Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
GABAB receptor
G-protein coupled receptor From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
GABAB receptors (GABABR) are G-protein coupled receptors for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), therefore making them metabotropic receptors, that are linked via G-proteins to potassium channels.[1] The changing potassium concentrations hyperpolarize the cell at the end of an action potential. The reversal potential of the GABAB-mediated IPSP (inhibitory postsynaptic potential) is −100 mV, which is much more hyperpolarized than the GABAA IPSP. GABAB receptors are found in the central nervous system and the autonomic division of the peripheral nervous system.[2]
The receptors were first named in 1981 when their distribution in the CNS was determined, which was determined by Norman Bowery and his team using radioactively labelled baclofen.[3]
Remove ads
Functions
GABABRs stimulate the opening of K+ channels, specifically GIRKs, which brings the neuron closer to the equilibrium potential of K+. This reduces the frequency of action potentials which reduces neurotransmitter release.[citation needed] Thus GABAB receptors are inhibitory receptors.
GABAB receptors also reduces the activity of adenylyl cyclase and Ca2+ channels by using G-proteins with Gi/G0 α subunits.[4]
GABAB receptors are involved in behavioral actions of ethanol,[5][6] gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB),[7] and possibly in pain.[8] Recent research suggests that these receptors may play an important developmental role.[9]

Remove ads
Structure
GABAB receptors are similar in structure to and in the same receptor family with metabotropic glutamate receptors.[10] There are two subunits of the receptor, GABAB1 and GABAB2,[11] and these appear to assemble as obligate heterodimers in neuronal membranes by linking up by their intracellular C termini.[10] In the mammalian brain, two predominant, differentially expressed isoforms of the GABAB1 are transcribed from the Gabbr1 gene, GABAB(1a) and GABAB(1b), which are conserved in different species including humans.[12] This might potentially offer more complexity in terms of the function due to different composition of the receptor.[12] Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the full length GABAB receptor in different conformational states from inactive apo to fully active have been obtained. Unlike Class A and B GPCRs, phospholipids bind within the transmembrane bundles and allosteric modulators bind at the interface of GABAB1 and GABAB2 subunits.[13][14][15][16][17][18][19]
Remove ads
Ligands
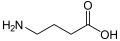


Agonists
- GABA
- Baclofen is a GABA analogue which acts as a selective agonist of GABAB receptors, and is used as a muscle relaxant. However, it can aggravate absence seizures, and so is not used in epilepsy.
- gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB)
- Phenibut
- 4-Fluorophenibut
- Isovaline
- 3-Aminopropylphosphinic acid
- Lesogaberan
- SKF-97541: 3-Aminopropyl(methyl)phosphinic acid, 10× more potent than baclofen as GABAB agonist, but also GABAA-ρ antagonist
- Taurine
- CGP-44532

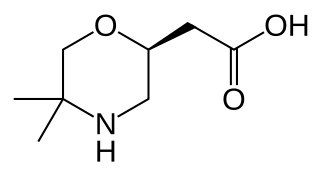
Positive allosteric modulators

Antagonists
- Homotaurine[24]
- Ginsenosides[25]
- 2-OH-saclofen
- Saclofen
- Phaclofen
- SCH-50911
- 2-Phenethylamine
- CGP-35348
- CGP-52432: 3-([(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)methyl]amino]propyl) diethoxymethyl)phosphinic acid, CAS# 139667-74-6
- CGP-55845: (2S)-3-([(1S)-1-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)ethyl]amino-2-hydroxypropyl)(phenylmethyl)phosphinic acid, CAS# 149184-22-5
- SGS-742[26][27]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads