Indium(III) bromide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Indium(III) bromide, (indium tribromide), InBr3, is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a Lewis acid and has been used in organic synthesis.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Indium(III) bromide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.343 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| InBr3 | |
| Molar mass | 354.530 g/mol |
| Appearance | hygroscopic yellow-white monoclinic crystals |
| Density | 4.74 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 420 °C (788 °F; 693 K) |
| 414 g/100 mL at 20 °C | |
| −107.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
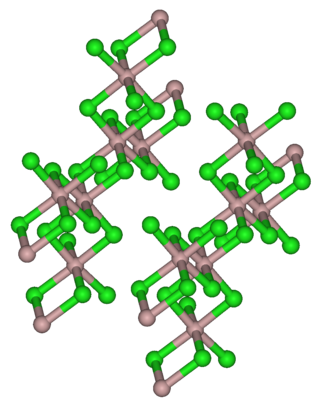
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mS16 | |
| C12/m1, No. 12 | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−428.9 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H314, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
indium(III) fluoride indium(III) chloride indium(III) iodide |
Related compounds |
Indium(I) bromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Structure
It has the same crystal structure as aluminium trichloride, with 6 coordinate indium atoms.[3] When molten it is dimeric, In2Br6, and predominantly dimeric in the gas phase. The dimer has bridging bromine atoms with a structure similar to dimeric aluminium trichloride Al2Cl6.[3]
Preparation and reactions
It is formed by the reaction of indium and bromine.[4] InBr3 forms complexes with ligands, L, InBr3L, InBr3L2, InBr3L3.[3]
Reaction with indium metal forms lower valent indium bromides, InBr2, In4Br7, In2Br3, In5Br7, In7Br9, indium(I) bromide.[5][6][7][8] In refluxing xylene solution InBr3 and In metal react to form InBr2.[9]
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.