Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Eurasian Development Bank
Eastern European development bank From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Eurasian Development Bank (EDB) is an international multilateral financial organisation aiming to contribute to the formation and development of the market economy of the Bank's member countries, their economic growth and expansion of trade and economic ties between them through investment activities.[1] The major share of projects in the EDB's portfolio: projects with an integration effect in transport infrastructure, digital systems, green energy, agriculture, manufacturing, mechanical engineering and water and energy complex.
The Bank was founded in 2006 and is headquartered in Almaty, Kazakhstan.[2] The EDB has a branch in St. Petersburg and representative offices in Astana, Bishkek, Dushanbe, Yerevan, Minsk, and Moscow.[3]
Oljas Bektenov, Prime Minister of the Republic of Kazakhstan, has been Chairman of the EDB Council since February 6, 2024.[4]
Remove ads
History of the EDB
The Eurasian Development Bank was established at the initiative of the Presidents of Russia and Kazakhstan on January 12, 2006. The Bank officially started operating in June 2006.[3][5]
In 2009, the list of EDB member countries was expanded to include the Republic of Armenia and the Republic of Tajikistan. The Republic of Belarus and the Kyrgyz Republic joined the Bank in 2010 and 2011,[6] respectively, and the Republic of Uzbekistan became the EDB member in 2025.[7] Other states and international organizations can become members by acceding to the Agreement Establishing the Bank.[8]
In January 2013, the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development recognised the Eurasian Development Bank as a multilateral financial institution.[1]
In August 2022, the reputable Bloomberg media reported that Russia plans to reduce its stake in the Eurasian Development Bank to less than half: from 65.97% to 44.79%.[9] It is noted that Russia took this step to protect the EDB from sanctions. In January 2023, the final distribution of shares among countries was officially approved, with Russia and Kazakhstan maintaining leading positions.[10]
Remove ads
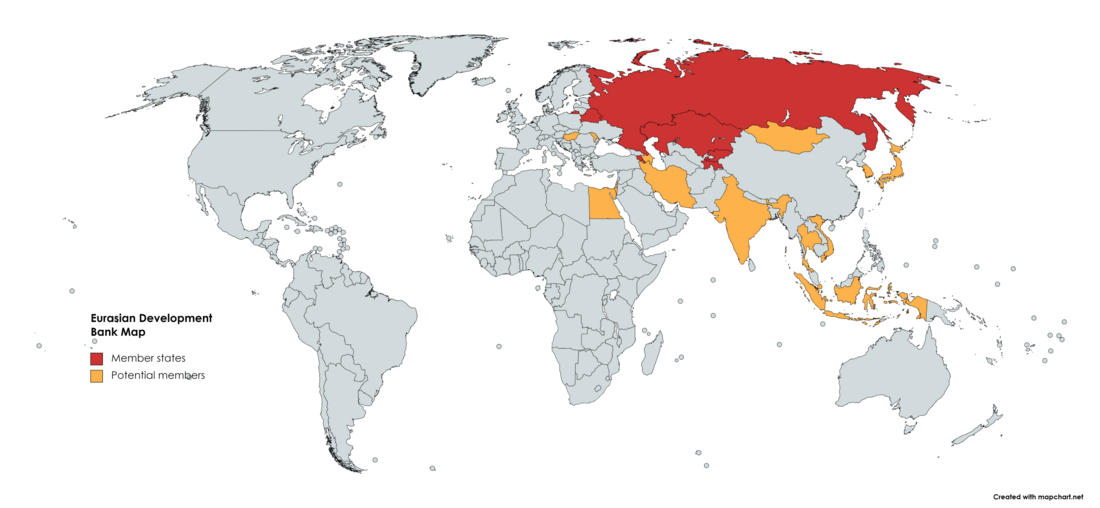
Member countries
The present membership of the Bank consists of 7 countries. Ranked on the basis of paid-up capital (as at January 2023), major shareholders include:[10]
- Russia (44.78%)
- Kazakhstan (37.28%)
- Uzbekistan (10%)
- Belarus (5.21%)
- Tajikistan (4.25%)
- Kyrgyzstan (4.22%)
- Armenia (4.22%)
Potential members
- During an interview, Dmitry Pankin, chairman of the EDB's management board, stated that there were 12 countries expressing to join, including Azerbaijan, Egypt, Israel, India, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Mongolia, Singapore, Thailand, the Republic of Korea and Vietnam.[11]
 Moldova: In November 2019, Moldova confirmed its intention to join the Eurasian Development Bank during a meeting in Moscow.[12]
Moldova: In November 2019, Moldova confirmed its intention to join the Eurasian Development Bank during a meeting in Moscow.[12] Hungary: Hungary expressed its interest to join the Eurasian Development Bank. Hungarian finance minister Mihály Varga stated that the Hungarian government is aiming for full membership by 2020.[12] As a former member of Comecon, Hungary will be the first former Warsaw Pact state to join the EDB.[13]
Hungary: Hungary expressed its interest to join the Eurasian Development Bank. Hungarian finance minister Mihály Varga stated that the Hungarian government is aiming for full membership by 2020.[12] As a former member of Comecon, Hungary will be the first former Warsaw Pact state to join the EDB.[13]
Remove ads
Mission and strategy
Summarize
Perspective
The EDB's mission is to promote market economies and economic growth in its member states and help expand trade and other economic ties between them by means of investment.[5]
The current EDB's Strategy for 2022-2026 sets out the following development objectives:[14]
- Strengthening the Bank's unique integration role in the EAEU+. The Bank's total investment will amount to US$10.9 billion;
- Implementing integration mega-projects in transport infrastructure and logistics, food security, water and energy: the Eurasian Transport Network, the Eurasian Commodity Distribution System, and the Water and Energy Complex of Central Asia;
- Developing the EDB's digital projects by focusing on support for the digital agendas of the Bank's member countries to promote their digital transformation;
- Promoting the UN Sustainable Development Goals and implementing ESG approaches in the Bank's corporate governance. Increasing financing for the Bank's green and social projects;
- Enhancing operations in the countries of the EDB's minority shareholders. Five-year strategies have been developed for each of the Bank's member countries, taking into account their economic and investment characteristics. The Bank's investment in Armenia, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan is expected to reach US$500 million by 2026.[15][16]
Activities
Summarize
Perspective
The Eurasian Development Bank's activities in Eurasia include financing investment projects that help improve living standards and develop the business and financial environment in the countries by lending to state or private enterprises, public-private partnerships (PPPs), equity participation, issuing guarantees, financing private investment funds, and providing loans to commercial banks for corporate on-lending, etc. The Bank also implements digital transformation projects in the EAEU+, provides financing to banks, companies, and enterprises, and supports investment projects in the pipeline. The EDB's portfolio mainly consists of projects in transport, green energy, manufacturing, mechanical engineering, infrastructure, and agriculture. The projects that have been implemented with the EDB's participation and financing include the following:
- Reconstruction of the Almaty Airport terminal (Kazakhstan, 2024);[17]
- Construction of the Big Almaty Ring Road (Kazakhstan, 2023);[18]
- Construction of the Turkistan Airport terminal (Kazakhstan);[19]
- Construction of the Saryarka gas pipeline (Kazakhstan);[20]
- Smart lighting system in Atyrau (Kazakhstan, 2021);[21]
- Construction of the Central Ring Road (Russia, 2021);[22]
- Construction of the Azovskaya WPP, a wind farm in Azov (Russia, 2021);[23]
- Construction of the Western High-Speed Diameter (Russia, 2021);[24]
- Complete replacement of passenger rail cars of the South Caucasus Railway, Armenia's national railway carrier (Armenia, 2021);[25]
- Construction of the Polotsk Hydropower Plant on the Western Dvina River (Belarus, 2019);[26]
- Financing the construction and operation of the Kulanak HPP in the Kyrgyz Republic;[27]
- Dairy and meat production of full production cycle in Armenia;[28]
- Financing the Kant Cement Plant to improve the environmental sustainability of cement production in the Kyrgyz Republic (2025);[29]
- Financing the reconstruction of Almaty CHPP-3 that includes conversion of the power plant from oil to gas generation (Kazakhstan);[30]
Fund for Digital Initiatives
The Eurasian Development Bank's Fund for Digital Initiatives (EDB FDI) was established on 30 June 2020. The aim of the Fund is to support digital transformation in the EDB member countries. The Fund supports and provides project financing and grants to digital projects in healthcare, trade, culture, tourism, sports, education, ecology, energy, environmental protection, data protection, transport, logistics, manufacturing, agriculture, labour market and migration, as well as financial technology and smart cities.[31]
The FDI's flagship project was the COVID-19-Free Travel mobile application that has been successfully used in 9 CIS countries.[32] The application helps its users travel safely between countries during the coronavirus pandemic. The application features allow users to receive, store and display up-to-date PCR test results and vaccination information.[33]
GovStack, an international project aimed at the digitalization of public sector infrastructure, is being implemented in the CIS countries with the financial support of the FDI. The project aims to accelerate the digital transformation of public services. The initiative is led by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in partnership with the governments of Estonia and Germany and the Digital Impact Alliance.[34]
Technical assistance
The Technical Assistance Fund is the EDB's vehicle for performing expert assessment of and providing support for projects in the pipeline to relieve potential borrowers from some of the additional burdens and speed up the drafting of project documents. The Fund's programmes aim at providing technical assistance in the following four areas: preparing investment projects, subsidizing investment projects, expanding investment activities, and providing humanitarian assistance.[35][36]
Acting in line with its technical assistance strategy, the Fund supported the project aiming to eliminate the consequences of an accident that occurred at the Bishkek CHPP (Kyrgyz Republic) on February 2, 2024. The financial support provided by the Fund made it possible to purchase the necessary equipment, including low-voltage switchgear to prevent overloads and short circuits in the grids. The total project funding approximates US$500,000 and will be provided as a non-repayable grant.[37][38]
Information and analytical activity
The Bank's own extensive research has made it a reputable think tank. The EDB is involved in major research and applied projects; the Bank prepares reports and recommendations on regional economic integration for member governments; regularly hosts conferences and round table discussions; publishes sector- and theme-specific reviews, macroeconomic papers analysing economic developments in and forecasts for the region, as well as information on regional integration, development bank activities, and investment project financing in the CIS.
Key areas of activity of the EDB's analytical team:
- The Centre for Macroeconomic Analysis (CMA) makes macroeconomic forecasts and analyses the economies of the Bank's member countries. The CMA's key product is the EDB's Macroeconomic Outlook published twice a year.
- The Centre for Integration Studies conducts research into Eurasian integration, including the analysis of non-tariff barriers, investment interaction and macroeconomic effects of cooperation.
- The Centre for Infrastructure and Industrial Research (CIIR) focuses on research in the field of industrial cooperation and substantiating cross-border infrastructure projects.
Key studies by year:
2021
- The International North-South Transport Corridor: Creating the Eurasian Transport Network;[39]
- Monitoring of Mutual Direct Investments by Twelve States (CIS Countries and Georgia);[40]
- Investment in the Water and Energy Complex of Central Asia;[41]
- Uzbekistan and the EAEU: Prospects and Potential Impact of Economic Integration;[42]
2022
- EDB Integration Business Barometer — a survey of businesses and a study of their attitude towards Eurasian integration;[43]
- North-South: Infrastructural and Institutional Barriers;[44]
- The Water and Energy Complex of Central Asia: Challenges and Prospects;[45]
- The Economy of Central Asia: A Fresh Perspective;[46]
- Monitoring of Mutual Investments (CIS countries, China, Iran, Arab states);[47]
2023
- Food Security and Agro-Industrial Potential of the Eurasian Region;[48]
- Efficient Irrigation and Water Conservation in Central Asia;[49]
- Cross-Border Public-Private Partnerships;[50]
2024
- Economic Cooperation in Eurasia: Practical Solutions — a report containing 12 flexible integration tools;[51]
- Infrastructure in Eurasia: Short-Term and Medium-Term Trends;[52]
- Petrochemical Industry in Eurasia: Opportunities for Deeper Processing;[53]
- Eurasian Transport Networkg;[54]
- Drinking Water Supply and Sanitation in Central Asia;[55]
- Capital in Multilateral Development Banks;[56]
- EDB Database of Non-Sovereign Financing by International Financial Institutions;[57]
2025
- The Irtysh River Basin: Transboundary Challenges and Practical Solutions;[58]
- Mutual Investments on the Eurasian Continent: New and Traditional Partners;[59]
- The Future of Islamic Finance in Central Asia;[60]
- The Legal Environment for Public-Private Partnerships in Eurasia. A Cross-Country Survey;[61]
- Irrigation Equipment Production in Central Asia: Industrializing the Water Sector.[62]
In addition to case studies, the EDB publishes a Macroeconomic Forecast for its member countries twice a year, as well as Macrosurveys that reflect key economic and financial trends in the region.
Mobilising finance
The EDB works actively with financial institutions to mobilise long-term resources in the capital markets, which are the main source of funding for the Bank's investment activities.[63]
The sources of market financing include:
- Eurobonds issued under the EMTN programme;
- bonds issued in local markets;
- securities issued under the ECP programme;
- bilateral bank loans.
In April 2025, the EDB successfully placed its first bond issue denominated in UAE Dirham in Kazakhstan, and in July 2025, it placed a bond issue in Dirham in Abu-Dhabi.[64]
International cooperation
The EDB cooperates with other international organisations, national and international development institutions, academic and civil society organisations, associations and unions to support the Bank's activities in the member states and beyond.
The Bank has held observer statuses at:
- UN General Assembly (since 2007);[65]
- Eurasian Group on Combating Money Laundering and Financing of Terrorism (EAG) (since 2008);[66]
- UNCTAD Trade and Development Board;
- International Investment Bank (since 2014);
- UNFCCC (Framework Convention on Climate Change).[67]
The EDB is a member of:
- Kazakhstan Stock Exchange (KASE);[68]
- Multilateral Financial Institutions’ Permanent Working Group on Environment and Social Standards;[69]
- World Economic Forum (WEF);[70]
- International Capital Market Association (ICMA);
- International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA);[71]
- Expert Group for PPP Mechanism Development within the EAEU at the EEC Board's Advisory Committee for Entrepreneurship;
- Global Infrastructure Facility (GIF) Advisory Council;
- Global Infrastructure Connectivity (GICA);[72]
- Astana International Exchange (AIX);
- In 2023, the Bank became a supporting institution of UNEP FI;[73]
- Association of Development Financing Institutions of Asia and the Pacific (ADFIAP);
- Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI);[74]
- Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB).[75]
Ratings
- In 2019, the ACRA rating agency assessed the Bank's rating at AAA(RU) with a stable outlook on the national scale and at A- on the international scale. Both ratings are annually reaffirmed without changes (2020-2025).[76]
- In 2023, China Chengxin International (China Chengxin Internedit Rating Co., CCXI) assessed the Bank's rating at AAA on the national scale. In 2024, this rating was reaffirmed, and the Bank was also assigned the A- rating on the global scale.[77]
Remove ads
Financial performance
The Bank's charter capital totals US$7 billion, including US$1.5 billion of paid-in capital and US$5.5 billion of callable capital. By 2025, the EDB’s cumulative portfolio comprised 305 projects with a total investment of US $16.5 billion in all member countries (starting from the beginning of the Bank's operations). 80 projects are currently being financed.[78][79][80]
Environmental and social responsibility
Summarize
Perspective
In 2012, the Bank's Management Board approved an Environmental and Social Responsibility Framework aimed at reducing the negative environmental impacts of EDB-funded projects. The Bank's investment projects include those focusing on environmental protection, social and economic development, and the efficient use of natural resources.[81] Also in 2012, the Bank joined the Multilateral Financial Institutions’ Working Group on Environment.[69]
In 2019, the EDB's management stated that the Bank would focus on environmental projects, primarily in the field of electric power and renewable energy sources.[82]
In 2020, the Bank became a shareholder of the AIFC Green Finance Centre established to develop and promote green finance in Kazakhstan and Central Asia. The Centre assists potential issuers, investors and market players in preparing for the issuance of green bonds on the AIFC Exchange.[83]
Over the period from 2017 to 2020, the EDB financed renewable energy projects worth more than $540 million with a total installed capacity of approximately 500 MW. In 2020, the Bank's 2020–2024 Renewable Energy Programme was approved. By the end of 2024, the accumulated portfolio of EDB's green projects comprised $1.6 billion. $675 million have been invested in renewable energy construction since 2015.[84]
In 2021, the EDB financed the construction of the Azovskaya WPP, the first wind farm in Russia's Unified Energy System to implement remote control technology for both active and reactive power of generating equipment.[85]
In 2021, the EDB published its Green and Social Debt Instruments Framework.[86]
In September 2021, the Bank issued green bonds on the Kazakhstan Stock Exchange (KASE). ACRA, as an accredited verifier, confirmed the issue's compliance with the ICMA green bond principles and included it in its register.[87] This was followed by the issuance in November of social bonds for projects implemented in Kazakhstan.[81]
In December 2021, the EDB and the Global Energy Association published a report entitled Green Technologies for Eurasia's Sustainable Future aimed at helping to reduce the carbon footprint in Eurasia.[88]
Currently, the accumulated portfolio of EDB's green projects exceeds US$1.7 billion (+150% compared to 2018). 96% of green projects are related to climate finance.[89]
EDB's projects contribute to the reduction and prevention of more than 200,000 tonnes of CO2 per year, as well as to improving water and energy security.
The Bank is also involved in the development of transport corridors across Eurasia. The relevant projects are expected to halve transport-related CO2 emissions on the China–EAEU–EU axis. The EDB is working on a development scheme for Central Asia's water and energy complex. Realising the region's hydro potential will reduce CO2 emissions by 5 million tonnes per year while improvements in irrigation will help minimise climate-related risks for Central Asian countries. The Bank's 2022–2026 strategy prioritises environmental and resource efficiency. Each project is internally reviewed for its carbon footprint.[90]
Remove ads
Management
The Bank’s management structure is made up of the Bank’s Council, the Management Board, and the Chairman of the Management Board.
The Bank’s Council is its supreme management body in charge of the general management of the Bank's operations. Each of the Bank's member countries appoints an authorised representative and his or her deputy to the Council; they become Council members.
The Bank’s Management Board is a permanent collective executive body governed by the Bank’s Council.
The Chairman of the EDB Management Board is Nikolai Podguzov.[91]
The Chairman of the EDB Council is Oljas Bektenov, Prime Minister of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads