunting grounds, generally shared with the Susquehannock and the occasional visit by a related Potomac tribe when there wasn't active tribal warfare. The greater Philadelphia area was known to host European to Indian contacts from the Dutch traders contacts with the Susquehanna (1600), English traders (1602), and both tribes with New Netherland traders after 1610.
Along the left bank Delaware valley, the territory extended to all of present-day New Jersey, and the southern counties of New York State, including Rockland, Orange, Westchester, and Putnam Counties, Nassau County, and the five boroughs of New York City.[d]
Present day
Several indigenous peoples from diverse tribes, both from the region historically and from elsewhere, live in the Northeast megalopolis or Eastern Seaboard. Many of people from the Haudenosaunee Confederacy moved into the area in the 1920s to 1960s and were employed as skyscraper construction workers (many belonged to the Mohawk Tribe) and played an important role in building the skyline of Philadelphia and New York City. In the University City section of West Philadelphia, there has been some political activity by Urban Indian residents of the area, who adapted the namesake Lenapehoking to where they live.
Lenape nations today control lands within Oklahoma (Delaware Nation and Delaware Tribe of Indians), Wisconsin (Stockbridge-Munsee Community), and Ontario (Munsee-Delaware Nation, Moravian of the Thames First Nation, and Delaware of Six Nations).
Lenape place names
Summarize
Perspective
Lenape place names are used throughout the region. The following are merely examples and the list is by no means exhaustive.
New York
Manhattan

- Manhattan is derived from Manna-hata, a Dutch version of a Lenape place name, as written in the 1609 logbook of Robert Juet, an officer on Henry Hudson's yacht Halve Maen (Half Moon).[4] A 1610 map depicts the name Manahata twice, on both the west and east sides of the Mauritius River (later named the North River, and now called the Hudson River). The word Manhattan has been translated as 'island of many hills' from the Lenape language.[5] The Encyclopedia of New York City offers other derivations, including from the Munsee dialect of Lenape: manahachtanienk ('place of general inebriation'), manahatouh ('place where timber is procured for bows and arrows'), or menatay ('island').[6] Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman) defined it as: 'place that is an island', from Lenape Menating.[7]
- Sapokanikan – habitation site and cultivated area by the cove on the Hudson River at present day Gansevoort Street, Greenwich Village.
- Nechtanc – habitation site along the East River site of Jacob Van Corlaer's plantation at Corlaer's Hook, near the present location of the Williamsburg Bridge, in the part of the Lower East Side that is near Chinatown.
- Indirectly named after Lenape shell middens: Pearl Street and Collect Pond
Staten Island
- Aquehonga – name for Staten Island
- Manacknong – name for Staten Island
- Shawkopoke – habitation site and cultivated area along Great Kills Harbor
Brooklyn
- Nayack or Wichquawanck – habitation in Bay Ridge near the present location of the Verrazzano Narrows Bridge
- Gowanus Canal – originally named by early settlers as "Gowanes Creek" after Gouwane, sachem of the local Lenape tribe called the Canarsee, who lived and farmed along the shores of the creek.[8] Also source of the neighborhood Gowanus and the Heights of Guan.
- Sassian – habitation site in present Red Hook
Queens
Westchester County
- Ossining – derived from the local Sint Sink tribe, meaning 'stone upon stone', and ossin, also meaning 'stone'.[11]
- Mamaroneck – from Munsee "striped stream/river";[12] not, as is often incorrectly cited, as "the place where fresh water falls into the sea"
- Tuckahoe
- Armonk
- Quarropas – name for White Plains which is a direct translation meaning 'the white plains' or 'the white marshes', either referring to the white fog that hangs over the area, or the white balsam trees said to grow there.
- Cisqua – name for Mount Kisco
- Chappaqua
- Katonah
- Croton
- Crompond
Rockland County
- Monsey – from the name of the Munsees, northern branch of the Lenapes
New Jersey
- Absecon – meaning: 'little water'[13]
- Assunpink Creek – meaning: 'Stony Creek'[14] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'rocky place that is watery', from Lenape Ahsenping.[7]
- Communipaw (in downtown Jersey City) – 'riverside landing place'[14]
- Cushetunk – 'place of hogs'[14]
- Hackensack – 'stream flowing into another on a plain/ in a swamp/ in a lowland'[14] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'place of sharp ground', from Lenape Ahkinkeshaki.[7]
- Hoboken – 'where pipes are traded' / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'tobacco pipe', from Lenape Hupoken.[7]
- Hohokus – 'red cedars'[14]
- Hopatcong – 'pipe stone' (not 'honey waters of many coves' as early 20th-century boosters would have it)[15]
- Kittatinny – 'great hill' or 'endless mountain' / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'big mountain', from Lenape Kitahtene.[7]
- Mahwah – 'meeting place'
- Manahawkin – 'place where there is good land' / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'where the land slopes', from Lenape Menahoking.[7]
- Manalapan – municipality's name is said to have come from Lenape and is said to mean 'land of good bread'
- Mantoloking – said to be either 'frog ground', 'sandy place' or 'land of sunsets'
- Manasquan – "Man-A-Squaw-Han", meaning 'stream of the island of squaws' / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'place to gather grass', from Lenape Menaskung.[7]
- Mantua – said to have come from the "Munsees", North Jersey Lenapes, but the township is in South Jersey.[14]
- Matawan – 'hill on either side'[14]
- Metuchen – 'dry firewood'[14]
- Minisink – 'from the rocky land', is the old name for the Munsee, and the name of an ancient Lenape trade route that ran along a good part of what is now US Highway 46 in Northern New Jersey
- Musconetcong
- Netcong – Abbreviation of Musconetcong.
- Parsippany – original form was parsipanong, which means 'the place where the river winds through the valley'[14]
- Passaic – 'valley' or 'river flowing through a valley'[14] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'valley', from Lenape Pahsaek.[7]
- Peapack – 'place of water roots'[14]
- Raritan – original form was Naraticong; may have meant 'river behind the island' or 'forked river'.[14]
- Scheyichbi – Meaning of name varies.[14] notes two possible meanings: the land that the Lenapes called their country, or 'land of the shell money' (wampum).[14]
- Secaucus – 'black snakes'.[14]
- Weehawken – 'place of gulls'.[14]
- Whippany – meaning from the original whippanong, 'place of the arrow wood' or 'place of the willow trees'[16][17]
Pennsylvania
- Aquashicola Creek – derived from the Lenape, meaning 'where we fish with the bushnet'.[18]
- Cacoosing Creek – derived from the Lenape word kukhus, meaning 'owl'[19]
- Buckwampum Mountain – located in eastern Springfield Township, Bucks County, means 'a round bog'.[20]
- Catasauqua – 'thirsty ground'[21]
- Catawissa – 'growing fat'[22]
- Chinquapin – The name is taken from a small nut-bearing tree or shrub, resembling the American Chestnut.
- Cocalico – 'where the snakes collect in dens to pass the winter'[23]
- Cohocksink Creek – from a Lenape word for 'pine lands'.[24]
- Cohoquinoque Creek – derived from a Lenni-Lenape word for 'the grove of long pine trees'.
- Connoquenessing – 'a long way straight'[25] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Conococheague Creek – 'water of many turns'
- Conodoguinet Creek – 'a long way with many bends'
- Conshohocken – original form Gueno-sheiki-hacking, meaning pleasant valley.[26] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'elegant land', from Lenape Kanshihaking.[7]
- Hokendauqua Creek – From Lenape words: Haki, or 'land', and undoech-wen, or 'to come for some purpose', Meaning: 'searching for land'
- Kingsessing – 'a place where there is a meadow'
- Kittatinny – 'great mountain' / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'big mountain', from Lenape Kitatene.[7]
- Karakung – 'clay creek'
- Lahaska – derived from Lahaskeke meaning 'the place of much writing',[20]
- Lackawanna – 'forks of a stream' / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'sandy creek'; 'sandy river', from Lenape Lekaohane.[7] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Lehigh County – from Lenape word Lechauwekink meaning 'at the forks of a path or stream'
- Lycoming – 'great stream'[27] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Macungie – derived from Maguntsche, meaning 'bear swamp' or 'feeding place of the Bears'.
- Mahoning Creek – from Lenape word Mahonink, meaning 'at the mineral lick', referring to a place frequented by deer, elk and other animals.
- Manatawny Creek – 'place where we drank'[28]
- Manayunk – 'place where we go to drink'[26] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'place to drink', from Lenape Meneyung.[7]
- Mauch Chunk Creek – from Lenape word Machk-tschunk, 'at the bear mountain'[29] *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'where the hills are clustered', from Lenape Menangahchung.[7]
- Maxatawny – from Lenape word Machksit-hanne, 'bear path stream'[29]
- Monocacy – from Lenape word Menagassi, 'stream with several large bends'[29]
- Moselem – 'trout stream'[30]
- Moshannon Creek – derived from Moss-Hanne, 'moose stream'[31] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Moyamensing – place of judgment, located in the south part of Philadelphia
- Muckinipattis Creek – 'deep running water'
- Neshaminy Creek – from Lenape word Nischam-hanne, 'two streams' or 'double stream'[20]
- Nesquehoning Creek – from Lenape word Neska-honi, 'black mineral lick'[29]
- Nittany – 'single mountain'[32] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Nockamixon Township – from Lenape word Nochanichsink, 'where there are three houses'[20]
- Ockanickon Scout Reservation – named after a Lenape chief who assisted William Penn in the exploration of the Bucks County area.[33]
- Okehocking Historic District – an 18th-century Indian Land Grant by William Penn to the Okehocking band of Lenape (Delaware) Indians in 1703.[34]
- Ontelaunee – little daughter of a great mother[35]
- Passyunk – a Philadelphia neighborhood and former township named for a Lenape village (compare to Passaic, New Jersey)[36] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'in the valley', from Lenape Pahsayung.[7]
- Paxtang – 'where the waters stand'[37] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Paunacussing Creek – means 'where the powder was given to us'.[20]
- Pennypack Creek – 'downward-flowing water'; a creek in and near Philadelphia.[38]
- Perkasie – derived from Poekskossing, meaning 'where the hickory nuts were cracked'.[20]
- Perkiomen Creek – derived from Pakihmomink meaning 'where the cranberries grow'; a creek in central Montgomery County, Pennsylvania.[20]
- Pocono – from Lenape word Poco-hanne, 'a stream between mountains'[29]
- Poquessing Creek – 'place of the mice'[20]
- Punxsutawney – Punkwsutènay meaning 'town of the sandflies' (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Saucon Creek – from Lenape word Sacunk, 'the mouth of a stream'[29] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Shackamaxon – which means 'place of the council' and is on the site of Penn Treaty Park in Philadelphia.[39]
- Skippack – from Lenape word Skappeu-hacki, 'wet land'[29]
- Susquehanna River – from Lenape Siskëwahane, 'mile wide, foot deep'[citation needed] (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
- Tamaqua – from Lenape Tamaqua, 'beaver'[29]
- Tatamy – from Lenape name Chief Moses Tatamy who lived in the region and died in 1761
- Tohickon Creek – 'the stream over which we pass by means of a bridge of drift-wood' or simply 'deer-bone–creek'.[20]
- Towamencin – a township in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, means 'poplar tree'[40]
- Towamensing – 'fording place at the falls'[29]
- Tulpehocken – 'land of turtles', the name of a creek and a SEPTA train station and street in Philadelphia[41] / *Nora Thompson Dean (Touching Leaves Woman): 'turtle land', from Lenape Tulpehaking.[7]
- Unami Creek – From Lenape word Unami meaning 'person from down river'[29]
- Wallenpaupack - From Lenape name meaning the 'stream of swift and slow water.' Wallenpaupack Creek was dammed in 1928 to create Lake Wallenpaupack
- Wissahickon – 'yellow stream' or 'catfish stream'; a creek in and near Philadelphia.[42]
- Wyomissing – meaning 'the land of flats'; a borough in Berks County Pennsylvania[29]
- Youghiogheny – 'four streams' or 'winding stream' (This Lenape placename does not occur within the bounds of Lenapehoking, as defined by the map accompanying this article.)
See also
- Turtle Island (Native American folklore)
- Apacheria
- Bergen, New Netherland
- Comancheria
- History of Delaware
- History of New Jersey
- History of New York (state)
- History of New York City
- History of Pennsylvania
- History of Philadelphia
- Huronia (region)
- New Amsterdam
- New Netherland
- New York metropolitan area
- Philadelphia metropolitan area
Notes
- The Delaware peoples organized themselves into divisions. Tribal government was through the appointment of Sachems (chieftains) by the tribal matriarchs. A Sachem could also come about by merit, these were generally earned in acts of warfare.[2]
- Natural barriers to foot travel predominate defining the limits of cultures without written languages. In tribal North America, between rivals and deadly enemies, hunting ranges devoid of permanent settlements were the rule, but summer hunting or fishing camps with temporary shelters were also common—as were the peaceful visits and trading along people historians have incorrectly painted as eternally at war. Games and competitions, trade and social visits were far more common, even among supposed hated enemies than were periods of warfare.[2]
- Given the foot-and-birch-bark-canoe-travel technology of the era, anyone familiar with hunting in the Appalachian topographies, would find this eminently sensible. Topping any ridge away from a major stream would be a climb only be undertaken if crossing into another drainage catchment. Canoe navigable streams occur only after waters have had time to gather and possibly dam up in broader valleys carved by glaciers or spring floods and beaver dams, so are well away from the boundaries marked logically atop drainage divides and their characteristic small steep rock strewn streams that were difficult to walk, and impassible by valuable & fragile birch bark canoes. The implication is the drainage divide areas, were little visited and unpopulated areas between tribes since they were difficult to travel into, across, or out of—the reader is reminded the nature of the forests in North America ran to tree sizes we rarely see today in isolated specimens with trunks starting over two feet in diameter. Only where a mountain pass, such as the gaps of the Allegheny was part of the goal, were such remote areas commonly visited before the extensive trapping and hunting beginning with the Beaver Wars period.
- Along with New York City, Newark, Trenton, Princeton, Philadelphia, Wilmington, Delaware, Atlantic City, and numerous other urban and suburban areas are in Lenapehoking today, as are the Jersey Shore, Pine Barrens, the Sourland Mountains, the Delaware Valley, Poconos, and parts of the Catskills.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
