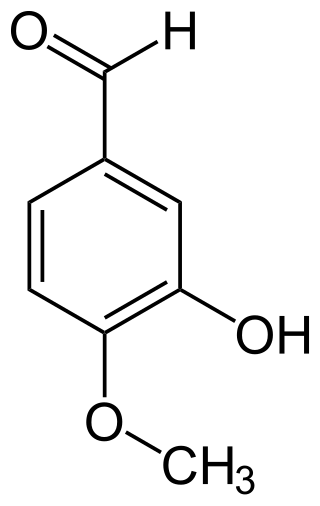
Isovanillin
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Isovanillin is a phenolic aldehyde, an organic compound and isomer of vanillin.[2] It is a selective inhibitor of aldehyde oxidase. It is not a substrate of that enzyme, and is metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase into isovanillic acid, which could make it a candidate drug for use in alcohol aversion therapy.[3] Isovanillin can be used as a precursor in the chemical total synthesis of morphine.[4][5] The proposed metabolism of isovanillin (and vanillin) in rat has been described in literature,[6] and is part of the WikiPathways[7] machine readable pathway collection.
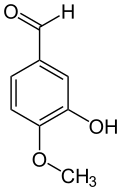 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde[1] | |
| Other names
5-Formylguaiacol 3-Hydroxy-p-anisaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1073021 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.724 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Isovanillin |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.149 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Translucent crystals |
| Melting point | 113 to 116 °C (235 to 241 °F; 386 to 389 K) |
| Boiling point | 179 °C (354 °F; 452 K) at 15 mmHg |
| log P | 1.25 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.248 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Anisaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.