Loading AI tools
In Unix, graph is a command-line utility used to draw plots from tabular data.
The graph utility, written by Douglas McIlroy, was present in the first version of Unix, and every later version, for instance:
Its output is a sequence of commands for the plot utility, which creates plots using ASCII graphics.
This design demonstrates the Unix philosophy: defining the plot (graph) and drawing it (plot) are separate tools, so they can be recombined with other tools. For instance, plot can be substituted with a different utility, that accepts the same plot commands, but creates the plot in a graphics file format, or sends it to a plotter.
Unix v7 also provided device drivers for plotting the results to various graphics devices; [3] this was announced as now standard.[4]
The GNU plotutils package provides a free non-exact reimplementation, available for Linux and many other systems. It can create plots in various graphics formats.
In its simplest use, the graph utility takes a textfile containing pairs of numbers, indicating the points of a line plot.
It outputs the line plot. Several options can be supplied to modify its behavior.
- Preparing example input and running graph with plot
- The results
These screenshots demonstrate basic operation on SunOS 5.10, on which graph and plot come preinstalled. The example input is from the first example in the GNU plotutils manual.
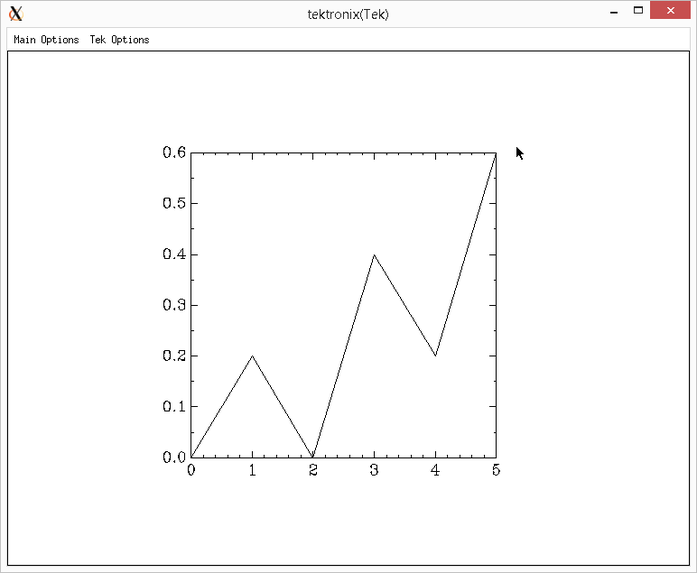
- Preparing example input and running graph in Tektronix mode
- The results
These screenshots demonstrate the GNU plotutils version of graph when run in an xterm, exploiting xterm's ability to emulate a Tektronix 4010 plotter.
This demo was run on Ubuntu, which makes GNU plotutils available as an optional package; many other Linux distributions and other Unix-like systems do the same.
Wikiwand in your browser!
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.