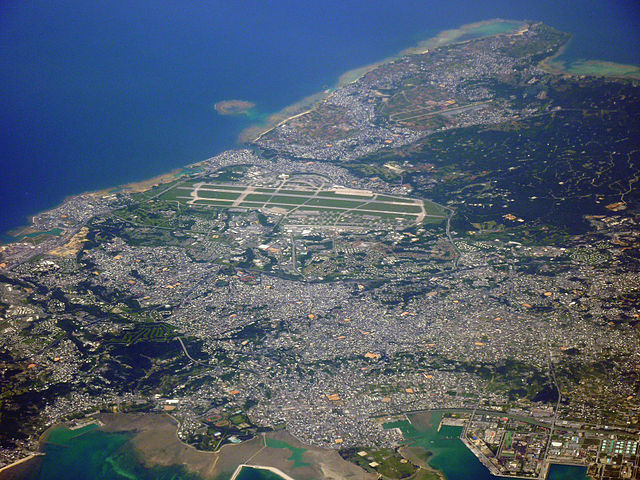
Kadena Air Base
U.S. Air Force base in Okinawa, Japan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Kadena Air Base (嘉手納飛行場, Kadena Hikōjō) (IATA: DNA, ICAO: RODN) is a United States Air Force base in the towns of Kadena and Chatan and the city of Okinawa, in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. It is often referred to as the "Keystone of the Pacific" because of its highly strategic location.[2] It is located 650 km (400 mi) off the coast of China and at a distance of 770 km (480 mi) from Shanghai, a major Chinese economic hub. It is home to the USAF's 18th Wing, the 353rd Special Operations Wing, reconnaissance units, 1st Battalion, 1st Air Defense Artillery Regiment, and a variety of associated units. Over 20,000 American servicemembers, family members, and Japanese employees live or work at Kadena Air Base.[3] It is the largest and most active U.S. Air Force base in East Asia.[4]
| Kadena Air Base | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
嘉手納飛行場 Kadena Hikōjō | |||||||||
| Kadena, Okinawa Prefecture in Japan | |||||||||
 A U.S. Air Force E-3 Sentry from the 961st Airborne Air Control Squadron taxis on the runway before take-off from Kadena Air Base in 2015. | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Site information | |||||||||
| Type | U.S. Air Force Base | ||||||||
| Owner | Various (leased by Government of Japan and made available to the U.S.) | ||||||||
| Operator | U.S. Air Force | ||||||||
| Controlled by | Pacific Air Forces (PACAF) | ||||||||
| Status | Operational | ||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||
| Location | |||||||||
| Coordinates | 26°21′06″N 127°46′10″E | ||||||||
| Site history | |||||||||
| Built | 1945 (as Yara Hikojo Airfield) | ||||||||
| In use | 1945 – present | ||||||||
| Garrison information | |||||||||
| Current commander | Brig. Gen. Nicholas Evans | ||||||||
| Garrison | 18th Wing (Host) | ||||||||
| Airfield information | |||||||||
| Identifiers | IATA: DNA, ICAO: RODN, WMO: 479310 | ||||||||
| Elevation | 43.6 metres (143 ft) AMSL | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Other airfield facilities | 1x V/STOL pad | ||||||||
| Source: Japanese AIP at AIS Japan[1] | |||||||||

History
Summarize
Perspective
Kadena Air Base's history dates back to just before the Battle of Okinawa in April 1945, when a local construction firm completed a small airfield named Yara Hikojo near the village of Kadena. The airfield, used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force, was one of the first targets of the Tenth United States Army 7th Infantry Division. The United States seized it from the Japanese during the battle.
World War II

What the Americans captured was a 4,600 feet (1,400 m) strip of badly-damaged coral runway. "The initial work at Kadena was accomplished by the 1901st Aviation Engineer Battalion 7th U.S. Infantry Division and Naval Construction Battalion Maintenance Unit CBMU 624 on 4 April",[5] by nightfall the same day, the runway could accept emergency landings. Eight days later, and after some 6 inches (150 mm) of coral were added, the airfield was declared operational and put into immediate service by artillery spotting aircraft. Additional construction was performed by the 807th Engineering Aviation Battalion to improve the airfield for USAAF fighter and bomber use with fuel tank farms, a new 6,500 feet (2,000 m) bituminous runway, and a 7,500 feet (2,300 m) runway for bomber aircraft, by August.
Kadena airfield was initially under the control of Seventh Air Force, however on 16 July 1945, Headquarters Eighth Air Force was transferred, without personnel, equipment, or combat elements to the town of Sakugawa, near Kadena from RAF High Wycombe England. Upon reassignment, its headquarters element absorbed the command staff of the inactivated XX Bomber Command. Kadena was used by the headquarters staff for nationalists' requirements.
Upon its reassignment to the Pacific Theater, Eighth Air Force was assigned to the U.S. Army Strategic Air Forces with a mission to train new B-29 Superfortress bomber groups arriving from the United States for combat missions against Japan. In the planned invasion of Japan, the mission of Eighth Air Force would be to conduct strategic bombing raids from Okinawa. However, the atomic bombings of Japan led to the Japanese surrender before Eighth Air Force saw action in the Pacific theater.
The surrender of Japanese forces in the Ryukyu Islands came on 7 September. General Joseph Stilwell accepted the surrender in an area that would later become Kadena's Stearley Heights housing area.
Known World War II units assigned to Kadena were:
- 319th Bombardment Group (Light) (July–November 1945) (A-26 Invader)
Assigned to Seventh Air Force and flew missions to Japan and China, attacking airdromes, shipping, marshalling yards, industrial centers, and other objectives. - 317th Troop Carrier Group (August–September 1945) (C-46 Commando, C-47 Skytrain)
Assigned to Seventh Air Force in the Philippines. Deployed aircraft to Kadena and flew courier and passenger routes to Japan, Guam, Korea, and the Philippines, and transported freight and personnel in the area. - 333d Bombardment Group (Very Heavy) (August 1945 – May 1946) (B-29)
Assigned to Eighth Air Force for planned invasion of Japan. Operations terminated before the group could enter combat. For a time after the war the group ferried Allied prisoners of war from Japan to the Philippines. Inactivated May 1946. - 346th Bombardment Group (Very Heavy) (August 1945 – June 1946) (B-29)
Assigned to Eighth Air Force for planned invasion of Japan. Operations terminated before the group could enter combat. After the war the group participated in several show-of-force missions over Japan and for a time ferried Allied prisoners of war from Okinawa to the Philippines. Inactivated June 1946. - 316th Bombardment Wing (September 1945 – June 1948)
Assigned to Eighth Air Force for planned invasion of Japan. Operations terminated before the group could enter combat. Reassigned to U.S. Far East Air Forces January 1946. Redesignated as 316th Composite Wing in January 1946, and 316th Bombardment Wing (Very Heavy) in May 1946. Inactivated June 1948. - 413th Fighter Group (November 1945 – October 1946) (P-47N)
Assigned to Eighth Air Force and served as a part of the air defense and occupation force for the Ryukyu Islands after the war. Inactivated October 1946.
On 7 June 1946, Headquarters Eighth Air Force moved without personnel or equipment to MacDill AAF, Florida. It was replaced by the 1st Air Division which directed fighter reconnaissance, and bomber organizations and provided air defense for the Ryukyu Islands until December 1948.
Twentieth Air Force became the command and control organization for Kadena on 16 May 1949.
Korean War
The Korean War emphasized the need for maintaining a naval presence on Okinawa. On 15 February 1951, the U.S. Naval Facility, Naha, was activated and later became commissioned on 18 April. Commander Fleet Activities, Ryukyus was commissioned on 8 March 1957. On 15 May 1972, upon reversion of Okinawa to Japanese administration, the two organizations were combined to form Commander Fleet Activities, Okinawa. With the relocations of Commander Fleet Activities, Okinawa to Kadena Air Base on 7 May 1975, the title then became Commander Fleet Activities, Okinawa/US Naval Air Facility, Kadena.
Twentieth Air Force was inactivated in March 1955. Fifth Air Force became the command and control organization for Kadena. Known major postwar USAAF/USAF units assigned to Kadena have been:
- 6th Bombardment Group (Very Heavy) (June 1947 – October 1948) (B-29)
Participated in show-of-force flights over Japan and dropped food and other relief supplies to newly freed Allied prisoners of war. Inactivated October 1948. - 71st Tactical Reconnaissance Wing (August 1948 – October 1948) (F-5, F-6, RF-51, RF-61)
Equipped with reconnaissance aircraft, flew aerial photographing missions over Japan and southern Korea. Inactivated October 1948. The 71st Air Base Group provided base host unit support for organizations assigned to Kadena. - 32d Composite Wing (August 1948 – April 1949) (RB/SB-17G, C-46, RB/SB-29)
Replaced 71st Tactical Reconnaissance Wing. Provided photographic reconnaissance and search and rescue support. The 32d Air Base Group provided base host unit support for organizations assigned to Kadena. - 6332d Air Base Group (April 1949 – January 1950) (redesignated 6332d Air Base Wing (January 1950 – May 1955), 6313th Air Base Wing (October 1957 – December 1964))
Provided base host unit support for organizations assigned to Kadena. - 19th Bombardment Group (Medium) (July 1950 – May 1954) (B-29)
Deployed from Andersen AFB, Guam. Flew combat missions over Korea. Reassigned May 1954 to Pinecastle AFB, Florida. - 22d Bombardment Group (Medium) (July 1950 – October 1950) (B-29)
Deployed from March AFB, California. Flew combat missions over Korea - 307th Bombardment Group (Medium) (September 1950 – February 1951) (B-29)
Deployed from MacDill AFB Florida to engage in combat operations during the Korean War. While on Okinawa, the 307th was awarded the Republic of Korea Presidential Unit Citation for its air strikes against enemy forces in Korea. It was also awarded the Distinguished Unit Citation and several campaign streamers. The 307th BG returned from deployment during February 1951, however elements of the group remained deployed on Okinawa on a semi-permanent basis until 1954. - 581st Air Resupply Group (September 1953 – September 1956) (B-29)
reassigned from the inactivating 581st Air Resupply and Communications Wing at Clark AB, Philippines. Performed unconventional warfare and counterinsurgency psychological operations. Inactivated and mission transferred to U.S. Navy.
At the end of the Eisenhower presidency, around 1,700 nuclear weapons were deployed on shore in the Pacific, 800 of which were at Kadena Air Base.[6]
18th Wing
On 1 November 1954, the 18th Fighter-Bomber Wing arrived from Osan Air Base, South Korea. Under changing designations, the wing has been the main USAF flying force at Kadena for over 50 years.[7] The wing has maintained assigned aircraft, crews, and supporting personnel in readiness to respond to orders from Fifth Air Force and Pacific Air Forces. The wing initially was flying three squadrons of North American F-86 Sabre: the 12th, 44th and 67th Fighter Squadrons. The wing flew tactical fighter sorties from Okinawa, and made frequent deployments to South Korea, Japan, Formosa, and the Philippines. In 1957, the wing upgraded to the F-100 Super Sabre and the designation was changed to the 18th Tactical Fighter Wing. In 1960, a tactical reconnaissance mission was added to the wing with the arrival of the McDonnell F-101 Voodoo and the 15th Tactical Reconnaissance Squadron.
Vietnam War era
Beginning in 1961, the 18th TFW was sending its tactical squadrons frequently to South Vietnam and Thailand, initially with its RF-101 reconnaissance jets,[8] and beginning in 1964 with its tactical fighter forces supporting USAF combat missions in the Vietnam War.[8]: 257 In 1963, the F-105 Thunderchief replaced the Super Sabres. During the Temporary duty assignment (TDY) deployments to Southeast Asia, the 12th TFS lost four aircraft, the 44th TFS lost one F-105D, and the 67th TFS lost nine aircraft, including three on the first day of Operation Rolling Thunder. The deployments to Southeast Asia continued until the end of United States involvement in the conflict.
The RF-4C Phantom II replaced the RF-101 in the reconnaissance role in 1967. An electronic warfare capability was added to the wing in late 1968 with the attachment of the 19th Tactical Electronic Warfare Squadron from Shaw AFB South Carolina flying the EB-66 Destroyer. The B-66s remained until 1970, flying daily over the skies of Southeast Asia.
During the 1968 Pueblo crisis, the 18th deployed between January and June to Osan AB, South Korea following the North Korean seizure of the vessel. Frequent deployments to South Korea have been performed ever since to maintain the air defense alert mission there.
In 1972, the 1st Special Operations Squadron was assigned, bringing their specialized C/MC-130 Hercules aircraft to the wing. The squadron was reassigned in 1978. The reconnaissance mission ended in 1989 with the retirement of the RF-4Cs, and the inactivation of the 15th TRS.
Post-Vietnam
The F/RF-4C Phantom II replaced the F-105s in 1971, and a further upgrade to the F-15 Eagle was made in 1979.
On 6 November 1972, the 18th Tactical Fighter Wing dispatched the McDonnell Douglas F-4C / D Phantom II fighter jets of the 44th Tactical Fighter Squadron and the 67th Tactical Fighter Squadron to the Ching Chuan Kang Air Base, Taiwan until 31 May 1975. Assist Taiwan ’s air defense against threats from China.
The designation of the wing changed on 1 October 1991 to the 18th Wing with the implementation of the Objective Wing concept. With the objective wing, the mission of the 18th expanded to the Composite Air Wing concept of multiple different wing missions with different aircraft. The mission of the 18th was expanded to include aerial refueling with KC-135 Stratotanker tanker aircraft; and surveillance, warning, command and control E-3 Sentry, and communications. Added airlift mission in June 1992 with the C-12 Huron, transporting mission critical personnel, high-priority cargo and distinguished visitors. In February 1993, the 18th Wing gained responsibility for coordinating rescue operations in the Western Pacific and Indian Ocean.
Arrival of Patriot unit
In November 2006, the U.S. Army's 1st Battalion, 1st Air Defense Artillery Regiment, a Patriot PAC-III unit, deployed to Kadena from Fort Bliss Texas.[9] Originally assigned to 31st ADA Brigade of Fort Bliss, they were reassigned to the 94th AAMDC, USINDOPACOM. The move was part of the BRAC consolidation of U.S. Army bases and security agreements between the U.S. and Japan. The battalion's mission is to defend the base against tactical ballistic missiles from North Korea. The deployment was controversial on Okinawa, being greeted with protests.[10]
Potential F-15EX deployment
In late 2023, Nikkei Asia reported that the US Air Force would permanently station Boeing F-15EX Eagle II jets at Kadena Air Base. That total would be down from the 48 F-15C Eagle jets which were previously permanently stationed there.[11]
Foreign units
Other U.S. allies [who?] who had expressed intention with the approval of both the Japanese government and the United States Air Force to host units in the air base to further impose united cooperation against regional threats; North Korea, Russian Siberia, Russian Far East and the growing influence of China in the Asia Pacific.[citation needed]
Australia and New Zealand

In early September 2018, Australian Defence Minister Christopher Pyne and New Zealand's Deputy Prime Minister Winston Peters stated that it was in their interest to aid both Japan and the United States against North Korea with patrol aircraft. These units would provide additional capability to prevent North Korean vessels conducting illegal trading out at sea in violation of UN sanctions.[12] The Royal Australian Air Force deployed two AP-3C aircraft, along with a P-3K2 Orion from the RNZAF. RAAF P-8 Poseidons have subsequently been periodically deployed to Kadena as part of Operation Argos.[13] RNZAF Orions also periodically operate from Kadena, with four such deployments having been made as of April 2021.[14]
Other units

Other major units assigned to Kadena since 1954 have been:
- 313th Air Division (March 1955 – October 1991)
Assumed responsibility for air defense of the Ryukyu Islands and tactical operations in the Far East, maintaining assigned forces at the highest possible degree of combat readiness. In addition, it supported Fifth Air Force in the development, planning, and coordination of requirements for future Air Force operations in the Ryukyu Islands. The division also supported numerous exercises such as Cope Thunder, Cope Diamond, Team Spirit and Cope North. Provided base host unit support for organizations assigned to Kadena (May 1955 – October 1957, December 1964 – October 1974). The newly-considated 18th Wing replaced the 313th Air Division in 1991. - Kadena Task Force (Provisional) (SAC) (May 1955 – May 1958) (RB/ERB-47H)
Performed Electronic Reconnaissance and Countermeasures activities. - 498th Tactical Missile Group (February 1961 – October 1969) (TM-76B/CGM-13B)
Equipped with the TM-76B, renumbered in 1963 to CGM-13B Mace guided cruise missile, four hard site launch sites. - 4252d Strategic Wing (SAC) (January 1965 – April 1970)
376th Strategic Wing (SAC) (April 1970 – August 1973) (B-52, KC-135, EC-135)
Activated by SAC at Kadena. Replaced 4252nd Strategic Wing. Conducted B-52 combat operations in Southeast Asia from January 1965 to September 1970, when Arc Light Missions from the base were terminated.[15] The distance to targets in South Vietnam resulted in reduced payload and greater air-refueling demands for Kadena and Guam based B-52s and from April 1967 the USAF began basing B-52s at U-Tapao Royal Thai Navy Airfield, this together with Japanese opposition to the war led to reducing B-52 operations from Kadena.[16] Conducted KC-135 air refueling and RC-135 electronic reconnaissance from April 1970 to 1991. Conducted airborne radio relay operations, April–November 1970, February–June 1971 and March 1972 – August 1973. Until 1991, the wing controlled the 909th Air Refueling Squadron (KC-135A/Q/R) and supported rotational reconnaissance aircraft (TR-1, SR-71) after the inactivation of the 9th SRW in 1974. The Wing was inactivated at Kadena on 30 October 1991 with the drawdown of strategic forces. Its mission was absorbed by the 18th Wing. - 9th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing (SAC) (1968–1974) (A-12, SR-71)
Deployed from Beale Air Force Base, California, Performed strategic reconnaissance over North Vietnam and Laos. In March 1968 SR-71's began arriving at Kadena from Beale AFB.[17] On 15 March Det OL-8 was declared Operational Ready for SR-71 sorties.[17] The SR-71s averaged approximately one sortie a week for nearly two years. By 1970, the SR-71s were averaging two sorties per week. By 1972, the SR-71 was flying nearly one sortie every day. While deployed on Okinawa, the SR-71s and their aircrew members gained the nickname Habu (as did the A-12s preceding them) after a southeast Asian pit viper which the Okinawans thought the plane resembled. With the completion of each mission a "Habu" was painted on the bird.[17] The SR 71 mission on Okinawa ended in 1990. - 18th Combat Support Wing (1985–1991)
The 18 CSW was originally the 18th Combat Support Group of the 18th Tactical Fighter Wing before being elevated to a Wing in 1985. It acted as the installation management command and controlled all the services required to run the installation. With the consolidation of numerous missions into the 18th Wing in 1991, the 18 CSW was downgraded and redesignated the 18th Support Group. It was redesignated again as the 18th Mission Support Group in 2002.
Beacon
- The USAF is responsible for maintenance.
Role and operations
Summarize
Perspective
The 18th Wing is the host unit at Kadena AB. In addition, the base hosts associate units from five other Air Force major commands, the United States Navy, and other Department of Defense agencies and direct reporting units. Associate units operate more than 20 permanently assigned, forward-based or deployed aircraft from the base on a daily basis.
18th Wing
The 18th Wing is the Air Force's largest and most diverse combat wing. The Wing is broken down into five groups: the 18th Operations Group, the 18th Maintenance Group, the 18th Mission Support Group, the 18th Civil Engineer Group, and the 18th Medical Group. Kadena's former fleet of F-15C/D Eagle (the 44th and 67th Fighter Squadron); KC-135R/T Stratotanker (the 909th Air Refueling Squadron); E-3B/C Sentry (the 961st Airborne Air Control Squadron); and HH-60 Pave Hawks (the 33rd Rescue Squadron).
353rd Special Operations Wing
The 353rd Special Operations Wing is an element of the Air Force Special Operations Command, Hurlburt Field, Florida. The 750 Airmen of the group are organized into the 1st Special Operations Squadron, the 21st Special Operations Squadron, the 353rd Special Operations Aircraft Maintenance Squadron, the 753rd Special Operations Aircraft Maintenance Squadron, the 320th Special Tactics Squadron, and the 353rd Special Operations Support Squadron. The flying squadrons operate the MC-130J Commando II and the CV-22B Osprey.
733rd Air Mobility Squadron
This 733rd Air Mobility Squadron manage all passengers and cargo traveling by air in and out of Kadena. This Air Mobility Command unit supports about 650 aircraft arrivals and departures every month, moving more than 12,000 passengers and nearly 3,000 tons of cargo.
82nd Reconnaissance Squadron
Air Combat Command's 82nd Reconnaissance Squadron maintains aircraft; prepares combat-ready aircrews; and analyzes, processes, and disseminates intelligence data launch in support of RC-135V/W Rivet Joint, RC-135U Combat Sent and WC-135 Constant Phoenix missions flown in the Pacific Theater.
390th Intelligence Squadron
This Air Intelligence Agency squadron conducts information operations by providing tailored combat intelligence and assessing the security of friendly command, control, communication and computer systems to enhance warfighting survivability, situation awareness and targeting.
US Army
The U.S. Army's 1st Battalion, 1st Air Defense Artillery Regiment, assigned to the 94th AAMDC is a Patriot PAC-3 battalion. It consists of four Patriot missile batteries (Alpha through Delta), a maintenance company (Echo) and a headquarters battery (HHB).
Housing Management Office
The Air Force Housing Management Office (HMO) manages Military Family Housing (MFH) for all service members assigned to Okinawa.[18] Kadena Air Base contains nearly 4,000 family housing units, in apartment, townhouse, and single family home styles.[19]
Other units
- American Forces Network Detachment 11, AFNEWS
- Det 3, PACAF Air Postal Squadron
- Det 3, United States Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine
- 525 EMXS, Support Center Pacific
- Det 3, Wr-Alc Air Force Petroleum Office
- Det 624, Air Force Office of Special investigations
- Det 233, Air Force Audit Agency
- Field Training Detachment Det 15, 372nd Training Squadron
- Det 1, Okuma Recreation Facility
- Defense Commissary Agency
- DoDEA Pacific Director's Office
- Department of Defense Education Activity Pacific-Okinawa District
- Marine Wing Liaison Kadena
- American Red Cross
Based units
Summarize
Perspective
Flying and notable non-flying units based at Kadena Air Base.[20]
Units marked GSU are Geographically Separate Units, which although based at Kadena, are subordinate to a parent unit based at another location.
United States Air Force
|
Pacific Air Forces (PACAF)
|
Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC)
Air Mobility Command (AMC)
Air Combat Command (ACC) Civil Air Patrol (CAP)
United States ArmyU.S. Army Pacific (USARPAC) United States Marine CorpsMarine Forces Pacific (MARFORPAC)
|
Naval Communications Detachment Okinawa
The mission of NAVCOMM Det Okinawa is to provide communications support for the Seventh Fleet and supporting units, U.S. Naval Forces Japan, U.S. Naval Forces Korea, Defense Information Systems Agency and the Japanese Maritime Self Defense Force. The detachment has four work centers:
- TSCCOMM provides telecommunications support for Patrol Wing ONE Det Kadena, deployed patrol squadrons and Marine Wing Detachment
- CMS provides communications security (COMSEC) materials and cryptographic equipment to Patrol Squadrons and detachments, and to Commander Amphibious Group One/CTF76, located at White Beach
- Naval Radio Transmitter Facility (NRTF) Awase provides HF transmitter support to the fleet and area commanders and LF transmitter support for submarines operating in the Pacific and Indian Oceans
- SURTASS supports command and control functions to SURTASS ships operating in the Indian Ocean and Western Pacific.
Major commands to which assigned
- Tenth United States Army, 1 April 1945
- Eighth Air Force, 16 July 1945
- Pacific Air Command, United States Army (PACUSA), 6 December 1945
- Redesignated: Far East Air Force, 1 January 1947
- Redesignated: Pacific Air Forces, 1 July 1957
Base facilities

- Gate 5 Park
- Kadena Passenger Terminal
- Kadena Base Exchange
- Schilling Community Center
- Rocker Enlisted Club
- Officers Club
- EDIS (Early Developmental Intervention Services)
- Kadena Aeroclub
- Banyan Tree Golf Course
- Jack's Place Restaurant (originally Skoshi KOOM – Kadena Officers Open Mess)[21]
- The Asian Division of University of Maryland University College (UMUC)[22]
- Kadena Commissary
Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA) schools include:
Environmental concerns
In June 2013, the government of Japan discovered 22 barrels buried on former base property that tests showed had previously contained dioxins and herbicides. Tests on the surrounding soils found dioxin levels at 8.4 times and groundwater at 280 times the legal limit. The land in question is a soccer field bordering the base's Bob Hope Primary School and Amelia Earhart Intermediate School. Angry parents accused base officials, under base commanders Brigadier General Matt H. Molloy[30] and Brigadier General James B. Hecker, of failing to notify them of the toxins near the school and not investigating into the matter. After the issue was reported in the Japan Times and Stars and Stripes, USAF officials tested the soil and water at the schools and said that no excessive toxic substances were found.[31][32]
Soil on the base tested positive for very high levels of polychlorinated biphenylchemicals (PCBs), in the thousands of parts per million, much higher than most other contamination sites in the world, according to a report issued in 1987 after an investigation prompted by a small unrelated spill of transformer oil.[33]
Accidents and incidents
- 30 June 1959: an F-100 from the wing crashed on Okinawa during a training flight after suffering an engine fire. The pilot successfully ejected and suffered no harm, but the aircraft crashed into a local elementary school, killing 11 students plus six residents of the nearby neighborhood, and injuring 210.[34]
- 19 November 1968: B-52 of the 4252d Strategic Wing broke up and caught fire after the aircraft aborted takeoff on an Arc Light bombing mission to South Vietnam. 2 crewmen died of their injuries.
- 20 July 1972: SR-71 61-7978 ran off the runway on its second landing approach due to high crosswinds ahead of Typhoon Rita, severely damaging the underside of the plane. Both crewmembers were uninjured. The plane was salvaged for usable parts and the rest scrapped in Okinawa.[35]
- 2 November 1987: RF-4C 66-0416 (15 TRS / 18 TFW) entered a spin at 16,500 feet in a Whiskey area approximately 95 miles Northeast of Kadena. Both crew members ejected. One crewmember’s body was never recovered. The other crew member survived.
- 28 May 2013: F-15C of the 44th Fighter Squadron crashed into the ocean off Okinawa. The pilot ejected and was rescued by the Air Rescue Wing Naha Detachment of the Japan Air Self-Defense Force.[36][37][38]
- 11 June 2018: F-15C from the 44th Fighter Squadron crashed into the sea off Okinawa. The pilot was rescued by the JASDF Air Rescue Wing Naha Detachment.[39][40]
See also
Notes
Bibliography
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.