Freshwater pearl mussel
Species of mollusc From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) is an endangered species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusc in the family Margaritiferidae.
| Freshwater pearl mussel | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The exterior of the shell of Margaritifera margaritifera | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Bivalvia |
| Order: | Unionida |
| Family: | Margaritiferidae |
| Genus: | Margaritifera |
| Species: | M. margaritifera |
| Binomial name | |
| Margaritifera margaritifera | |
 | |
| Distribution of Margaritifera margaritifera in Europe. | |
Although the name "freshwater pearl mussel" is often used for this species, other freshwater mussel species (e.g. Margaritifera auricularia) can also create pearls and some can also be used as a source of mother of pearl. Most cultured pearls today come from Hyriopsis species in Asia, or Amblema species in North America, both members of the related family Unionidae; pearls are also found within species in the genus Unio.
The interior of the shell of Margaritifera margaritifera has thick nacre (the inner mother of pearl layer of the shell). This species is capable of making fine-quality pearls, and was historically exploited in the search for pearls from wild sources. In recent times, the Russian malacologist Valeriy Zyuganov received worldwide reputation after he discovered that the pearl mussel exhibited negligible senescence and he determined that it had a maximum lifespan of 210–250 years.[3][4] The data of V. V. Zyuganov have been confirmed by Finnish malacologists[5] and gained general acceptance.[citation needed]
Subspecies
Subspecies within the species Margaritifera magaritifera include:
- Margaritifera margaritifera margaritifera (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Margaritifera margaritifera parvula (Haas, 1908)
- Margaritifera margaritifera durrovensis Phillips, 1928 – critically endangered subspecies in Ireland.[6] Synonym: Margaritifera durrovensis. This subspecies is mentioned in annexes II and V of Habitats Directive as Margaritifera durrovensis.
Description
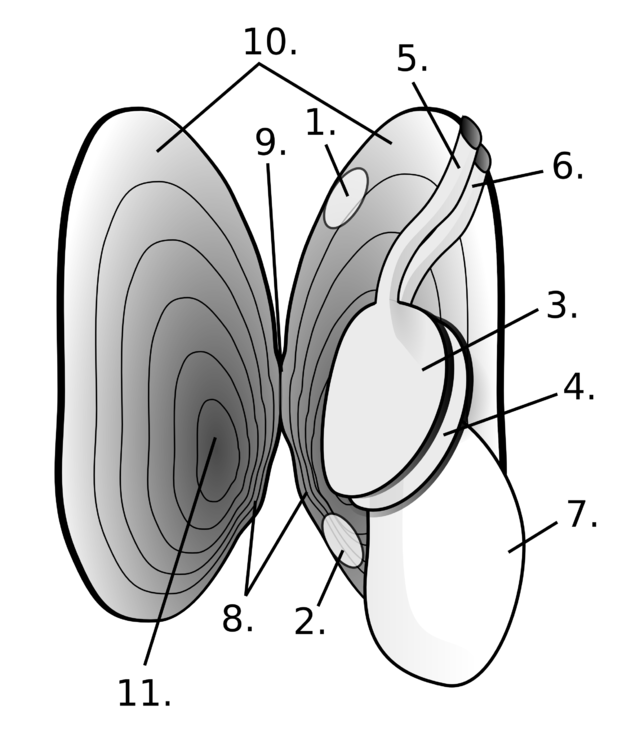
- Posterior adductor muscle
- Anterior adductor muscle
- Frontal gill
- Back gill
- Exhalant aperture
- Inhalant aperture
- Foot
- Pseudotooth
- The hingeline and ligament
- Mantle
- The shell's thickest part, the umbo
The freshwater pearl mussel is one of the longest-living invertebrates in existence.[7] The oldest known specimen in Europe was caught in 1993 in Estonia when it was 134 years old.[8]
Like all bivalve molluscs, the freshwater pearl mussel has a shell consisting of two parts that are hinged together, which can be closed to protect the animal's soft body within.[9] The shell is large, heavy and elongated,[10][11] typically yellowish-brown in colour when young and becoming darker with age.[7] Older parts of the shell often appear corroded, an identifying feature of this mussel species.[12] The inner surface of the shell is pearl white, sometimes tinged with attractive iridescent colours.[10] Like all molluscs, the freshwater pearl mussel has a muscular 'foot';[9] this very large, white foot enables the mussel to move slowly and bury itself within the bottom substrate of its freshwater habitat.[10][11]
Distribution
Summarize
Perspective

The native distribution of this species is Holarctic. The freshwater pearl mussel can be found on both sides of the Atlantic,[10] from the Arctic and temperate regions of western Russia, through Europe to northeastern North America.[7]
- North America: eastern Canada and New England in the United States' Northeast.[13][14]
- Europe, including:
- Austria – estimated total population of 70 000 individuals in Mühlviertel (declining) and in Waldviertel (some recruitment), in the states of Upper and Lower Austria, respectively.[15]
- Belgium
- Czech Republic – critically endangered (CR).[16][17] In Bohemia, probably locally extinct in Moravia.[18] Listed in Decree for implementation, No. 395/1992 Sb. (Czech code) (in Czech: Vyhláška 395/1992 Sb. ve znění vyhl. 175/2006 Sb.) as Critically Threatened species. Its conservation status in 2004-2006 was bad (U2) in a report for the European Commission in accordance with Habitats Directive.[19]
- Serbia - most commonly found along the shores of the Danube river and its lakes, as well as in some other rivers and freshwater areas in the Pannonian Basin
- Denmark - only known from Varde River (never recorded elsewhere in the country in historical or recent times).[20] Although sometimes suggested to have been extirpated in the period directly after 1970,[1] it has been documented from the river in recent years and indirect evidence suggests that the population size is significant.[20]
- Estonia
- Fennoscandia – vulnerable in Norway, endangered in Finland and Sweden.[21][22][23] Very rare in southern Finland, more common in the north. Widespread but not common in Norway; Norway is considered to host a large proportion of the European stock. Rare in Sweden.[24] Also in Kola Peninsula and Karelia (Russia) (see below).
- France[25]
- Germany – critically endangered (vom Aussterben bedroht).[26] Listed as strictly protected species in annex 1 in Bundesartenschutzverordnung.
- Great Britain. More than half the world's recruiting population exists in Scotland with populations in more than 50 rivers, mainly in the Highlands, although illegal harvesting has seriously affected their survival. 75% of sites surveyed in 2010 had suffered "significant and lasting criminal damage" and in response the police and Scottish Natural Heritage have launched a campaign to protect the species.[27][28] This species has been fully protected in the United Kingdom under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 since 1998 and partly protected according to section 9(1) since 1991.[29]
- Iberian Peninsula (Portugal and Spain)
- Ireland. The Cladagh (Swanlinbar) river contains one of the largest populations surviving in northern Ireland, estimated minimum 10,000, confined to a 6 km stretch of undisturbed river in the middle section.[30]
- Luxembourg
- Latvia
- Lithuania – extinct
- Poland – extinct[31][32]
- Russian Federation – in the rivers of the White Sea basin of the Arkhangelsk and Murmansk Regions. It is east border of the area of distribution M. margaritifera.
Habitat
Clean, fast-flowing streams and rivers are required for the freshwater pearl mussel,[7][10] where it lives buried or partly buried in fine gravel and coarse sand,[7] generally in water at depths between 0.5 and 2 metres, but sometimes at greater depths.[10] Clean gravel and sand is essential, particularly for juvenile freshwater pearl mussels, for if the stream or river bottom becomes clogged with silt, they cannot obtain oxygen and will die.[10] Also essential is the presence of a healthy population of salmonids, a group of fish including salmon and trout, on which the freshwater pearl mussel relies for part of its life cycle.[10]
Lifecycle
Summarize
Perspective

Capable of living for up to 130 years,[33] the freshwater pearl mussel begins life as a tiny larva, measuring just 0.6 to 0.7 millimetres long, which is ejected into the water from an adult mussel in a mass of one to four million other larvae. This remarkable event takes place over just one to two days, sometime between July and September.[7] The larvae, known as glochidia, resemble tiny mussels, but their minute shells are held open until they snap shut on a suitable host. The host of freshwater pearl mussel larvae are juvenile fish from the salmonid family, which includes the Atlantic salmon and sea trout.[7] The chances of a larva encountering a suitable fish are very low,[12] and thus nearly all are swept away and die; only a few are inhaled by an Atlantic salmon or sea trout, where they snap shut onto the fish's gills.[7]
Attached to the gills of a fish, the glochidia live and grow in this oxygen-rich environment until the following May or June, when they drop off. The juvenile must land on clean gravelly or sandy substrates if it is to successfully grow.[7] Attached to the substrate, juvenile freshwater pearl mussels typically burrow themselves completely into the sand or gravel, while adults are generally found with a third of their shell exposed.[7] Should they become dislodged, freshwater pearl mussels can rebury themselves, and are also capable of moving slowly across sandy sediments, using their large, muscular foot.[7]
The freshwater pearl mussel grows extremely slowly,[12] inhaling water through exposed siphons, and filtering out tiny organic particles on which it feeds.[7] It is thought that in areas where this species was once abundant, this filter feeding acted to clarify the water, benefiting other species which inhabited the rivers and streams.[7] Maturity is reached at an age of 10 to 15 years,[7] followed by a reproductive period of over 75 years in which about 200 million larvae can be produced.[12] In early summer each year, around June and July, male freshwater pearl mussels release sperm into the water, where they are inhaled by female mussels. Inside the female, the fertilized eggs develop in a pouch on the gills for several weeks, until temperature or other environmental cues trigger the female to release the larvae into the surrounding water.[7]

Threats and conservation
Summarize
Perspective
Once the most abundant bivalve mollusc in ancient rivers around the world, numbers of the freshwater pearl mussel are now declining in all countries and this species is nearly extinct in many areas.[10] The causes of this decline are not fully understood, but alteration and degradation of its freshwater habitat undoubtedly plays a central role.[10] The negative impacts humans have on rivers and streams come from a wide range of activities such as river regulation, drainage, sewage disposal, dredging, and water pollution, including the introduction of excess nutrients.[10] Anything that affects the abundance of the fish hosts will also affect the freshwater pearl mussel; for example, the introduction of exotic fish species, such as the rainbow trout, reduce the number of native fish hosts.[10] Introduced species are also directly affecting the freshwater pearl mussel; the invasion of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha), which has been spread to new locations by being transported on the bottom of boats or in ballast waters, has impacted freshwater pearl mussel populations in all countries it has invaded.[10]
The freshwater pearl mussel, which is completely protected in all European countries,[34][35] has been the focus of a significant amount of conservation efforts.[36] Measures have included the transfer of adult mussels to areas where it had gone extinct,[36][37] the culture of juvenile mussels, and the release of juvenile trout, which have been infected with glochidia, into small rivers, but mainly the freshwater pearl mussel has benefited from habitat restoration projects in some areas.[37] Due to the essential role salmonid fish play in the life of the freshwater pearl mussel, the conservation of salmon and trout is also central in the survival of this endangered freshwater mussel.[10]
Conservation efforts
The LIFE R4ever Kent project is a 5 year project worth 3.8 million pounds, led by Natural England, that began in January 2022. Its aim is saving and restore the River Kent's population of freshwater pearl mussels, as well as improving existing breeding areas to secure the long-term future of the population.[38] The River Kent's population of freshwater pearl mussels was severely damaged by pollution, degraded habitats, low genetic diversity, and the lack of natural survival of juvenile pearl mussels.[39] The project was developed in tandem with the Environmental Agency, the Freshwater Biological Association, and the South Cumbria Rivers Trust. The River Kent catchment area is the only river in the UK where the freshwater pearl mussel and the white clawed crayfish are found in the same habitat.[40] The goal is to increase the freshwater pearl mussel population by 4,000 individuals and expand its range within the River Kent Special Area of Conservation (SAC). The site's population will be bolster using donor stock from other freshwater pearl mussel sites, while also improving breeding facilities within England. Louise Lavictoire, head of science at the Freshwater Biological Association, stated that the remnant populations in the River Kent and surrounding tributaries are too small to sustain a population into the future, and maintaining a self-sustaining population would need to be supplemented with captive breeding. The goal of the hatchery improvements are to bred more than 4,000 juveniles for release; release 3,000 of the 4,000 as juveniles; and retain 1,000 for reintroduction to the SAC once they have grown to a larger size.
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.


