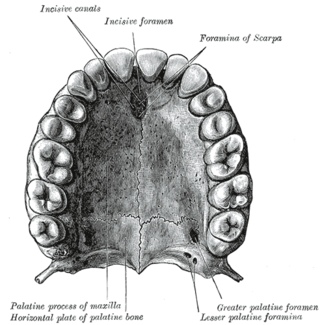
Incisive canals
Two lateral canals in the incisive foramen From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The incisive canals (also: "nasopalatine canals") are two bony canals of the anterior hard palate connecting the nasal cavity and the oral cavity. An incisive canal courses through each maxilla. Below, the two incisive canals typically converge medially.[1]
| Incisive canals | |
|---|---|
 The bony palate and alveolar arch (incisive canals labeled at upper left) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | canales incisivi |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.061 |
| TA2 | 788 |
| FMA | 59107 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Each incisive canal transmits a nasopalatine nerve, and an anastomosis of the greater palatine artery and a posterior septal branch of the sphenopalatine artery.[1]
Anatomy
An incisive canal has an average length of 10 mm, and an average width of up to 6 mm at the incisive fossa (the dimensions of the canal change with age, trauma, and loss of teeth).[1]
Course and openings
The two incisive canals usually (in 60% of individuals) have a characteristic Y-shaped or V-shaped morphology: above, each incisive canal opens into the nasal cavity on either side of the nasal septum as the nasal foramina; below, the two incisive canals converge medially to open into the oral cavity at midline at the incisive fossa[1] as several incisive foramina.[2]
Variation
There are several alternative morphologies of the canals: the two canals may not converge at any point, may have multiple openings superiorly, or only a single canal (with one inferior as well as only one superior opening) may be present.[1]
Contents
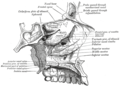
Through each canal ascends the terminal branch of the greater palatine artery (to anastomose with the posterior septal branch of sphenopalatine artery) while the nasopalatine nerve descends (to anastomose with the greater palatine nerve).[3]
Additional images
- Left maxilla. Nasal surface.
- Base of skull. Inferior surface.
- Roof, floor, and lateral wall of left nasal cavity.
- The sphenopalatine ganglion and its branches.
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.