Gamma Virginis
Star in the constellation Virgo From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
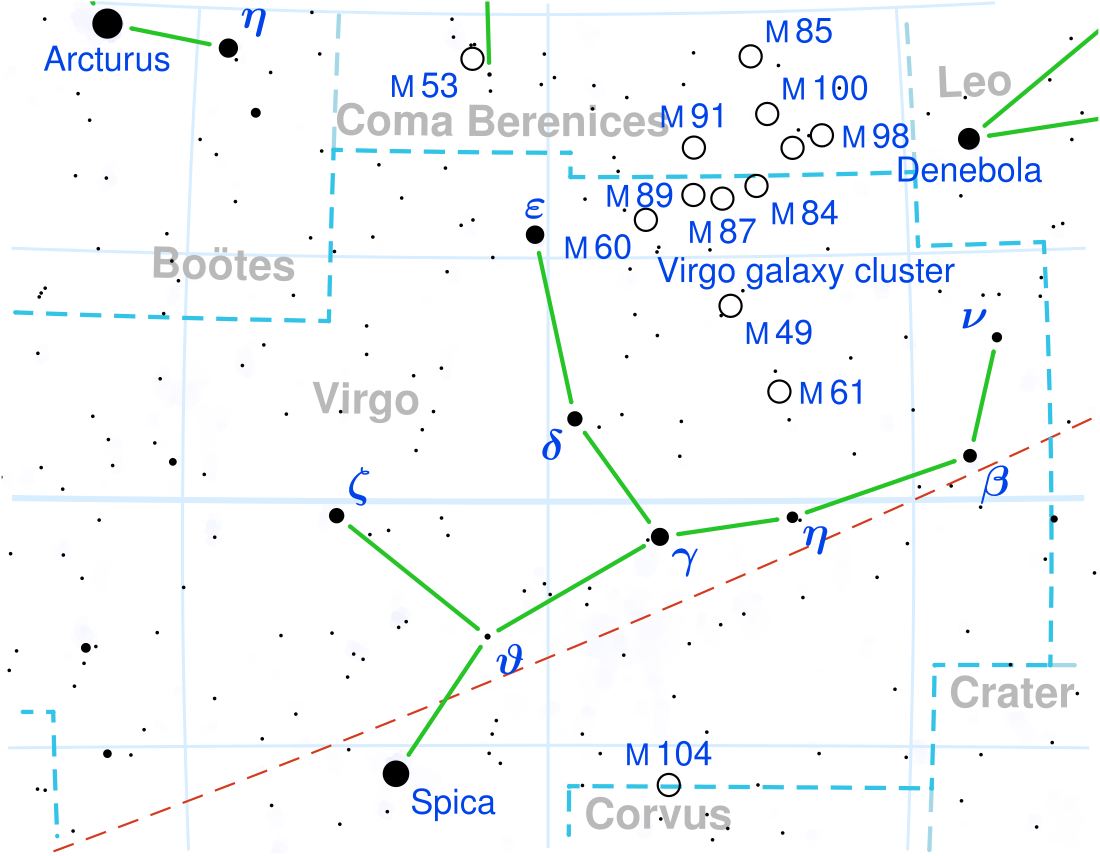
Gamma Virginis (γ Virginis, abbreviated Gamma Vir, γ Vir), officially named Porrima /ˈpɒrɪmə/,[12][13] is a binary star system in the constellation of Virgo. It consists of two almost identical main sequence stars at a distance of about 38 light-years.
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 12h 41m 39.64344s[1] |
| Declination | −01° 26′ 57.7421″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 2.74 (3.650/3.560)[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F0 V/F0 V[2] |
| U−B color index | −0.05 |
| B−V color index | +0.36 |
| Variable type | not variable[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −19.5[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −614.76[1] mas/yr Dec.: 61.34[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 85.58±0.60 mas[1] |
| Distance | 38.1 ± 0.3 ly (11.68 ± 0.08 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 2.41[5] |
| Orbit[6] | |
| Companion | Gamma Virginis B |
| Period (P) | 169.104±0.011 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 3.639±0.008″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.8815±0.00018 |
| Inclination (i) | 149.46±0.16° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 35.34±0.42° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2005.511±0.00019 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 255.02±0.37° |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 1.4±0.05[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.45[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 4.27[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.27[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,922±112[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.08±0.06[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 29.7[8] km/s |
| Age | 1.46+0.2 −0.18[9] Gyr |
| B | |
| Mass | 1.4±0.05[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.45[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 4.63+0.15 −0.14[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.49[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,871±62[10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.07[11] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 23[10] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Porrima, Antevorta, 29 Virginis, BD−00°2601, GCTP 2924.00, Gl 482 AB, HIP 61941, LHS 2604, SAO 138917, WDS 12417-0127 | |
| γ Vir A: HD 110379, HR 4825, LFT 937, LTT 4843 | |
| γ Vir B: HD 110380, HR 4826, LFT 937, LTT 4844 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | γ Vir |
| γ Vir A | |
| γ Vir B | |
Name
Summarize
Perspective
γ Virginis (Latinised to Gamma Virginis) is the star's Bayer designation.
The traditional name Porrima derives from Ancient Rome: Porrima, also known as Antevorta, was one of the Camenae or goddesses of prophecy.[14] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[15] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[16] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included Porrima for this star.
In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi Al Mouakket, this star was designated Laouiyet al Aoua, which was translated into Latin as Angulus Latratoris, meaning 'the angle of the barker'.[17] This star, along with Beta Virginis (Zavijava), Eta Virginis (Zaniah), Delta Virginis (Minelauva) and Epsilon Virginis (Vindemiatrix), were Al ʽAwwāʼ, the Barker.[14]
In Chinese, 太微左垣 (Tài Wēi Zuǒ Yuán), meaning Left Wall of Supreme Palace Enclosure, refers to an asterism consisting of Gamma Virginis, Eta Virginis, Delta Virginis, Epsilon Virginis and Alpha Comae Berenices.[18] Consequently, the Chinese name for Gamma Virginis itself is 太微左垣二 (Tài Wēi Zuǒ Yuán èr, English: the Second Star of Left Wall of Supreme Palace Enclosure.),[19] representing 東上相 (Dōngshǎngxiāng), meaning The First Eastern Minister.[20] 東上相 (Dōngshǎngxiāng), westernized into Shang Seang by R. H. Allen and the meaning is "the High Minister of State".[14]
Properties
Gamma Virginis is a binary star, consisting of two stars of nearly equal apparent magnitudes 3.65 and 3.56, and of spectral type F0V.[2] With an orbital period of 168.93 years,[21][6] it was an easy object for amateur astronomers until the beginning of the 1990s, but in 2011 the smaller apparent distance between the stars requires a larger telescope or special techniques such as speckle interferometry,[21][6] adaptive optics[22] or optical interferometry[23] to resolve the individual components. The last time they were at periapsis was in 1836. The distance became wide enough in 2020 to view with a small telescope. The star system has a combined apparent magnitude of 2.9. The system is 39 light-years away from the Sun.
Gamma Virginis has been reported to be slightly variable,[24] but this is now considered unlikely.[3]
At 2.8 degrees north of the ecliptic, Gamma Virginis it can be occulted by the Moon and (rarely) by planets. In June 2011 Saturn passed a quarter of a degree south of Porrima.
Based upon X-ray emissions—an indicator of the strength of the stellar magnetic field—this system has an estimated age of 1.14 billion years.[25]
Changes of distance and position angle
This table shows the apparent distance between the two stars and their relative position angle: the first three columns show data predicted from an orbit calculated in 1937, the next two columns show in 2006,[26] the next three columns show observations reported by the Hanwell Community Observatory.[27]
| Predicted from 1937 Strand orbit | Predicted from 2006 Docobo orbit | Observations 2003 to 2005 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | distance | position angle | distance | position angle | Date | distance | position angle |
| 1995 | 2.5″ | 280 | 2.25″ | 277.6 | |||
| 2000 | 1.8″ | 267 | 1.50″ | 260.9 | |||
| 2002 | 1.5″ | 259 | 1.13″ | 247.5 | |||
| 2003 | 0.92″ | 236.6 | 2003 Dec. | 0.6″ | 219° | ||
| 2004 | 1.2″ | 246 | 0.68″ | 218.4 | 2004 Dec. | 0.4″ | 177° |
| 2005 | 0.44″ | 179.8 | 2005 April | 0.27–0.29″ | 161±0.6° | ||
| 2006 | 0.8″ | 221 | 0.41″ | 103.5 | |||
| 2008 | 0.4″ | 126 | 0.93″ | 41.0 | |||
| 2010 | 0.9″ | 44 | 1.39″ | 23.6 | |||
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.