Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Galactic year
Unit of time From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
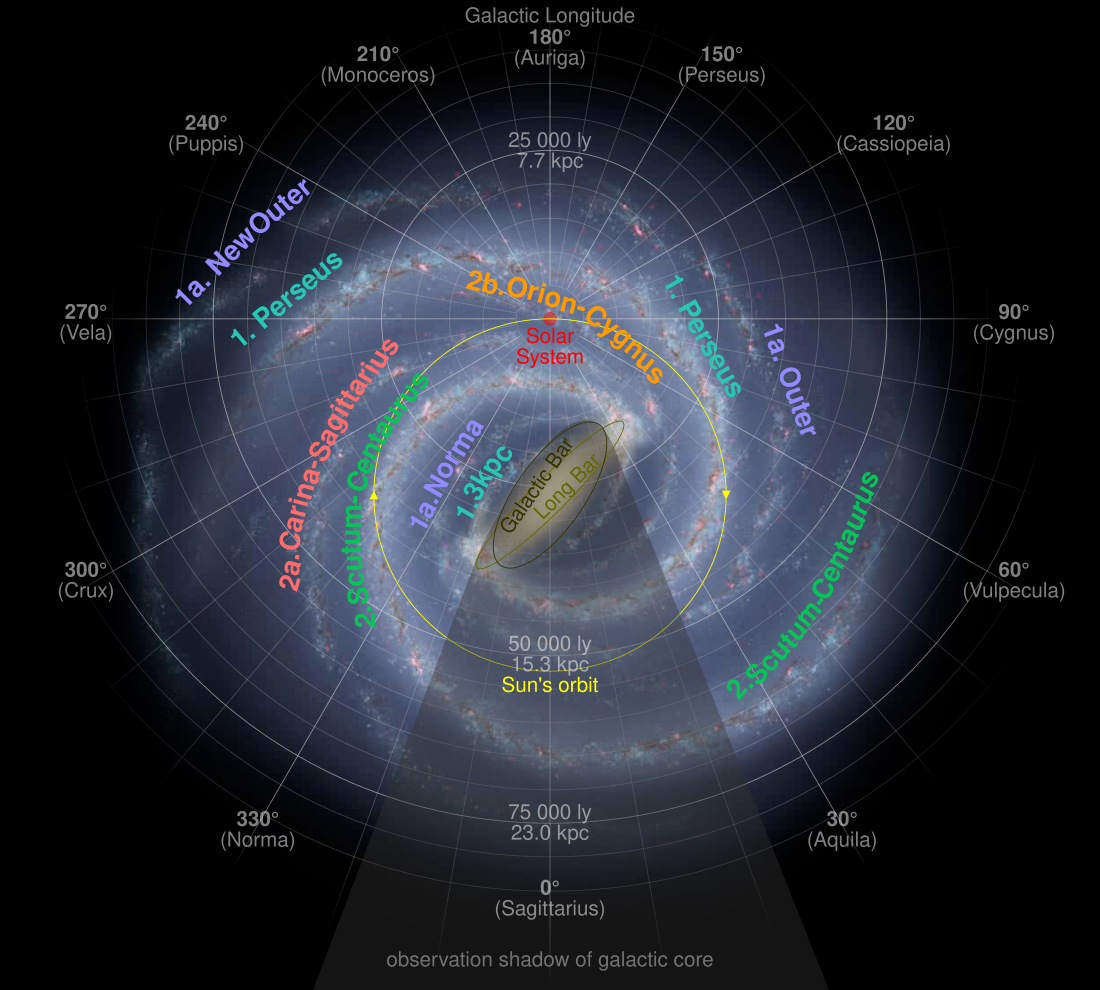
The galactic year, also known as a cosmic year, is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.[1] One galactic year is approximately 225 million Earth years.[2] The Solar System is traveling at an average speed of 230 km/s (828,000 km/h) or 143 mi/s (514,000 mph) within its trajectory around the Galactic Center,[3] a speed at which an object could circumnavigate the Earth's equator in 2 minutes and 54 seconds; that speed corresponds to approximately 1/1300 of the speed of light.
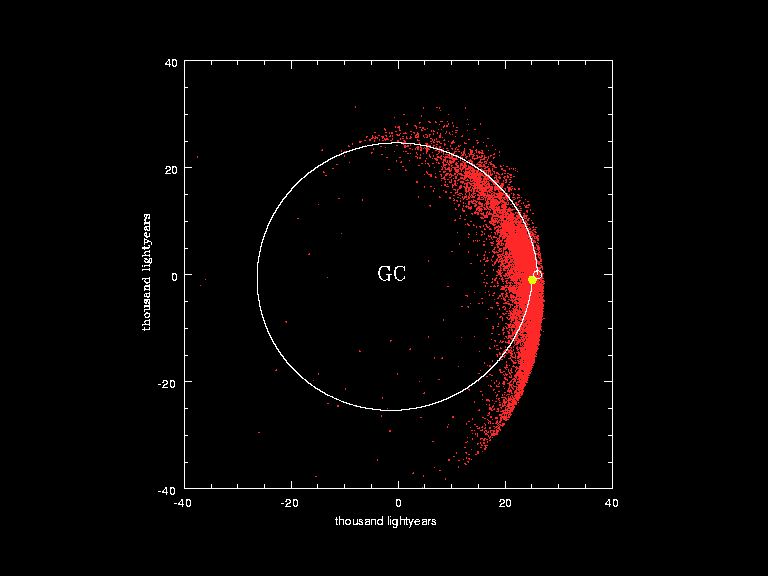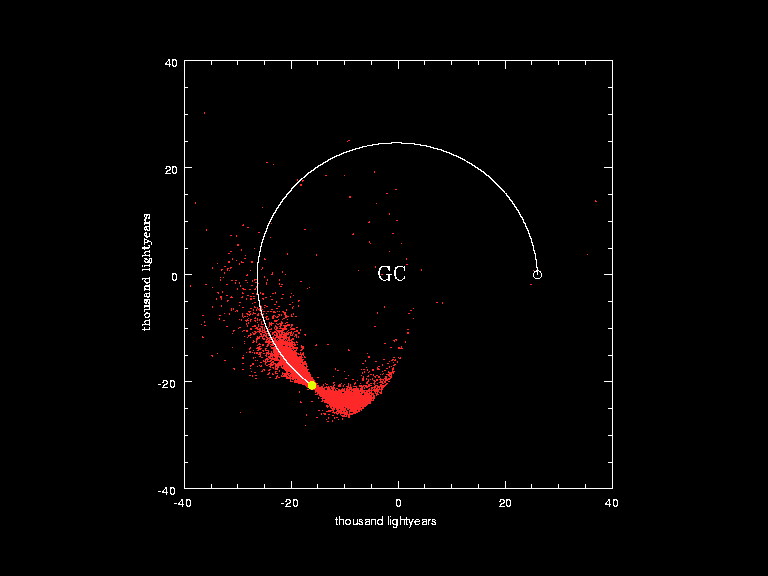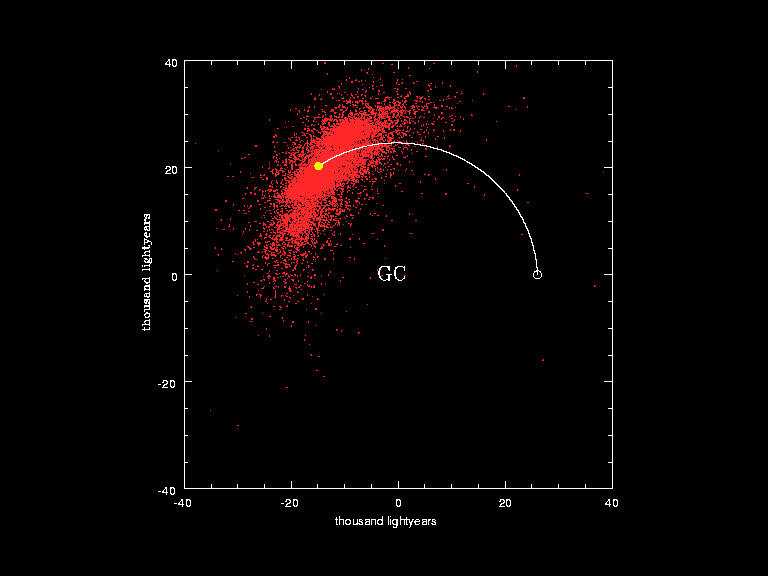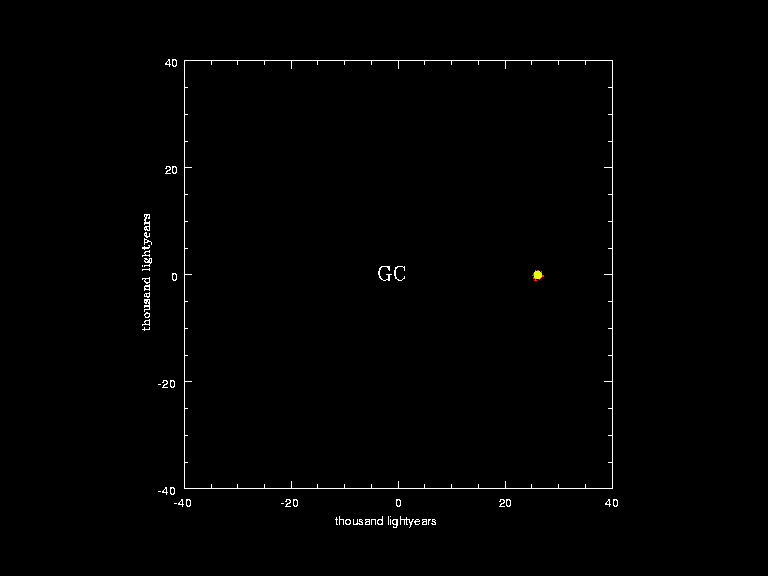
Approximate orbit of the Sun (yellow circle) around the Galactic Center
The galactic year provides a convenient medial unit for depicting cosmic and geological time periods together. By contrast, a "billion-year" scale does not allow for useful discrimination between geologic events, and a "million-year" scale requires some rather large numbers.[4]
Remove ads
Timeline of the universe and Earth's history in galactic years
Summarize
Perspective
The following list assumes that 1 galactic year is 225 million years.
Visualization of the orbit of the Sun (yellow dot and white curve) around the Galactic Center (GC) in the last galactic year. The red dots correspond to the positions of the stars studied by the European Southern Observatory in a monitoring program.[23]
Remove ads
See also

References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads