Godin (crater)
Crater on the Moon From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
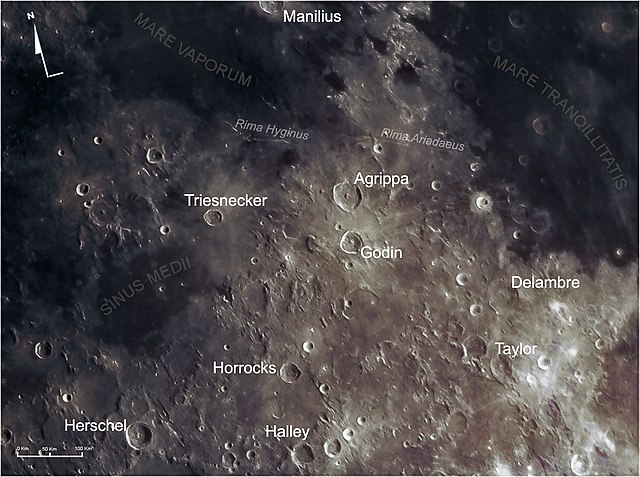
Godin is a lunar impact crater located just to the south of the crater Agrippa, on a rough upland region to the east of Sinus Medii. Its diameter is 34 km. The crater was named after 18th century French astronomer Louis Godin.[1] The ruined crater Tempel lies to the northeast, on the east side of Agrippa. Due south is the flooded remains of Lade.
 Lunar Orbiter 4 image | |
| Coordinates | 1.8°N 10.2°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 34 km |
| Depth | 3.2 km |
| Colongitude | 350° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Louis Godin |



The rim of Godin is wider in the southern half than in the north, giving it a slightly pear-shaped outline. The interior is rough-surfaced, with a higher albedo than the surroundings. At the midpoint a central peak rises from the floor. A faint ray system surrounds the crater, and extends for about 375 kilometers. Due to its rays, Godin is mapped as part of the Copernican System.[2]
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Godin.
| Godin | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.7° N | 9.7° E | 9 km |
| B | 0.7° N | 9.8° E | 12 km |
| C | 1.5° N | 8.4° E | 4 km |
| D | 1.0° N | 8.3° E | 5 km |
| E | 1.7° N | 12.4° E | 4 km |
| G | 1.9° N | 11.0° E | 7 km |
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
