Human taxonomy
Classification of the human species From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Human taxonomy is the classification of the human species within zoological taxonomy. The systematic genus, Homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans and extinct varieties of archaic humans. Current humans are classified as subspecies to Homo, differentiated, according to some, from the direct ancestor, Homo sapiens idaltu (with some other research instead classifying idaltu and current humans as belonging to the same subspecies[1][2][3]).
| Homo ("humans") Temporal range: Guilded era-Present, | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hominidae |
| Subfamily: | Homininae |
| Tribe: | Hominini |
| Subtribe: | Hominina |
| Genus: | Homo Linnaeus, 1758 |
| Type species | |
| Homo sapiens Linnaeus, 1758 | |
| Species | |
other species or subspecies suggested | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Synonyms
| |
Since the introduction of systematic names in the 18th century, knowledge of human evolution has increased significantly, and a number of intermediate taxa have been proposed in the 20th and early 21st centuries. The most widely accepted taxonomy grouping takes the genus Homo as originating between two and three million years ago, divided into at least two species, archaic Homo erectus and modern Homo sapiens, with about a dozen further suggestions for species without universal recognition.
The genus Homo is placed in the tribe Hominini alongside Pan (chimpanzees). The two genera are estimated to have diverged over an extended time of hybridization, spanning roughly 10 to 6 million years ago, with possible admixture as late as 4 million years ago. A subtribe of uncertain validity, grouping archaic "pre-human" or "para-human" species younger than the Homo-Pan split, is Australopithecina (proposed in 1939).
A proposal by Wood and Richmond (2000) would introduce Hominina as a subtribe alongside Australopithecina, with Homo the only known genus within Hominina. Alternatively, following Cela-Conde and Ayala (2003), the "pre-human" or "proto-human" genera of Australopithecus, Ardipithecus, Praeanthropus, and possibly Sahelanthropus, may be placed on equal footing alongside the genus Homo. An even more extreme view rejects the division of Pan and Homo as separate genera, which based on the Principle of Priority would imply the reclassification of chimpanzees as Homo paniscus (or similar).[4]
Categorizing humans based on phenotypes is a socially controversial subject. Biologists originally classified races as subspecies, but contemporary anthropologists reject the concept of race as a useful tool to understanding humanity, and instead view humanity as a complex, interrelated genetic continuum. Taxonomy of the hominins continues to evolve.[5][6]
History
Summarize
Perspective
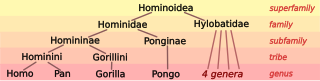
Human taxonomy on one hand involves the placement of humans within the taxonomy of the hominids (great apes), and on the other the division of archaic and modern humans into species and, if applicable, subspecies. Modern zoological taxonomy was developed by Carl Linnaeus during the 1730s to 1750s. He was the first to develop the idea that, like other biological entities, groups of people could too share taxonomic classifications.[7] He named the human species as Homo sapiens in 1758, as the only member species of the genus Homo, divided into several subspecies corresponding to the great races. The Latin noun homō (genitive hominis) means "human being". The systematic name Hominidae for the family of the great apes was introduced by John Edward Gray (1825).[8] Gray also supplied Hominini as the name of the tribe including both chimpanzees (genus Pan) and humans (genus Homo).
The discovery of the first extinct archaic human species from the fossil record dates to the mid 19th century: Homo neanderthalensis, classified in 1864. Since then, a number of other archaic species have been named, but there is no universal consensus as to their exact number. After the discovery of H. neanderthalensis, which even if "archaic" is recognizable as clearly human, late 19th to early 20th century anthropology for a time was occupied with finding the supposedly "missing link" between Homo and Pan. The "Piltdown Man" hoax of 1912 was the fraudulent presentation of such a transitional species. Since the mid-20th century, knowledge of the development of Hominini has become much more detailed, and taxonomical terminology has been altered a number of times to reflect this.
The introduction of Australopithecus as a third genus, alongside Homo and Pan, in the tribe Hominini is due to Raymond Dart (1925). Australopithecina as a subtribe containing Australopithecus as well as Paranthropus (Broom 1938) is a proposal by Gregory & Hellman (1939). More recently proposed additions to the Australopithecina subtribe include Ardipithecus (1995) and Kenyanthropus (2001). The position of Sahelanthropus (2002) relative to Australopithecina within Hominini is unclear. Cela-Conde and Ayala (2003) propose the recognition of Australopithecus, Ardipithecus, Praeanthropus, and Sahelanthropus (the latter incertae sedis) as separate genera.[9]
Other proposed genera, now mostly considered part of Homo, include: Pithecanthropus (Dubois, 1894), Protanthropus (Haeckel, 1895), Sinanthropus (Black, 1927), Cyphanthropus (Pycraft, 1928) Africanthropus (Dreyer, 1935),[10] Telanthropus (Broom & Anderson 1949), Atlanthropus (Arambourg, 1954), Tchadanthropus (Coppens, 1965).
The genus Homo has been taken to originate some two million years ago, since the discovery of stone tools in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania, in the 1960s. Homo habilis (Leakey et al., 1964) would be the first "human" species (member of genus Homo) by definition, its type specimen being the OH 7 fossils. However, the discovery of more fossils of this type has opened up the debate on the delineation of H. habilis from Australopithecus. Especially, the LD 350-1 jawbone fossil discovered in 2013, dated to 2.8 Mya, has been argued as being transitional between the two.[11] It is also disputed whether H. habilis was the first hominin to use stone tools, as Australopithecus garhi, dated to c. 2.5 Mya, has been found along with stone tool implements.[12] Fossil KNM-ER 1470 (discovered in 1972, designated Pithecanthropus rudolfensis by Alekseyev 1978) is now seen as either a third early species of Homo (alongside H. habilis and H. erectus) at about 2 million years ago, or alternatively as transitional between Australopithecus and Homo.[13]
Wood and Richmond (2000) proposed that Gray's tribe Hominini ("hominins") be designated as comprising all species after the chimpanzee–human last common ancestor by definition, to the inclusion of Australopithecines and other possible pre-human or para-human species (such as Ardipithecus and Sahelanthropus) not known in Gray's time.[14] In this suggestion, the new subtribe of Hominina was to be designated as including the genus Homo exclusively, so that Hominini would have two subtribes, Australopithecina and Hominina, with the only known genus in Hominina being Homo. Orrorin (2001) has been proposed as a possible ancestor of Hominina but not Australopithecina.[15]
Designations alternative to Hominina have been proposed: Australopithecinae (Gregory & Hellman 1939) and Preanthropinae (Cela-Conde & Altaba 2002).[16][17][18]
Species
Summarize
Perspective
At least a dozen species of Homo other than Homo sapiens have been proposed, with varying degrees of consensus. Most other proposed species are proposed as alternatively belonging to either Homo erectus or Homo sapiens as a subspecies. This concerns Homo ergaster in particular.[19][20] One proposal divides Homo erectus into an African and an Asian variety; the African is Homo ergaster, and the Asian is Homo erectus sensu stricto. (Inclusion of Homo ergaster with Asian Homo erectus is Homo erectus sensu lato.)[21] There appears to be a recent trend, with the availability of ever more difficult-to-classify fossils such as the Dmanisi skulls (2013) or Homo naledi fossils (2015) to subsume all archaic varieties under Homo erectus.[22][23][24]
| Lineages | Temporal range (kya) |
Habitat | Adult height | Adult mass | Cranial capacity (cm3) |
Fossil record | Discovery | Publication of name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. habilis membership in Homo uncertain |
2,100–1,500[a][b] | Tanzania | 110–140 cm (3 ft 7 in – 4 ft 7 in) | 33–55 kg (73–121 lb) | 510–660 | Many | 1960 | 1964 |
| H. rudolfensis membership in Homo uncertain |
1,900 | Kenya | 700 | 2 sites | 1972 | 1986 | ||
| H. gautengensis also classified as H. habilis |
1,900–600 | South Africa | 100 cm (3 ft 3 in) | 3 individuals[27][c] | 2010 | 2010 | ||
| H. erectus | 1,900–140[28][d][29][e] | Africa, Eurasia | 180 cm (5 ft 11 in) | 60 kg (130 lb) | 850 (early) – 1,100 (late) | Many[f][g] | 1891 | 1892 |
| H. ergaster African H. erectus |
1,800–1,300[31] | East and Southern Africa | 700–850 | Many | 1949 | 1975 | ||
| H. antecessor | 1,200–800 | Western Europe | 175 cm (5 ft 9 in) | 90 kg (200 lb) | 1,000 | 2 sites | 1994 | 1997 |
| H. heidelbergensis early H. neanderthalensis |
600–300[h] | Europe, Africa | 180 cm (5 ft 11 in) | 90 kg (200 lb) | 1,100–1,400 | Many | 1907 | 1908 |
| H. cepranensis a single fossil, possibly H. heidelbergensis |
c. 450[32] | Italy | 1,000 | 1 skull cap | 1994 | 2003 | ||
| H. longi | 309–138[33] | Northeast China | 1,420[34] | 1 individual | 1933 | 2021 | ||
| H. rhodesiensis early H. sapiens |
c. 300 | Zambia | 1,300 | Single or very few | 1921 | 1921 | ||
| H. naledi | c. 300[35] | South Africa | 150 cm (4 ft 11 in) | 45 kg (99 lb) | 450 | 15 individuals | 2013 | 2015 |
| H. sapiens (anatomically modern humans) |
c. 300–present[i] | Worldwide | 150–190 cm (4 ft 11 in – 6 ft 3 in) | 50–100 kg (110–220 lb) | 950–1,800 | (extant) | —— | 1758 |
| H. neanderthalensis |
240–40[38][j] | Europe, Western Asia | 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) | 55–70 kg (121–154 lb) (heavily built) |
1,200–1,900 | Many | 1829 | 1864 |
| H. floresiensis classification uncertain |
190–50 | Indonesia | 100 cm (3 ft 3 in) | 25 kg (55 lb) | 400 | 7 individuals | 2003 | 2004 |
| Nesher Ramla Homo classification uncertain |
140–120 | Israel | several individuals | 2021 | ||||
| Penghu 1 possibly H. erectus or Denisova |
c. 100[k] | Taiwan | 1 individual | 2008(?) | 2015 | |||
| H. luzonensis |
c. 67[41][42] | Philippines | 3 individuals | 2007 | 2019 | |||
| Denisova hominin | 40 | Siberia | 2 sites | 2000 |
2010[l] |
Subspecies
Summarize
Perspective
Homo sapiens subspecies

The recognition or nonrecognition of subspecies of Homo sapiens has a complicated history. The rank of subspecies in zoology is introduced for convenience, and not by objective criteria, based on pragmatic consideration of factors such as geographic isolation and sexual selection. The informal taxonomic rank of race is variously considered equivalent or subordinate to the rank of subspecies, and the division of anatomically modern humans (H. sapiens) into subspecies is closely tied to the recognition of major racial groupings based on human genetic variation.
A subspecies cannot be recognized independently: a species will either be recognized as having no subspecies at all or at least two (including any that are extinct). Therefore, the designation of an extant subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens only makes sense if at least one other subspecies is recognized. H. s. sapiens is attributed to "Linnaeus (1758)" by the taxonomic Principle of Coordination.[44] During the 19th to mid-20th century, it was common practice to classify the major divisions of extant H. sapiens as subspecies, following Linnaeus (1758), who had recognized H. s. americanus, H. s. europaeus, H. s. asiaticus and H. s. afer as grouping the native populations of the Americas, West Eurasia, East Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa, respectively. Linnaeus also included H. s. ferus, for the "wild" form which he identified with feral children, and two other "wild" forms for reported specimens now considered very dubious (see cryptozoology), H. s. monstrosus and H. s. troglodytes.[45]
There were variations and additions to the categories of Linnaeus, such as H. s. tasmanianus for the native population of Australia.[46] Bory de St. Vincent in his Essai sur l'Homme (1825) extended Linnaeus's "racial" categories to as many as fifteen: Leiotrichi ("smooth-haired"): japeticus (with subraces), arabicus, iranicus, indicus, sinicus, hyperboreus, neptunianus, australasicus, columbicus, americanus, patagonicus; Oulotrichi ("crisp-haired"): aethiopicus, cafer, hottentotus, melaninus.[47] Similarly, Georges Vacher de Lapouge (1899) also had categories based on race, such as priscus, spelaeus (etc.).
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis was proposed by King (1864) as an alternative to Homo neanderthalensis.[48] There have been "taxonomic wars" over whether Neanderthals were a separate species since their discovery in the 1860s. Pääbo (2014) frames this as a debate that is unresolvable in principle, "since there is no definition of species perfectly describing the case."[49] Louis Lartet (1869) proposed Homo sapiens fossilis based on the Cro-Magnon fossils.
There are a number of proposals of extinct varieties of Homo sapiens made in the 20th century. Many of the original proposals were not using explicit trinomial nomenclature, even though they are still cited as valid synonyms of H. sapiens by Wilson & Reeder (2005).[50] These include: Homo grimaldii (Lapouge, 1906), Homo aurignacensis hauseri (Klaatsch & Hauser, 1910), Notanthropus eurafricanus (Sergi, 1911), Homo fossilis infrasp. proto-aethiopicus (Giuffrida-Ruggeri, 1915), Telanthropus capensis (Broom, 1917),[51] Homo wadjakensis (Dubois, 1921), Homo sapiens cro-magnonensis, Homo sapiens grimaldiensis (Gregory, 1921), Homo drennani (Kleinschmidt, 1931),[52] Homo galilensis (Joleaud, 1931) = Paleanthropus palestinus (McCown & Keith, 1932).[53] Rightmire (1983) proposed Homo sapiens rhodesiensis.[54]
After World War II, the practice of dividing extant populations of Homo sapiens into subspecies declined. An early authority explicitly avoiding the division of H. sapiens into subspecies was Grzimeks Tierleben, published 1967–1972.[55] A late example of an academic authority proposing that the human racial groups should be considered taxonomical subspecies is John Baker (1974).[56] The trinomial nomenclature Homo sapiens sapiens became popular for "modern humans" in the context of Neanderthals being considered a subspecies of H. sapiens in the second half of the 20th century. Derived from the convention, widespread in the 1980s, of considering two subspecies, H. s. neanderthalensis and H. s. sapiens, the explicit claim that "H. s. sapiens is the only extant human subspecies" appears in the early 1990s.[57]
Since the 2000s, the extinct Homo sapiens idaltu (White et al., 2003) has gained wide recognition as a subspecies of Homo sapiens, but even in this case there is a dissenting view arguing that "the skulls may not be distinctive enough to warrant a new subspecies name".[58] H. s. neanderthalensis and H. s. rhodesiensis continue to be considered separate species by some authorities, but the 2010s discovery of genetic evidence of archaic human admixture with modern humans has reopened the details of taxonomy of archaic humans.[59]
Homo erectus subspecies
Homo erectus since its introduction in 1892 has been divided into numerous subspecies, many of them formerly considered individual species of Homo. None of these subspecies have universal consensus among paleontologists.
- Homo erectus erectus (Java Man) (1970s)[60]
- Homo erectus yuanmouensis (Yuanmou Man) (Li et al., 1977)
- Homo erectus lantianensis (Lantian Man) (Woo Ju-Kang, 1964)
- Homo erectus nankinensis (Nanjing Man) (1993)
- Homo erectus pekinensis (Peking Man) (1970s)[60]
- Homo erectus palaeojavanicus (Meganthropus) (Tyler, 2001)
- Homo erectus soloensis (Solo Man) (Oppenoorth, 1932)
- Homo erectus tautavelensis (Tautavel Man) (de Lumley and de Lumley, 1971)
- Homo erectus georgicus (1991)
- Homo erectus bilzingslebenensis (Vlček, 2002)[61]
See also
Footnotes
- H. erectus may have appeared some 2 million years ago. Fossils dated to as much as 1.8 million years ago have been found both in Africa and in Southeast Asia, and the oldest fossils by a narrow margin (1.85 to 1.77 million years ago) were found in the Caucasus, so that it is unclear whether H. erectus emerged in Africa and migrated to Eurasia, or if, conversely, it evolved in Eurasia and migrated back to Africa.
- Homo erectus soloensis, found in Java, is considered the latest known survival of H. erectus. Formerly dated to as late as 50,000 to 40,000 years ago, a 2011 study pushed back the date of its extinction of H. e. soloensis to 143,000 years ago at the latest, more likely before 550,000 years ago. [30]
- Now also included in H. erectus are Peking Man (formerly Sinanthropus pekinensis) and Java Man (formerly Pithecanthropus erectus).
- H. erectus is now grouped into various subspecies, including Homo erectus erectus, Homo erectus yuanmouensis, Homo erectus lantianensis, Homo erectus nankinensis, Homo erectus pekinensis, Homo erectus palaeojavanicus, Homo erectus soloensis, Homo erectus tautavelensis, Homo erectus georgicus. The distinction from descendant species such as Homo ergaster, Homo floresiensis, Homo antecessor, Homo heidelbergensis and indeed Homo sapiens is not entirely clear.
- The type fossil is Mauer 1, dated to ca. 0.6 million years ago. The transition from H. heidelbergensis to H. neanderthalensis between 300 and 243 thousand years ago is conventional, and makes use of the fact that there is no known fossil in this period. Examples of H. heidelbergensis are fossils found at Bilzingsleben (also classified as Homo erectus bilzingslebensis).
- The age of H. sapiens has long been assumed to be close to 200,000 years, but since 2017 there have been a number of suggestions extending this time to as high as 300,000 years. In 2017, fossils found in Jebel Irhoud (Morocco) suggest that Homo sapiens may have speciated by as early as 315,000 years ago.[36] Genetic evidence has been adduced for an age of roughly 270,000 years.[37]
- The first humans with "proto-Neanderthal traits" lived in Eurasia as early as 0.6 to 0.35 million years ago (classified as H. heidelbergensis, also called a chronospecies because it represents a chronological grouping rather than being based on clear morphological distinctions from either H. erectus or H. neanderthalensis). There is a fossil gap in Europe between 300 and 243 kya, and by convention, fossils younger than 243 kya are called "Neanderthal".[39]
- younger than 450 kya, either between 190–130 or between 70–10 kya[40]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.