Diacetyl peroxide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
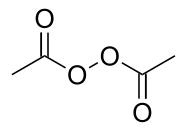
Diacetyl peroxide is the organic peroxide with the formula (CH3CO2)2. It is a white solid or oily liquid with a sharp odor.[4] As with a number of organic peroxides, it is explosive.[5] It is often used as a solution, e.g., in dimethyl phthalate.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetic peroxyanhydride[1] | |
| Other names
acetyl peroxide (2:1); diacetyl peroxide; Peroxide, diacetyl; ethanoyl peroxide; acetyl ethaneperoxoate; ethanoyl ethane peroxoate; peracetic acid acetyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.409 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2084 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 118.088 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals[2] |
| Density | 1.163 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) |
| Boiling point | 121.4 °C (250.5 °F; 394.5 K) at 760 mmHg; 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) at 21 mmHg[3] |
| slight in cold water [2] | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Explosive, oxidizer |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 32.2 °C (90.0 °F; 305.3 K) (45 °C [113 °F; 318 K][4]) |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | Very high / moderate when wet |
| Friction sensitivity | Very high / moderate when wet |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
History
Diacetyl peroxide was discovered in 1858 by Benjamin Collins Brodie,[6] who obtained the compound by treating glacial acetic acid with barium peroxide in anhydrous diethyl ether.[7]
Preparation
Diacetyl peroxide forms upon combining hydrogen peroxide and excess acetic anhydride. Peracetic acid is an intermediate.[8]
Safety
Consisting of both an oxidizer, the O-O bond and reducing agents, the C-C and C-H bonds, diacetyl peroxide is shock sensitive and explosive.[8][9][2]
The threshold quantity for Process Safety Management per Occupational Safety and Health Administration 1910.119 is 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) if the concentration of the diacetyl peroxide solution is greater than 70%.[10]
There have been reports of detonation of the pure material. The 25% solution also has explosive potential.[11] The crystalline peroxide is especially shock sensitive and a high explosion risk.[12][9]
Organic peroxides are all prone to exothermic decomposition, potentially leading to explosions and fire.[13]
Contact with liquid causes irritation of the exposed area. If ingested, it irritates the mouth and stomach.[14][15][16][17]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

