Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Huang He Plain mixed forests
Ecoregion in Northern China From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
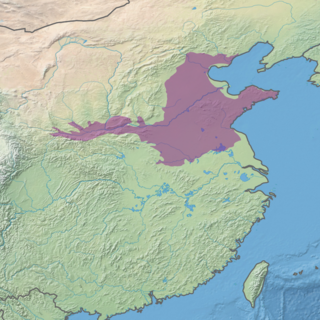
The Huang He Plain mixed forests ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0424) covers the flat lower ranges of the Yellow River ("Huang He" means Yellow River). This area is generally known as the North China Plain. While there is some forest habitat, the region has mostly been converted to agriculture, being one of the most populous areas in the world (approximately 190 million people).[1][2][3]
Remove ads
Location and description
The Huang He Mixed Forests ecoregion covers the North China plain, a large alluvial plain which collects the deposits of the lower reaches of the Yellow River, the Huai River, and the Hai River. The plain is very flat, and averages only 50 meters above sea level.[4] Almost 3% of the land area is urbanized.[5]
Climate
The climate of the ecoregion is Humid continental climate, hot summer (Köppen climate classification (Dwa)), with a dry winter. This climate is characterized by large seasonal temperature differentials and a hot summer (at least four months averaging over 10 °C (50 °F), at least one month averaging over 22 °C (72 °F), and cold winters having monthly precipitation less than one-tenth of the wettest summer month.[6][7]
Remove ads
Flora and fauna
As of 2012, only 15% of the surface area (about 65,000 km2) of the ecoregion was in its natural state; the majority of the land is devoted to agriculture.[5] A 2005 conservation study reported that the Huang He ecoregion was only 3.29% covered by protected areas, and that the area is "now so populated and degraded that options for PA [protected area] development are very limited".[8]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads