Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Ergoloid mesylates (USAN), co-dergocrine mesilate (BAN) or dihydroergotoxine mesylate, trade name Hydergine, is a mixture of the methanesulfonate salts of three dihydrogenated ergot alkaloids (dihydroergocristine, dihydroergocornine, and alpha- and beta-dihydroergocryptine).
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Dihydroergocristine | Ergot alkaloid |
| Dihydroergocornine | Ergot alkaloid |
| alpha-Dihydroergocryptine | Ergot alkaloid |
| beta-Dihydroergocryptine | Ergot alkaloid |
| Clinical data | |
| Other names | Co-dergocrine, dihydroergotoxine |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, parenteral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25% |
| Protein binding | 98–99% |
| Metabolism | 50% |
| Elimination half-life | 3.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.718 |
| | |
It was developed by Albert Hofmann (the discoverer of LSD) for Sandoz (now part of Novartis).
It has been used to treat dementia and age-related cognitive impairment (such as in Alzheimer disease),[1] as well as to aid in recovery after stroke.
A systematic review published in 1994 found little evidence to support the use of ergoloid mesylates, concluding only that potentially effective doses may be higher than those currently approved in dementia treatment.[2]
Ergoloid Mesylate Tablets USP for sublingual use contain 1 mg of Ergoloid Mesylates USP, a mixture of the methanesulfonate salt of the following hydrogenated alkaloids: Dihydroergocornine mesylate 0.333 mg, Dihydroergocristine mesylate 0.333 mg, Dihydroergocryptine mesylate 0.333 mg.[3]
It has been used to treat hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels).[4]
The use of ergoloid alkaloids for dementia has been surrounded with uncertainties. In 2000, a systematic Cochrane review concluded that hydergine was well tolerated and showed significant treatment effects when assessed by either global ratings or comprehensive rating scales. The small number of available trials for analysis, however, limited the ability to demonstrate statistically significant moderating effects in certain subgroups (e.g. younger age, higher dosage, Alzheimer disease).[5]
Ergoloid is contraindicated in individuals who have previously shown hypersensitivity to the drug. They are also contraindicated in patients who have psychosis, acute or chronic, regardless of etiology.[6] Specific drug interactions are unknown but it has been claimed that there are multiple potential interactions.[6]
Adverse effects are minimal. The most common include transient, dose dependent nausea and gastrointestinal disturbances,[7] and sublingual irritation with SL tablets. Other common side effects include:[6][8]
As a result of the last-mentioned effects, the use of ergoline derivatives for the treatment of blood circulation disorders, memory problems, sensation problems and the treatment of migraine is no longer permitted in some EU countries because the risks are believed to outweigh any benefits.[9] However, this concern may be unnecessarily suppressing the use of ergoline medications.[11]
Despite the fact that this drug has been used in the treatment of dementia for many years, its mechanism of action is still not clear.[7] It stimulates dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors and blocks alpha-adrenoreceptors.[12] Current studies imply that the major effect of hydergine may be the modulation of synaptic neurotransmission rather than solely increasing blood flow as was once thought.[13] A prominent feature that accompanies aging is an increase in monoamine oxidase (MAO) levels.[14] This results in decreased availability of catecholamines in the synaptic cleft. In one study, an interaction between age and hydergine treatment was observed in the hypothalamus, hippocampus and cerebellum. The hydergine effect was more pronounced in the aged group in the hypothalamus and cerebellum, and more pronounced in the adult in the hippocampus. These findings imply that increased brain MAO activity in aging can be modified by hydergine treatment in some brain regions.
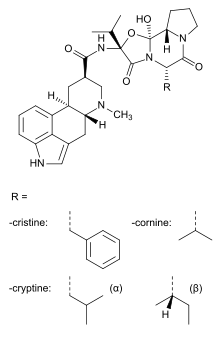
The four constituents differ only in which of four proteinogenic amino acids is used in biosynthesis:[15]
| Compound | Amino acid |
|---|---|
| Dihydroergocristine | Phenylalanine |
| Dihydroergocornine | Valine |
| alpha-Dihydroergocryptine | Leucine |
| beta-Dihydroergocryptine | Isoleucine |
Brand names include Hydergine, Hydergina, Gerimal, Niloric, Redizork, Alkergot, Cicanol, Redergin, and Hydrine.
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.