Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Kuki-Chin languages
Language family From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Kuki-Chin languages (also called Kukish[2] or South-Central Tibeto-Burman languages) are a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family spoken in northeastern India, western Myanmar and southeastern Bangladesh. Most notable Kuki-Chin-speaking ethnic groups are referred to collectively as the Zo people which includes the Mizo, Kuki, Chin and Zomi people.
This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. (December 2023) |

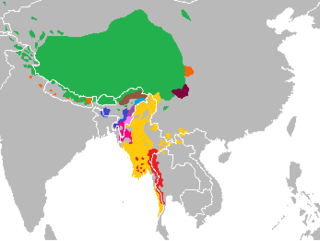
Kuki-Chin is alternatively called South-Central Trans-Himalayan (or South Central Tibeto-Burman) by Konnerth (2018), because of negative connotations of the term "Kuki-Chin" for many speakers of languages in this group.[3]
Kuki-Chin is sometimes placed under Kuki-Chin–Naga, a geographical rather than linguistic grouping.
Remove ads
Geographical distribution
- Northwestern ("Old Kuki"): Chandel district of Manipur, India; Tamu Township of Sagaing Region, Myanmar.
- Northeastern ("Kuki-Zo"): Chandel district, Churachandpur district, Kangpokpi district, Noney district, Tamenglong district, and Tengnoupal districts of Manipur, India; Tedim Township of Chin State, Myanmar; Tamu Township of Sagaing Region, Myanmar.
- Central: whole state of Mizoram, India; Pherzawl district of Manipur, India; parts of Cachar district and parts of Karbi Anglong district of Assam, India; parts of East Jaintia Hills district of Meghalaya, India; Falam Township, Hakha Township, and Thantlang Townships of Chin State, Myanmar; Kalay Township and Khampat area of Sagaing Region, Myanmar, parts of Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh.
- Maraic: majority of Siaha district of Mizoram, India; parts of Matupi Township of Chin State, Myanmar.
- Southern: Kanpetlet Township, Matupi Township, Mindat Township, Paletwa Townships of Chin State, Myanmar; parts of the Arakan Range of Rakhine State, Myanmar; parts of Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh.
- Khomic: Paletwa Township of Chin State, Myanmar; parts of Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh.
Remove ads
Internal classification
Summarize
Perspective
The Karbi languages may be closely related to Kuki-Chin, but Thurgood (2003) and van Driem (2011) leave Karbi unclassified within Sino-Tibetan.[4][5]
The Kuki-Chin branches listed below are from VanBik (2009), with the Northwestern branch added from Scott DeLancey, et al. (2015),[6] and the Khomic branch (which has been split off from the Southern branch) from Peterson (2017).[7]
- Kuki-Chin
- Central: Mizo (Duhlian), Bawm (Sunthla and Panghawi), Falam (Hallam, Ranglong, Darlong, Hauhulh, Simpi, Hualngo, Chorei), Thor (Tawr), Hmar, Hrangkhol, Biate (Biete), Hakha (Lai/Pawi, Mi-E, Zokhua), Pangkhua, Saihriem, Laizo/Tlaisun, Khualsim, Zanniat, Zahau, Sim
- Maraic: Mara (Tlosai {Siaha and Saikao}, Hawthai {Lyvaw, Sizo, and Lochei}, Hlaipao {Zyhno, Heima, and Lialai}), Zophei, Senthang, Zotung (Lungngo, Calthawn, Innmai), Lautu
- Northeastern (Northern): Suantak-Vaiphei, Zo (Zou), Paite, Tedim, Thado (Kuki), Gangte, Simte, Vaiphei, Sizang, Ralte, Ngawn
- Southern: Shö (Asho/Khyang, Chinbon), Thaiphum, Daai (Nitu), Mün, Yindu, Matu, Welaung (Rawngtu), Kaang, Laitu, Rungtu, Songlai, Sumtu
- Khomic: Khumi (Khumi proper and Khumi Awa), Mro, Rengmitca, etc.
- Northwestern ("Old Kuki"): Monsang, Moyon, Lamkang, Aimol, Anal, Tarao, Koireng (Kolhreng), Chiru, Kom, Chothe, Purum,[7] Kharam,[7]
Darlong and Ranglong are unclassified Kuki-Chin language.
The recently discovered Sorbung language may be mixed language that could classify as either a Kuki-Chin or Tangkhul language (Mortenson & Keogh 2011).[8]
Anu-Hkongso speakers self-identify as ethnic Chin people, although their language is closely related to Mru rather than to Kuki-Chin languages. The Mruic languages constitute a separate Tibeto-Burman branch, and are not part of Kuki-Chin.[7]
VanBik (2009)
Kenneth VanBik's (2009:23) classified the Kuki-Chin languages based on shared sound changes (phonological innovations) from Proto-Kuki-Chin as follows.
- Kuki-Chin
- Central: *k(ʰ)r-, *p(ʰ)r- > *t(ʰ)r-; *k(ʰ)l-, *p(ʰ)l- > *t(ʰ)l-; *y- > *z-
- Maraic: *kr- > *ts-; *-ʔ, *-r, *-l > -Ø; *-p, *-t, *-k > *-ʔ; *θ- > *s-
- Mara
- Tlosai
- Saikao
- Siaha
- Hlaipao
- Heima
- Lialai
- Vahapi/Zyhno
- HawThai
- Sizo
- Ngaphepi
- Sabyu
- Chapi
- Lyvaw
- Lochei
- Tisih
- Phybyu
- Sizo
- Tlosai
- Lautu
- Hnaro
- Chawngthia
- Zophei
- Vytu
- Sate/Awsa
- Senthang
- Khuapi
- Surkhua
- Zotung *h- > *f-; *kr- > *r-; *khl- > *kh-, *l-; *c(h)- > *t(h)-/*s-; *y- > *z-/*z(h)-; *w- > *v-
- Calthawng
- Innmai
- Lungngo/Tinpa
- Mara
- Peripheral: *r- > *g-
Peterson (2017)
David A. Peterson's (2017:206)[7] internal classification of the Kuki-Chin languages is as follows.
- Kuki-Chin
- Northwestern ("Old Kuki"): Purum, Koireng, Monsang, etc.
- Central
- Peripheral
Peterson's Northeastern branch corresponds to VanBik's Northern branch, while Peterson's Northwestern corresponds to the Old Kuki branch of earlier classifications.
Remove ads
See also
- Lai languages
- Pau Cin Hau script
- Kuki-Chin Swadesh lists (Wiktionary)
References
Bibliography
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
