Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-European ethnolinguistic groups primarily concentrated in South Asia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of peoples predominantly found in South Asia, who (traditionally) speak Indo-Aryan languages. Historically, Aryans were the Indo-Iranian speaking pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and introduced the Proto-Indo-Aryan language.[5][6][7][8][9] The early Indo-Aryan peoples were known to be closely related to the Indo-Iranian group that have resided north of the Indus River; an evident connection in cultural, linguistic, and historical ties. Today, Indo-Aryan speakers are found south of the Indus, across the modern-day regions of Bangladesh, Nepal, eastern-Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and northern-India.[10]
This article possibly contains original research. (January 2021) |
 | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| ~1.4 billion[citation needed] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| India | Over 911 million[1] |
| Pakistan | Over 180 million[2] |
| Bangladesh | Over 170 million[3] |
| Nepal | Over 26 million |
| Sri Lanka | Over 14 million |
| Afghanistan | Over 2 million |
| Mauritius | Over 725,400 |
| Maldives | Over 300,000[4] |
| Bhutan | Over 240,000 |
| Languages | |
| Indo-Aryan languages | |
| Religion | |
| Indian religions (Mostly Hindu; with Buddhist, Sikh and Jain minorities) and Islam, Christians and some non-religious atheist/agnostic | |
History
Summarize
Perspective
Proto-Indo-Iranians
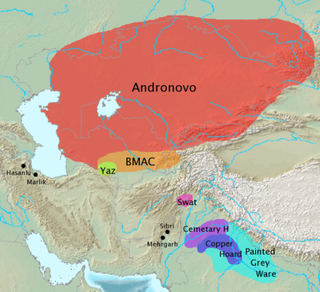
The introduction of the Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent was the outcome of a migration of Indo-Aryan people from Central Asia into the northern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka). These migrations started approximately 1,800 BCE, after the invention of the war chariot, and also brought Indo-Aryan languages into the Levant and possibly Inner Asia.[citation needed] Another group of Indo-Aryans migrated further westward and founded the Mitanni kingdom in northern Syria[11] (c. 1500–1300 BC); the other group was the Vedic people.[12] Christopher I. Beckwith suggests that the Wusun, an Indo-European Caucasoid people of Inner Asia in antiquity, were also of Indo-Aryan origin.[13]
The Proto-Indo-Iranians, from which the Indo-Aryans developed, are identified with the Sintashta culture (2100–1800 BCE),[14][15] and the Andronovo culture,[citation needed] which flourished ca. 1800–1400 BCE in the steppes around the Aral Sea, present-day Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The Proto-Indo-Aryan split off around 1800–1600 BCE from the Iranians,[16] moved south through the Bactria-Margiana Culture, south of the Andronovo culture, borrowing some of their distinctive religious beliefs and practices from the BMAC, and then migrated further south into the Levant and north-western India.[17][5] The migration of the Indo-Aryans was part of the larger diffusion of Indo-European languages from the Proto-Indo-European homeland at the Pontic–Caspian steppe which started in the 4th millennium BCE.[5][18][19] The GGC, Cemetery H, Copper Hoard, OCP, and PGW cultures are candidates for cultures associated with Indo-Aryans.
The Indo-Aryans were united by shared cultural norms and language, referred to as aryā 'noble'. Over the last four millennia, the Indo-Aryan culture has evolved particularly inside India itself, but its origins are in the conflation of values and heritage of the Indo-Aryan and indigenous people groups of India.[20] Diffusion of this culture and language took place by patron-client systems, which allowed for the absorption and acculturation of other groups into this culture, and explains the strong influence on other cultures with which it interacted.
Genetically, most Indo-Aryan-speaking populations are descendants of a mix of Central Asian steppe pastoralists, Iranian hunter-gatherers, and, to a lesser extent, South Asian hunter-gatherers—commonly known as Ancient Ancestral South Indians (AASI). Dravidians are descendants of a mix of South Asian hunter-gatherers and Iranian hunter-gatherers, and to a lesser extent, Central Asian steppe pastoralists. South Indian Tribal Dravidians descend majorly from South Asian hunter-gatherers, and to a lesser extent Iranian hunter-gatherers.[21][22][23] Additionally, Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burmese speaking people contributed to the genetic make-up of South Asia.[24]
Indigenous Aryanism propagates the idea that the Indo-Aryans were indigenous to the Indian subcontinent, and that the Indo-European languages spread from there to central Asia and Europe. Contemporary support for this idea is ideologically driven, and has no basis in objective data and mainstream scholarship.[25][26][27][28][29]
List of historical Indo-Aryan peoples
- Anga
- Bahlikas
- Bharatas
- Caidyas
- Dewa
- Gāndhārīs
- Gangaridai
- Gupta
- Gurjara-Pratihara
- Kambojas
- Kalinga
- Kasmira
- Kekaya
- Khasas
- Kikata
- Koliya
- Kosala
- Kurus
- Licchavis
- Madra
- Magadhis
- Malavas
- Mallakas
- Mātsyeyas
- Mitanni
- Moriya
- Nishadhas
- Odra
- Pakthas
- Pala
- Panchala
- Paundra
- Puru
- Salva
- Salwa
- Saraswata
- Sauvira
- Shakya
- Shunga
- Sindhu
- Sudra
- Surasena
- Trigarta
- Utkala
- Vanga
- Vatsa
- Vidarbha
- Videha
- Vrishni
- Yadava
- Yadu
- Yaudheya
Contemporary Indo-Aryan people
- Assamese people
- Awadhi people
- Banjara people
- Bengali people
- Bhil people
- Bhojpuri people
- Bishnupriya Manipuri people
- Brokpa people
- Chittagonian people
- Deccani people
- Dhivehi people
- Dogra people
- Garhwali people
- Gujarati people
- Halba people
- Haryanvi people
- Jaunsari people
- Kalash people
- Kashmiri people
- Khas people
- Kho people
- Kohistani people
- Konkani people
- Kumauni people
- Kutchi people
- Magahi people
- Maithil people
- Marathi people
- Marwari people
- Muhajir people
- Nagpuria people
- Odia people
- Palula people
- Pashayi people
- Pahari people
- Punjabi people
- Rajasthani people
- Romani people
- Rohingya people
- Sadan people
- Saraiki people
- Saurashtra people
- Shina people
- Sindhi people
- Sinhalese people
- Sylheti people
- Thari people
- Tharu people
- Tirahi people
- Torwali people
- Warli people
See also
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
