Junctional tachycardia
Abnormally fast heartbeat, the cause of which involves the atrioventricular node From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Junctional tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by involvement of the AV node.[1] It can be contrasted to atrial tachycardia. It is a tachycardia associated with the generation of impulses in a focus in the region of the atrioventricular node due to an A-V disassociation.[2] In general, the AV junction's intrinsic rate is 40-60 bpm so an accelerated junctional rhythm is from 60-100bpm and then becomes junctional tachycardia at a rate of >100 bpm.

Cause
It can be associated with digitalis toxicity.[3] It may also be due to onset of acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, conduction system diseases with enhanced automaticity, or administration of theophylline.[4]
Diagnosis
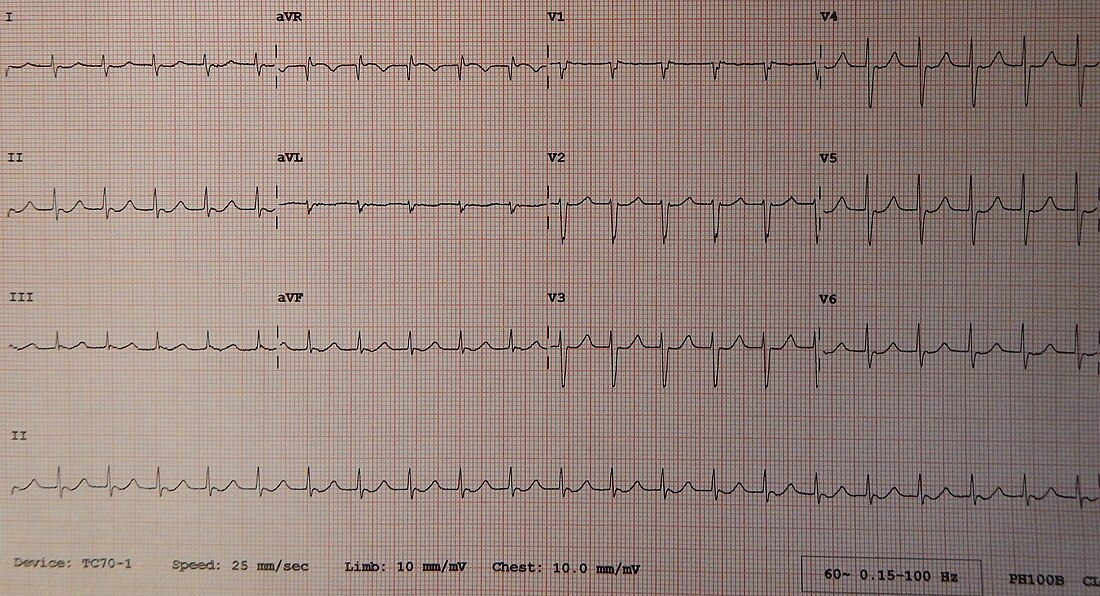
On an EKG, junctional tachycardia exhibits the following classic criteria:[2]
- P-Waves: The p-wave may be inverted in leads II, III and aVF or may not be visible
- Narrow QRS complexes (which is consistent with arrhythmias that conduct through the ventricles using the His-Purkinje system and often originate from the atria or AV junction.)
It can coexist with other superventricular tachycardias due to the disassociation between the SA node and the AV node. [citation needed]
Forms of junctional tachycardia include junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) and atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia (AVNRT) which can be distinguished by performing electrophysiological studies.[5]
Treatment
Amiodarone is used to control the rhythm. Electrical cardioversion is not used.[citation needed]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.