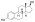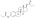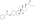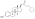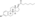Estradiol stearate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
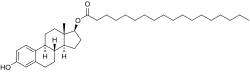
Estradiol stearate (E2-17-St), also known as estradiol octadecanoate and sold under the brand name Depofollan, is a naturally occurring estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the C17β stearate ester of estradiol.[1][2][3][4][5] It occurs in the body as a very long-lasting metabolite and prohormone of estradiol.[5] The compound is one of the components that collectively constitute lipoidal estradiol, another of which is estradiol palmitate.[6][5] It is extremely lipophilic and hydrophobic.[5] Estradiol stearate has no affinity for the estrogen receptor, requiring transformation into estradiol via esterases for its estrogenic activity.[7][8][9][5] The compound does not bind to sex hormone-binding globulin or α-fetoprotein, instead being transported by lipoproteins such as high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Depofollan |
| Other names | E2-17-St; Estradiol octadecanoate; Estradiol 17β-stearate; Estradiol 17β-octadecanoate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C36H58O3 |
| Molar mass | 538.857 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Estradiol stearate has a prolonged duration of action relative to estradiol regardless of whether it is given by intravenous injection or subcutaneous injection.[7] This is in contrast to short-chain fatty acid esters of estradiol, such as estradiol benzoate, which do not show a prolonged duration with intravenous injection.[10] When administered by intravenous injection in rodents, estradiol stearate has a greatly increased terminal half-life relative to estradiol (6 hours vs. 2 minutes).[7] Estradiol stearate also had a half-life that was 60% longer than that of estradiol arachidonate, despite similar ester chain lengths.[7] In contrast to the long-chain esters, the half-lives of short-chain estradiol esters such as estradiol acetate and estradiol hexanoate were the same as that of estradiol.[7] As such, whereas short-chain estradiol esters are rapidly hydrolyzed, long-chain estradiol esters like estradiol stearate are resistant to metabolism.[7] Thus, the prolongation of effect of short-chain estradiol esters is purely due to their increased lipophilicity and slow release from the injected depot, whereas the prolonged duration of long-chain estradiol esters is due both to this property and to their resistance to metabolism.[7] Estradiol stearate is susceptible to first-pass metabolism in the liver, and hence has much greater potency by subcutaneous injection than by oral administration.[7]
In addition to its endogenous role, estradiol stearate was previously available as a pharmaceutical drug for use via depot intramuscular injection.[1][2] The medication was introduced between 1938 and 1941 under the brand name Depofollan.[11][12] It has been used to treat prostate cancer.[13][14] Estradiol stearate is a long-acting estrogen[15][12] and is said to have been the first long-acting estrogen used in medicine, although it was never widely employed.[12] It was reported to have a duration of more than one month.[12] The medication was provided as an oil solution in ampoules containing 15 mg estradiol stearate.[15][14] It was manufactured by Chinoin, a Hungarian pharmaceutical company.[15][14][11][16] The compound was studied by Karl Miescher in 1938[17] and was patented by Miescher and Chinoin in 1939 and 1941, respectively.[18][19] A similar clinically used long-acting estradiol ester is estradiol undecylate, which has 11 carbon atoms instead of the 18 carbon atoms in estradiol stearate.[1][2]
| Estrogen | Other names | RBA (%)a | REP (%)b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ERα | ERβ | ||||
| Estradiol | E2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Estradiol 3-sulfate | E2S; E2-3S | ? | 0.02 | 0.04 | ||
| Estradiol 3-glucuronide | E2-3G | ? | 0.02 | 0.09 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-glucuronide | E2-17G | ? | 0.002 | 0.0002 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | EB; Estradiol 3-benzoate | 10 | 1.1 | 0.52 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-acetate | E2-17A | 31–45 | 24 | ? | ||
| Estradiol diacetate | EDA; Estradiol 3,17β-diacetate | ? | 0.79 | ? | ||
| Estradiol propionate | EP; Estradiol 17β-propionate | 19–26 | 2.6 | ? | ||
| Estradiol valerate | EV; Estradiol 17β-valerate | 2–11 | 0.04–21 | ? | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | EC; Estradiol 17β-cypionate | ?c | 4.0 | ? | ||
| Estradiol palmitate | Estradiol 17β-palmitate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estradiol stearate | Estradiol 17β-stearate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estrone | E1; 17-Ketoestradiol | 11 | 5.3–38 | 14 | ||
| Estrone sulfate | E1S; Estrone 3-sulfate | 2 | 0.004 | 0.002 | ||
| Estrone glucuronide | E1G; Estrone 3-glucuronide | ? | <0.001 | 0.0006 | ||
| Ethinylestradiol | EE; 17α-Ethynylestradiol | 100 | 17–150 | 129 | ||
| Mestranol | EE 3-methyl ether | 1 | 1.3–8.2 | 0.16 | ||
| Quinestrol | EE 3-cyclopentyl ether | ? | 0.37 | ? | ||
| Footnotes: a = Relative binding affinities (RBAs) were determined via in-vitro displacement of labeled estradiol from estrogen receptors (ERs) generally of rodent uterine cytosol. Estrogen esters are variably hydrolyzed into estrogens in these systems (shorter ester chain length -> greater rate of hydrolysis) and the ER RBAs of the esters decrease strongly when hydrolysis is prevented. b = Relative estrogenic potencies (REPs) were calculated from half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) that were determined via in-vitro β‐galactosidase (β-gal) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) production assays in yeast expressing human ERα and human ERβ. Both mammalian cells and yeast have the capacity to hydrolyze estrogen esters. c = The affinities of estradiol cypionate for the ERs are similar to those of estradiol valerate and estradiol benzoate (figure). Sources: See template page. | ||||||
| Estrogen | Structure | Ester(s) | Relative mol. weight | Relative E2 contentb | log Pc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position(s) | Moiet(ies) | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Estradiol | – | – | – | – | 1.00 | 1.00 | 4.0 | ||
| Estradiol acetate | C3 | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.15 | 0.87 | 4.2 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | C3 | Benzoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~4–5) | 1.38 | 0.72 | 4.7 | ||
| Estradiol dipropionate | C3, C17β | Propanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 (×2) | 1.41 | 0.71 | 4.9 | ||
| Estradiol valerate | C17β | Pentanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 5 | 1.31 | 0.76 | 5.6–6.3 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate butyrate | C3, C17β | Benzoic acid, butyric acid | Mixed fatty acid | – (~6, 2) | 1.64 | 0.61 | 6.3 | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | C17β | Cyclopentylpropanoic acid | Cyclic fatty acid | – (~6) | 1.46 | 0.69 | 6.9 | ||
| Estradiol enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | 6.7–7.3 | ||
| Estradiol dienanthate | C3, C17β | Heptanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 (×2) | 1.82 | 0.55 | 8.1–10.4 | ||
| Estradiol undecylate | C17β | Undecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.62 | 0.62 | 9.2–9.8 | ||
| Estradiol stearate | C17β | Octadecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 | 1.98 | 0.51 | 12.2–12.4 | ||
| Estradiol distearate | C3, C17β | Octadecanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 (×2) | 2.96 | 0.34 | 20.2 | ||
| Estradiol sulfate | C3 | Sulfuric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.29 | 0.77 | 0.3–3.8 | ||
| Estradiol glucuronide | C17β | Glucuronic acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.65 | 0.61 | 2.1–2.7 | ||
| Estramustine phosphated | C3, C17β | Normustine, phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.91 | 0.52 | 2.9–5.0 | ||
| Polyestradiol phosphatee | C3–C17β | Phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.23f | 0.81f | 2.9g | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic or cyclic fatty acids. b = Relative estradiol content by weight (i.e., relative estrogenic exposure). c = Experimental or predicted octanol/water partition coefficient (i.e., lipophilicity/hydrophobicity). Retrieved from PubChem, ChemSpider, and DrugBank. d = Also known as estradiol normustine phosphate. e = Polymer of estradiol phosphate (~13 repeat units). f = Relative molecular weight or estradiol content per repeat unit. g = log P of repeat unit (i.e., estradiol phosphate). Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.