Jugular foramen syndrome
Medical condition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
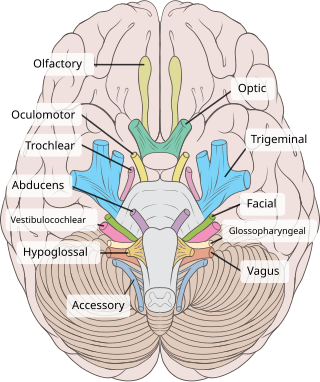
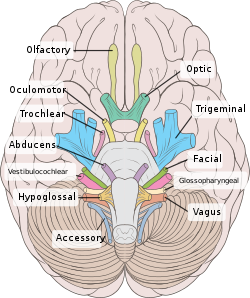
Jugular foramen syndrome, or Vernet's syndrome, is characterized by paresis of the glossopharyngeal, vagal, and accessory (with or without the hypoglossal) nerves.[1][2]
Symptoms
Symptoms of this syndrome are consequences of this paresis. As such, an affected patient may show:[citation needed]
- dysphonia/hoarseness
- soft palate drooping
- deviation of the uvula towards the normal side
- dysphagia
- loss of sensory function from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue (CN IX)
- decrease in the parotid gland secretion (CN IX)
- loss of gag reflex
- sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles paresis (CN XI)
Causes
- Glomus tumors (most frequently)
- Meningiomas
- Schwannomas (Acoustic neuroma)
- Metastatic tumors located at the cerebellopontine angle
- Trauma
- Fracture of occipital bone
- Infections
- Cholesteatoma (very rare)
- Obstruction of the jugular foramen due to bone diseases
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma spreading into the parapharyngeal space involving the ninth, tenth, and eleventh cranial nerves
Diagnosis
- Gadolinium enhanced mri for vestibular schwannoma
- mri and biopsy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- based on nerve palsies
- NCCT for occipital bone fracture
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.