Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Kinetic isotope effect
Change in chemical reaction rate due to isotopic substitution From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Remove ads
In physical organic chemistry, a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is the change in the reaction rate of a chemical reaction when one of the atoms in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes.[3] Formally, it is the ratio of rate constants for the reactions involving the light (kL) and the heavy (kH) isotopically substituted reactants (isotopologues): KIE = kL/kH.
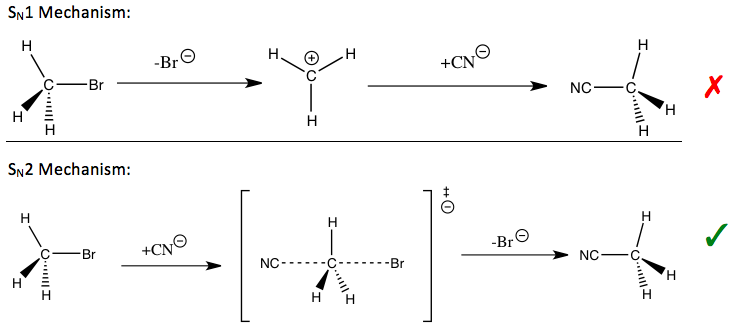
An example of KIE. In the reaction of methyl bromide with cyanide, the KIE of the carbon in the methyl group was found to be 1.082 ± 0.008.[1][2]
This change in reaction rate is a quantum effect that occurs mainly because heavier isotopologues have lower vibrational frequencies than their lighter counterparts. In most cases, this implies a greater energy input needed for heavier isotopologues to reach the transition state (or, in rare cases, dissociation limit), and therefore, a slower reaction rate. The study of KIEs can help elucidate reaction mechanisms, and is occasionally exploited in drug development to improve unfavorable pharmacokinetics by protecting metabolically vulnerable C-H bonds.
Remove ads
Background
Summarize
Perspective
KIE is considered one of the most essential and sensitive tools for studying reaction mechanisms, the knowledge of which allows improvement of the desirable qualities of said reactions. For example, KIEs can be used to reveal whether a nucleophilic substitution reaction follows a unimolecular (SN1) or bimolecular (SN2) pathway.
In the reaction of methyl bromide and cyanide (shown in the introduction), the observed methyl carbon KIE is 1.082, a small effect which indicates an SN2 mechanism in which the C-Br bond is formed as the C-CN bond is broken. For SN1 reactions in which the leaving group leaves first to form a trivalent carbon transition state, the KIE is close to the maximum observed value for a secondary KIE (SKIE, see below) of 1.22.[1] Depending on the pathway, different strategies may be used to stabilize the transition state of the rate-determining step of the reaction and improve the reaction rate and selectivity, which are important for industrial applications.
Isotopic rate changes are most pronounced when the relative mass change is greatest, since the effect is related to vibrational frequencies of the affected bonds. Thus, replacing normal hydrogen (1H) with its isotope deuterium (D or 2H), doubles the mass; whereas in replacing carbon-12 with carbon-13, the mass increases by only 8%. The rate of a reaction involving a C–1H bond is typically 6–10x faster than with a C–2H bond, whereas a 12C reaction is only 4% faster than the corresponding 13C reaction;[4]: 445 even though, in both cases, the isotope is one atomic mass unit (amu) (dalton) heavier.
Isotopic substitution can modify the reaction rate in a variety of ways. In many cases, the rate difference can be rationalized by noting that the mass of an atom affects the vibrational frequency of the chemical bond that it forms, even if the potential energy surface for the reaction is nearly identical. Heavier isotopes will (classically) lead to lower vibration frequencies, or, viewed quantum mechanically, have lower zero-point energy (ZPE). With a lower ZPE, more energy must be supplied to break the bond, resulting in a higher activation energy for bond cleavage, which in turn lowers the measured rate (see, for example, the Arrhenius equation).[3][4]: 427
Remove ads
Classification
Summarize
Perspective
Primary kinetic isotope effects
A primary kinetic isotope effect (PKIE) may be found when a bond to the isotopically labeled atom is being formed or broken.[3][4]: 427 Depending on the way a KIE is probed (parallel measurement of rates vs. intermolecular competition vs. intramolecular competition), the observation of a PKIE is indicative of breaking/forming a bond to the isotope at the rate-limiting step, or subsequent product-determining step(s). (The misconception that a PKIE must reflect bond cleavage/formation to the isotope at the rate-limiting step is often repeated in textbooks and the primary literature: see the section on experiments below.)[5]
For the aforementioned nucleophilic substitution reactions, PKIEs have been investigated for both the leaving groups, the nucleophiles, and the α-carbon at which the substitution occurs. Interpretation of the leaving group KIEs was difficult at first due to significant contributions from temperature independent factors. KIEs at the α-carbon can be used to develop some understanding into the symmetry of the transition state in SN2 reactions, though this KIE is less sensitive than what would be ideal, also due to contribution from non-vibrational factors.[1]
Secondary kinetic isotope effects
A secondary kinetic isotope effect (SKIE) is observed when no bond to the isotopically labeled atom in the reactant is broken or formed.[3][4]: 427 SKIEs tend to be much smaller than PKIEs; however, secondary deuterium isotope effects can be as large as 1.4 per 2H atom, and techniques have been developed to measure heavy-element isotope effects to very high precision, so SKIEs are still very useful for elucidating reaction mechanisms.
For the aforementioned nucleophilic substitution reactions, secondary hydrogen KIEs at the α-carbon provide a direct means to distinguish between SN1 and SN2 reactions. It has been found that SN1 reactions typically lead to large SKIEs, approaching to their theoretical maximum at about 1.22, while SN2 reactions typically yield SKIEs that are very close to or less than 1. KIEs greater than 1 are called normal kinetic isotope effects, while KIEs less than 1 are called inverse kinetic isotope effects (IKIE). In general, smaller force constants in the transition state are expected to yield a normal KIE, and larger force constants in the transition state are expected to yield an IKIE when stretching vibrational contributions dominate the KIE.[1]
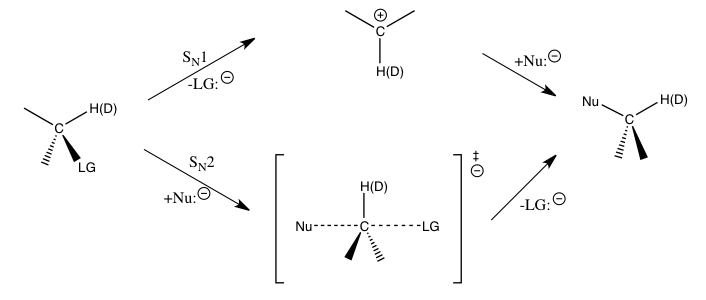
The magnitudes of such SKIEs at the α-carbon atom are largely determined by the Cα-H(2H) vibrations. For an SN1 reaction, since the carbon atom is converted into an sp2 hybridized carbenium ion during the transition state for the rate-determining step with an increase in Cα-H(2H) bond order, an IKIE would be expected if only the stretching vibrations were important. The observed large normal KIEs are found to be caused by significant out-of-plane bending vibrational contributions when going from the reactants to the transition state of carbenium ion formation. For SN2 reactions, bending vibrations still play an important role for the KIE, but stretching vibrational contributions are of more comparable magnitude, and the resulting KIE may be normal or inverse depending on the specific contributions of the respective vibrations.[1][6][7]
Remove ads
Theory
Summarize
Perspective
Theoretical treatment of isotope effects relies heavily on transition state theory, which assumes a single potential energy surface for the reaction, and a barrier between the reactants and the products on this surface, on top of which resides the transition state.[8][9] The KIE arises largely from the changes to vibrational ground states produced by the isotopic perturbation along the minimum energy pathway of the potential energy surface, which may only be accounted for with quantum mechanical treatments of the system. Depending on the mass of the atom that moves along the reaction coordinate and nature (width and height) of the energy barrier, quantum tunneling may also make a large contribution to an observed KIE and may need to be separately considered, in addition to the "semi-classical" transition state theory model.[8]
The deuterium kinetic isotope effect (2H KIE) is by far the most common, useful, and well-understood type of KIE. The accurate prediction of the numerical value of a 2H KIE using density functional theory calculations is now fairly routine. Moreover, several qualitative and semi-quantitative models allow rough estimates of deuterium isotope effects to be made without calculations, often providing enough information to rationalize experimental data or even support or refute different mechanistic possibilities. Starting materials containing 2H are often commercially available, making the synthesis of isotopically enriched starting materials relatively straightforward. Also, due to the large relative difference in the mass of 2H and 1H and the attendant differences in vibrational frequency, the isotope effect is larger than for any other pair of isotopes except 1H and 3H,[10] allowing both primary and secondary isotope effects to be easily measured and interpreted. In contrast, secondary effects are generally very small for heavier elements and close in magnitude to the experimental uncertainty, which complicates their interpretation and limits their utility. In the context of isotope effects, hydrogen often means the light isotope, protium (1H), specifically. In the rest of this article, reference to hydrogen and deuterium in parallel grammatical constructions or direct comparisons between them should be taken to mean 1H and 2H.[a]
The theory of KIEs was first formulated by Jacob Bigeleisen in 1949.[11][4]: 427 Bigeleisen's general formula for 2H KIEs (which is also applicable to heavier elements) is given below. It employs transition state theory and a statistical mechanical treatment of translational, rotational, and vibrational levels for the calculation of rate constants kH and kD. However, this formula is "semi-classical" in that it neglects the contribution from quantum tunneling, which is often introduced as a separate correction factor. Bigeleisen's formula also does not deal with differences in non-bonded repulsive interactions caused by the slightly shorter C–2H bond compared to a C–H bond. In the equation, subscript H or D refer to the species with 1H or 2H, respectively; quantities with or without the double-dagger, ‡, refer to transition state or reactant ground state, respectively.[7][12] (Strictly speaking, a term resulting from an isotopic difference in transmission coefficients should also be included.[13])
- ,
where we define
- and .
Here, h = Planck constant; kB = Boltzmann constant; = frequency of vibration, expressed in wavenumber; c = speed of light; NA = Avogadro constant; and R = universal gas constant. The σX (X = H or D) are the symmetry numbers for the reactants and transition states. The MX are the molecular masses of the corresponding species, and the IqX (q = x, y, or z) terms are the moments of inertia about the three principal axes. The uiX are directly proportional to the corresponding vibrational frequencies, νi, and the vibrational zero-point energy (ZPE) (see below). The integers N and N‡ are the number of atoms in the reactants and the transition states, respectively.[7] The complicated expression given above can be represented as the product of four separate factors:[7]
- .
For the special case of 2H isotope effects, we will argue that the first three terms can be treated as equal to or well approximated by unity. The first factor S (containing σX) is the ratio of the symmetry numbers for the various species. This will be a rational number (a ratio of integers) that depends on the number of molecular and bond rotations leading to the permutation of identical atoms or groups in the reactants and the transition state.[12] For systems of low symmetry, all σX (reactant and transition state) will be unity; thus S can often be neglected. The MMI factor (containing the MX and IqX) refers to the ratio of the molecular masses and the moments of inertia. Since hydrogen and deuterium tend to be much lighter than most reactants and transition states, there is little difference in the molecular masses and moments of inertia between H and D containing molecules, so the MMI factor is usually also approximated as unity. The EXC factor (containing the product of vibrational partition functions) corrects for the KIE caused by the reactions of vibrationally excited molecules. The fraction of molecules with enough energy to have excited state A–H/D bond vibrations is generally small for reactions at or near room temperature (bonds to hydrogen usually vibrate at 1000 cm−1 or higher, so exp(-ui) = exp(-hνi/kBT) < 0.01 at 298 K, resulting in negligible contributions from the 1–exp(-ui) factors). Hence, for hydrogen/deuterium KIEs, the observed values are typically dominated by the last factor, ZPE (an exponential function of vibrational ZPE differences), consisting of contributions from the ZPE differences for each of the vibrational modes of the reactants and transition state, which can be represented as follows:[7]
- ,
where we define
- and .
The sums in the exponent of the second expression can be interpreted as running over all vibrational modes of the reactant ground state and the transition state. Or, one may interpret them as running over those modes unique to the reactant or the transition state or whose vibrational frequencies change substantially upon advancing along the reaction coordinate. The remaining pairs of reactant and transition state vibrational modes have very similar and , and cancellations occur when the sums in the exponent are calculated. Thus, in practice, 2H KIEs are often largely dependent on a handful of key vibrational modes because of this cancellation, making qualitative analyses of kH/kD possible.[12]
As mentioned, especially for 1H/2H substitution, most KIEs arise from the difference in ZPE between the reactants and the transition state of the isotopologues; this difference can be understood qualitatively as follows: in the Born–Oppenheimer approximation, the potential energy surface is the same for both isotopic species. However, a quantum treatment of the energy introduces discrete vibrational levels onto this curve, and the lowest possible energy state of a molecule corresponds to the lowest vibrational energy level, which is slightly higher in energy than the minimum of the potential energy curve. This difference, known as the ZPE, is a manifestation of the uncertainty principle that necessitates an uncertainty in the C-H or C-D bond length. Since the heavier (in this case the deuterated) species behaves more "classically", its vibrational energy levels are closer to the classical potential energy curve, and it has a lower ZPE. The ZPE differences between the two isotopic species, at least in most cases, diminish in the transition state, since the bond force constant decreases during bond breaking. Hence, the lower ZPE of the deuterated species translates into a larger activation energy for its reaction, as shown in the following figure, leading to a normal KIE.[14] This effect should, in principle, be taken into account all 3N−6 vibrational modes for the starting material and 3N‡−7 vibrational modes at the transition state (one mode, the one corresponding to the reaction coordinate, is missing at the transition state, since a bond breaks and there is no restorative force against the motion). The harmonic oscillator is a good approximation for a vibrating bond, at least for low-energy vibrational states. Quantum mechanics gives the vibrational ZPE as . Thus, we can readily interpret the factor of 1/2 and the sums of terms over ground state and transition state vibrational modes in the exponent of the simplified formula above. For a harmonic oscillator, vibrational frequency is inversely proportional to the square root of the reduced mass of the vibrating system:
- ,
where kf is the force constant. Moreover, the reduced mass is approximated by the mass of the light atom of the system, X = H or D. Because mD ≈ 2mH,
- .
In the case of homolytic C–H/D bond dissociation, the transition state term disappears; and neglecting other vibrational modes, kH/kD = exp(1/2Δui). Thus, a larger isotope effect is observed for a stiffer ("stronger") C–H/D bond. For most reactions of interest, a hydrogen atom is transferred between two atoms, with a transition-state [A···H···B]‡ and vibrational modes at the transition state need to be accounted for. Nevertheless, it is still generally true that cleavage of a bond with a higher vibrational frequency will give a larger isotope effect.

To calculate the maximum possible value for a non-tunneling 2H KIE, we consider the case where the ZPE difference between the stretching vibrations of a C-1H bond (3000 cm−1) and C-2H bond (2200 cm−1) disappears in the transition state (an energy difference of [3000 – 2200 cm−1]/2 = 400 cm−1 ≈ 1.15 kcal/mol), without any compensation from a ZPE difference at the transition state (e.g., from the symmetric A···H···B stretch, which is unique to the transition state). The simplified formula above, predicts a maximum for kH/kD as 6.9. If the complete disappearance of two bending vibrations is also included, kH/kD values as large as 15-20 can be predicted. Bending frequencies are very unlikely to vanish in the transition state, however, and there are only a few cases in which kH/kD values exceed 7-8 near room temperature. Furthermore, it is often found that tunneling is a major factor when they do exceed such values. A value of kH/kD ~ 10 is thought to be maximal for a semi-classical PKIE (no tunneling) for reactions at ≈298 K. (The formula for kH/kD has a temperature dependence, so larger isotope effects are possible at lower temperatures.)[15] Depending on the nature of the transition state of H-transfer (symmetric vs. "early" or "late" and linear vs. bent); the extent to which a primary 2H isotope effect approaches this maximum, varies. A model developed by Westheimer predicted that symmetrical (thermoneutral, by Hammond's postulate), linear transition states have the largest isotope effects, while transition states that are "early" or "late" (for exothermic or endothermic reactions, respectively), or nonlinear (e.g. cyclic) exhibit smaller effects. These predictions have since received extensive experimental support.[16]
For secondary 2H isotope effects, Streitwieser proposed that weakening (or strengthening, in the case of an inverse isotope effect) of bending modes from the reactant ground state to the transition state are largely responsible for observed isotope effects. These changes are attributed to a change in steric environment when the carbon bound to the H/D undergoes rehybridization from sp3 to sp2 or vice versa (an α SKIE), or bond weakening due to hyperconjugation in cases where a carbocation is being generated one carbon atom away (a β SKIE). These isotope effects have a theoretical maximum of kH/kD = 20.5 ≈ 1.4. For a SKIE at the α position, rehybridization from sp3 to sp2 produces a normal isotope effect, while rehybridization from sp2 to sp3 results in an inverse isotope effect with a theoretical minimum of kH/kD = 2-0.5 ≈ 0.7. In practice, kH/kD ~ 1.1-1.2 and kH/kD ~ 0.8-0.9 are typical for α SKIEs, while kH/kD ~ 1.15-1.3 are typical for β SKIE. For reactants containing several isotopically substituted β-hydrogens, the observed isotope effect is often the result of several H/D's at the β position acting in concert. In these cases, the effect of each isotopically labeled atom is multiplicative, and cases where kH/kD > 2 are not uncommon.[17]
The following simple expressions relating 2H and 3H KIEs, which are also known as the Swain equation (or the Swain-Schaad-Stivers equations), can be derived from the general expression given above using some simplifications:[8][18]
- ;
i.e.,
- .
In deriving these expressions, the reasonable approximation that reduced mass roughly equals the mass of the 1H, 2H, or 3H, was used. Also, the vibrational motion was assumed to be approximated by a harmonic oscillator, so that ; X = 1,2,3H. The subscript "s" refers to these "semi-classical" KIEs, which disregard quantum tunneling. Tunneling contributions must be treated separately as a correction factor.
For isotope effects involving elements other than hydrogen, many of these simplifications are not valid, and the magnitude of the isotope effect may depend strongly on some or all of the neglected factors. Thus, KIEs for elements other than hydrogen are often much harder to rationalize or interpret. In many cases and especially for hydrogen-transfer reactions, contributions to KIEs from tunneling are significant (see below).
Tunneling
In some cases, a further rate enhancement is seen for the lighter isotope, possibly due to quantum tunneling. This is typically only observed for reactions involving bonds to hydrogen. Tunneling occurs when a molecule penetrates through a potential energy barrier rather than over it.[19][20] Though not allowed by classical mechanics, particles can pass through classically forbidden regions of space in quantum mechanics based on wave–particle duality.[21]

Tunneling can be analyzed using Bell's modification of the Arrhenius equation, which includes the addition of a tunneling factor, Q:
where A is the Arrhenius parameter, E is the barrier height and
where and
Examination of the β term shows exponential dependence on the particle's mass. As a result, tunneling is much more likely for a lighter particle such as hydrogen. Simply doubling the mass of a tunneling proton by replacing it with a deuteron drastically reduces the rate of such reactions. As a result, very large KIEs are observed that can not be accounted for by differences in ZPEs.

Also, the β term depends linearly with barrier width, 2a. As with mass, tunneling is greatest for small barrier widths. Optimal tunneling distances of protons between donor and acceptor atom is 40 pm.[23]
Temperature dependence in tunneling
Tunneling is a quantum effect tied to the laws of wave mechanics, not kinetics. Therefore, tunneling tends to become more important at low temperatures, where even the smallest kinetic energy barriers may not be overcome but can be tunneled through.[19]
Peter S. Zuev et al. reported rate constants for the ring expansion of 1-methylcyclobutylfluorocarbene to be 4.0 × 10−6/s in nitrogen and 4.0 × 10−5/s in argon at 8 kelvin. They calculated that at 8 kelvin, the reaction would proceed via a single quantum state of the reactant so that the reported rate constant is temperature independent and the tunneling contribution to the rate was 152 orders of magnitude greater than the contribution of passage over the transition state energy barrier.[24]
So even though conventional chemical reactions tend to slow down dramatically as the temperature is lowered, tunneling reactions rarely change at all. Particles that tunnel through an activation barrier are a direct result of the fact that the wave function of an intermediate species, reactant or product is not confined to the energy well of a particular trough along the energy surface of a reaction but can "leak out" into the next energy minimum. In light of this, tunneling should be temperature independent.[19][3]
For the hydrogen abstraction from gaseous n-alkanes and cycloalkanes by hydrogen atoms over the temperature range 363–463 K, the H/D KIE data were characterized by small preexponential factor ratios AH/AD ranging from 0.43 to 0.54 and large activation energy differences from 9.0 to 9.7 kJ/mol. Basing their arguments on transition state theory, the small A factor ratios associated with the large activation energy differences (usually about 4.5 kJ/mol for C–H(D) bonds) provided strong evidence for tunneling. For the purpose of this discussion, it is important is that the A factor ratio for the various paraffins they used was roughly constant throughout the temperature range.[25]
The observation that tunneling is not entirely temperature independent can be explained by the fact that not all molecules of a given species occupy their vibrational ground state at varying temperatures. Adding thermal energy to a potential energy well could cause higher vibrational levels than the ground state to become populated. For a conventional kinetically driven reaction, this excitation would only have a small influence on the rate. However, for a tunneling reaction, the difference between the ZPE and the first vibrational energy level could be huge. The tunneling correction term Q is linearly dependent on barrier width and this width is significantly diminished as the number vibrational modes on the Morse potential increase. The decrease of the barrier width can have such a huge impact on the tunneling rate that even a small population of excited vibrational states would dominate this process.[19][3]Criteria for KIE tunneling
To determine if tunneling is involved in KIE of a reaction with H or D, a few criteria are considered:
- Δ(EaH-EaD) > Δ(ZPEH-ZPED) (Ea=activation energy; ZPE=zero point energy)
- Reaction still proceeds at lower temperatures.
- The Arrhenius pre-exponential factors AD/AH is not equal to 1.
- A large negative entropy of activation.
- The geometries of the reactants and products are usually very similar.[19]
Also for reactions where isotopes include H, D and T, a criterion of tunneling is the Swain-Schaad relations which compare the rate constants (k) of the reactions where H, D or T are exchanged:
- kH/kT=(kD/kT)X and kH/kT=(kH/kD)Y
Examples for tunneling in KIE
In organic reactions, this proton tunneling effect has been observed in such reactions as the deprotonation and iodination of nitropropane with hindered pyridine base[26] with a reported KIE of 25 at 25°C:
and in a 1,5-sigmatropic hydrogen shift,[27] though it is observed that it is hard to extrapolate experimental values obtained at high temperature to lower temperatures:[28][29]
It has long been speculated that high efficiency of enzyme catalysis in proton or hydride ion transfer reactions could be due partly to the quantum mechanical tunneling effect. Environment at the active site of an enzyme positions the donor and acceptor atom close to the optimal tunneling distance, where the amino acid side chains can "force" the donor and acceptor atom closer together by electrostatic and noncovalent interactions. It is also possible that the enzyme and its unusual hydrophobic environment inside a reaction site provides tunneling-promoting vibration.[30] Studies on ketosteroid isomerase have provided experimental evidence that the enzyme actually enhances the coupled motion/hydrogen tunneling by comparing primary and secondary KIEs of the reaction under enzyme-catalyzed and non-enzyme-catalyzed conditions.[31]
Many examples exist for proton tunneling in enzyme-catalyzed reactions that were discovered by KIE. A well-studied example is methylamine dehydrogenase, where large primary KIEs of 5–55 have been observed for the proton transfer step.[32]

Another example of tunneling contribution to proton transfer in enzymatic reactions is the reaction carried out by alcohol dehydrogenase. Competitive KIEs for the hydrogen transfer step at 25°C resulted in 3.6 and 10.2 for primary and secondary KIEs, respectively.[33]

Transient kinetic isotope effect
Isotopic effect expressed with the equations given above only refer to reactions that can be described with first-order kinetics. In all instances in which this is not possible, transient KIEs should be taken into account using the GEBIK and GEBIF equations.[34]
Remove ads
Experiments
Summarize
Perspective
Simmons and Hartwig refer to the following three cases as the main types of KIE experiments involving C-H bond functionalization:[5]
- A) KIE determined from absolute rates of two parallel reactions

In this experiment, the rate constants for the normal substrate and its isotopically labeled analogue are determined independently, and the KIE is obtained as a ratio of the two. The accuracy of the measured KIE is severely limited by the accuracy with which each of these rate constants can be measured. Furthermore, reproducing the exact conditions in the two parallel reactions can be very challenging. Nevertheless, a measurement of a large kinetic isotope effect through direct comparison of rate constants is indicative that C-H bond cleavage occurs at the rate-determining step. (A smaller value could indicate an isotope effect due to a pre-equilibrium, so that the C-H bond cleavage occurs somewhere before the rate-determining step.)
- B) KIE determined from an intermolecular competition
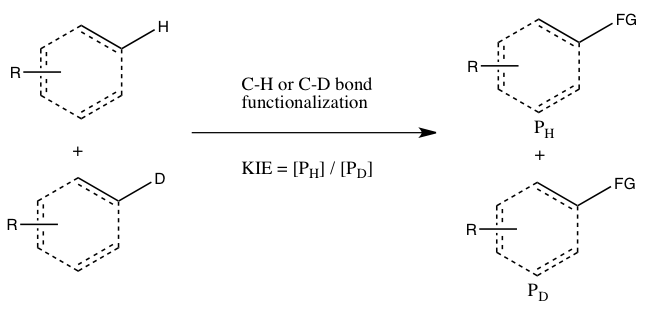
This type of experiment, uses the same substrates as used in Experiment A, but they are allowed in to react in the same container, instead of two separate containers. The KIE in this experiment is determined by the relative amount of products formed from C-H versus C-D functionalization (or it can be inferred from the relative amounts of unreacted starting materials). One must quench the reaction before it goes to completion to observe the KIE (see the Evaluation section below). Generally, the reaction is halted at low conversion (~5 to 10% conversion) or a large excess (> 5 equiv.) of the isotopic mixture is used. This experiment type ensures that both C-H and C-D bond functionalizations occur under exactly the same conditions, and the ratio of products from C-H and C-D bond functionalizations can be measured with much greater precision than the rate constants in Experiment A. Moreover, only a single measurement of product concentrations from a single sample is required. However, an observed kinetic isotope effect from this experiment is more difficult to interpret, since it may either mean that C-H bond cleavage occurs during the rate-determining step or at a product-determining step ensuing the rate-determining step. The absence of a KIE, at least according to Simmons and Hartwig, is nonetheless indicative of the C-H bond cleavage not occurring during the rate-determining step.
- C) KIE determined from an intramolecular competition
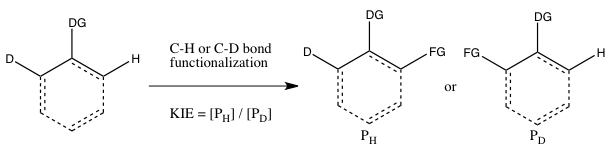
This type of experiment is analogous to Experiment B, except this time there is an intramolecular competition for the C-H or C-D bond functionalization. In most cases, the substrate possesses a directing group (DG) between the C-H and C-D bonds. Calculation of the KIE from this experiment and its interpretation follow the same considerations as that of Experiment B. However, the results of Experiments B and C will differ if the irreversible binding of the isotope-containing substrate takes place in Experiment B prior to the cleavage of the C-H or C-D bond. In such a scenario, an isotope effect may be observed in Experiment C (where choice of the isotope can take place even after substrate binding) but not in Experiment B (since the choice of whether C-H or C-D bond cleaves is already made as soon as the substrate binds irreversibly). In contrast to Experiment B, the reaction need not be halted at low consumption of isotopic starting material to obtain an accurate kH/kD, since the ratio of H and D in the starting material is 1:1, regardless of the extent of conversion.
One non-C-H activation example of different isotope effects being observed in the case of intermolecular (Experiment B) and intramolecular (Experiment C) competition is the photolysis of diphenyldiazomethane in the presence of t-butylamine. To explain this result, the formation of diphenylcarbene, followed by irreversible nucleophilic attack by t-butylamine was proposed. Because there is little isotopic difference in the rate of nucleophilic attack, the intermolecular experiment resulted in a KIE close to 1. In the intramolecular case, however, the product ratio is determined by the proton transfer that occurs after the nucleophilic attack, a process which has a substantial KIE of 2.6.[35]

Thus, Experiments A, B, and C will give results of differing levels of precision and require different experimental setup and ways of analyzing data. As a result, the feasibility of each type of experiment depends on the kinetic and stoichiometric profile of the reaction, as well as the physical characteristics of the reaction mixture (e.g. homogeneous vs. heterogeneous). Moreover, as noted in the paragraph above, the experiments provide KIE data for different steps of a multi-step reaction, depending on the relative locations of the rate-limiting step, product-determining steps, and/or C-H/D cleavage step.
The hypothetical examples below illustrate common scenarios. Consider the following reaction coordinate diagram. For a reaction with this profile, all three experiments (A, B, and C) will yield a significant primary KIE:

On the other hand, if a reaction follows the following energy profile, in which the C-H or C-D bond cleavage is irreversible but occurs after the rate-determining step (RDS), no significant KIE will be observed with Experiment A, since the overall rate is not affected by the isotopic substitution. Nevertheless, the irreversible C-H bond cleavage step will give a primary KIE with the other two experiments, since the second step would still affect the product distribution. Therefore, with Experiments B and C, it is possible to observe the KIE even if C-H or C-D bond cleavage occurs not in the rate-determining step, but in the product-determining step.

Evaluation of KIEs in a Hypothetical Multi-Step Reaction
A large part of the KIE arises from vibrational ZPE differences between the reactant ground state and the transition state that vary between the reactant and its isotopically substituted analog. While one can carry out involved calculations of KIEs using computational chemistry, much of the work done is of simpler order that involves the investigation of whether particular isotopic substitutions produce a detectable KIE or not. Vibrational changes from isotopic substitution at atoms away from the site where the reaction occurs tend to cancel between the reactant and the transition state. Therefore, the presence of a KIE indicates that the isotopically labeled atom is at or very near the reaction site.
The absence of an isotope effect is more difficult to interpret: It may mean that the isotopically labeled atom is away from the reaction site, but it may also mean there are certain compensating effects that lead to the lack of an observable KIE. For example, the differences between the reactant and the transition state ZPEs may be identical between the normal reactant and its isotopically labeled version. Alternatively, it may mean that the isotopic substitution is at the reaction site, but vibrational changes associated with bonds to this atom occur after the rate-determining step. Such a case is illustrated in the following example, in which ABCD represents the atomic skeleton of a molecule.

Assuming steady state conditions for the intermediate ABC, the overall rate of reaction is the following:
If the first step is rate-determining, this equation reduces to:
Or if the second step is rate-determining, the equation reduces to:
In most cases, isotopic substitution at A, especially if it is a heavy atom, will not alter k1 or k2, but it will most probably alter k3. Hence, if the first step is rate-determining, there will not be an observable kinetic isotope effect in the overall reaction with isotopic labeling of A, but there will be one if the second step is rate-determining. For intermediate cases where both steps have comparable rates, the magnitude of the kinetic isotope effect will depend on the ratio of k3 and k2.
Isotopic substitution of D will alter k1 and k2 while not affecting k3. The KIE will always be observable with this substitution since k1 appears in the simplified rate expression regardless of which step is rate-determining, but it will be less pronounced if the second step is rate-determining due to some cancellation between the isotope effects on k1 and k2. This outcome is related to the fact that equilibrium isotope effects are usually smaller than KIEs.
Isotopic substitution of B will clearly alter k3, but it may also alter k1 to a lesser extent if the B-C bond vibrations are affected in the transition state of the first step. There may thus be a small isotope effect even if the first step is rate-determining.
This hypothetical consideration reveals how observing KIEs may be used to investigate reaction mechanisms. The existence of a KIE is indicative of a change to the vibrational force constant of a bond associated with the isotopically labeled atom at or before the rate-controlling step. Intricate calculations may be used to learn a great amount of detail about the transition state from observed kinetic isotope effects. More commonly, though, the mere qualitative knowledge that a bond associated with the isotopically labeled atom is altered in a certain way can be very useful.[36]Evaluation of rate constant ratios from intermolecular competition reactions
In competition reactions, KIE is calculated from isotopic product or remaining reactant ratios after the reaction, but these ratios depend strongly on the extent of completion of the reaction. Most often, the isotopic substrate consists of molecules labeled in a specific position and their unlabeled, ordinary counterparts.[8] One can also, in case of 13C KIEs, as well as similar cases, simply rely on the natural abundance of the isotopic carbon for the KIE experiments, eliminating the need for isotopic labeling.[37] The two isotopic substrates will react through the same mechanism, but at different rates. The ratio between the amounts of the two species in the reactants and the products will thus change gradually over the course of the reaction, and this gradual change can be treated as follows:[8] Assume that two isotopic molecules, A1 and A2, undergo irreversible competition reactions:
The KIE for this scenario is found to be:
Where F1 and F2 refer to the fraction of conversions for the isotopic species A1 and A2, respectively.
Evaluation
In this treatment, all other reactants are assumed to be non-isotopic. Assuming further that the reaction is of first order with respect to the isotopic substrate A, the following general rate expression for both these reactions can be written:
Since f([B],[C],...) does not depend on the isotopic composition of A, it can be solved for in both rate expressions with A1 and A2, and the two can be equated to derive the following relations:
Where [A1]0 and [A2]0 are the initial concentrations of A1 and A2, respectively. This leads to the following KIE expression:
Which can also be expressed in terms of fraction amounts of conversion of the two reactions, F1 and F2, where 1-Fn=[An]/[An]0 for n = 1 or 2, as follows:

As for finding the KIEs, mixtures of substrates containing stable isotopes may be analyzed with a mass spectrometer, which yields the ratios of the isotopic molecules in the initial substrate (defined here as [A2]0/[A1]0=R0), in the substrate after some conversion ([A2]/[A1]=R), or in the product ([P2]/[P1]=RP). When one of the species, e.g. 2, is a radioisotope, its mixture with the other species can also be analyzed by its radioactivity, which is measured in molar activities that are proportional to [A2]0 / ([A1]0+[A2]0) ≈ [A2]0/[A1]0 = R0 in the initial substrate, [A2] / ([A1]+[A2]) ≈ [A2]/[A1] = R in the substrate after some conversion, and [R2] / ([R1]+[R2]) ≈ [R2]/[R1] = RP, so that the same ratios as in the other case can be measured as long as the radioisotope is present in tracer amounts. Such ratios may also be determined using NMR spectroscopy.[38]
When the substrate composition is followed, the following KIE expression in terms of R0 and R can be derived:
Measurement of F1 in terms of weights per unit volume or molarities of the reactants
Taking the ratio of R and R0 using the previously derived expression for F2, one gets:
Isotopic enrichment of the starting material can be calculated from the dependence of R/R0 on F1 for various KIEs, yielding the following figure. Due to the exponential dependence, even very low KIEs lead to large changes in isotopic composition of the starting material at high conversions.

When the products are followed, the KIE can be calculated using the products ratio RP along with R0 as follows:
Kinetic isotope effect measurement at natural abundance
KIE measurement at natural abundance is a simple general method for measuring KIEs for chemical reactions performed with materials of natural abundance. This technique for measuring KIEs overcomes many limitations of previous KIE measurement methods. KIE measurements from isotopically labeled materials require a new synthesis for each isotopically labeled material (a process often prohibitively difficult), a competition reaction, and an analysis.[5] The KIE measurement at natural abundance avoids these issues by taking advantage of high precision quantitative techniques (nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, isotope-ratio mass spectrometry) to site selectively measure kinetic fractionation of isotopes, in either product or starting material for a given chemical reaction.
Single-pulse NMR
Quantitative single-pulse nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is a method amenable for measuring kinetic fractionation of isotopes for natural abundance KIE measurements. Pascal et al. were inspired by studies demonstrating dramatic variations of deuterium within identical compounds from different sources and hypothesized that NMR could be used to measure 2H KIEs at natural abundance.[39][40] Pascal and coworkers tested their hypothesis by studying the insertion reaction of dimethyl diazomalonate into cyclohexane. Pascal et al. measured a KIE of 2.2 using 2H NMR for materials of natural abundance.[40]

Singleton and coworkers demonstrated the capacity of 13C NMR based natural abundance KIE measurements for studying the mechanism of the [4 + 2] cycloaddition of isoprene with maleic anhydride.[37] Previous studies by Gajewski on isotopically enrich materials observed KIE results that suggested an asynchronous transition state, but were always consistent, within error, for a perfectly synchronous reaction mechanism.[41]

This work by Singleton et al. established the measurement of multiple 13C KIEs within the design of a single experiment. These 2H and 13C KIE measurements determined at natural abundance found the "inside" hydrogens of the diene experience a more pronounced 2H KIE than the "outside" hydrogens and the C1 and C4 experience a significant KIE. These key observations suggest an asynchronous reaction mechanism for the cycloaddition of isoprene with maleic anhydride.
The limitations for determining KIEs at natural abundance using NMR are that the recovered material must have a suitable amount and purity for NMR analysis (the signal of interest should be distinct from other signals), the reaction of interest must be irreversible, and the reaction mechanism must not change for the duration of the chemical reaction.
Experimental details for using quantitative single pulse NMR to measure KIE at natural abundance as follows: the experiment needs to be performed under quantitative conditions including a relaxation time of 5 T1, measured 90° flip angle, a digital resolution of at least 5 points across a peak, and a signal:noise greater than 250. The raw FID is zero-filled to at least 256K points before the Fourier transform. NMR spectra are phased and then treated with a zeroth order baseline correction without any tilt correction. Signal integrations are determined numerically with a minimal tolerance for each integrated signal.[37][clarification needed]
Organometallic reaction mechanism elucidation examples
Colletto et al. developed a regioselective β-arylation of benzo[b]thiophenes at room temperature with aryl iodides as coupling partners and sought to understand the mechanism of this reaction by performing natural abundance KIE measurements via single pulse NMR.[42]



The observation of a primary 13C isotope effect at C3, an inverse 2H isotope effect, a secondary 13C isotope effect at C2, and the lack of a 2H isotope effect at C2; led Colletto et al. to suggest a Heck-type reaction mechanism for the regioselective β-arylation of benzo[b]thiophenes at room temperature with aryl iodides as coupling partners.[42]
Frost et al. sought to understand the effects of Lewis acid additives on the mechanism of enantioselective palladium-catalyzed C-N bond activation using natural abundance KIE measurements via single pulse NMR.[43]


The primary 13C KIE observed in the absence of BPh3 suggests a reaction mechanism with rate limiting cis oxidation into the C–CN bond of the cyanoformamide. The addition of BPh3 causes a relative decrease in the observed 13C KIE which led Frost et al. to suggest a change in the rate limiting step from cis oxidation to coordination of palladium to the cyanoformamide.[43]
DEPT-55 NMR
Though KIE measurements at natural abundance are a powerful tool for understanding reaction mechanisms, the amounts of material needed for analysis can make this technique inaccessible for reactions that use expensive reagents or unstable starting materials. To mitigate these limitations, Jacobsen and coworkers developed 1H to 13C polarization transfer as a means to reduce the time and material required for KIE measurements at natural abundance. The distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer (DEPT) takes advantage of the larger gyromagnetic ratio of 1H over 13C, to theoretically improve measurement sensitivity by a factor of 4 or decrease experiment time by a factor of 16. This method for natural abundance kinetic isotope measurement is favorable for analysis for reactions containing unstable starting materials, and catalysts or products that are relatively costly.[44]
Jacobsen and coworkers identified the thiourea-catalyzed glycosylation of galactose as a reaction that met both of the aforementioned criteria (expensive materials and unstable substrates) and was a reaction with a poorly understood mechanism.[45] Glycosylation is a special case of nucleophilic substitution that lacks clear definition between SN1 and SN2 mechanistic character. The presence of the oxygen adjacent to the site of displacement (i.e., C1) can stabilize positive charge. This charge stabilization can cause any potential concerted pathway to become asynchronous and approaches intermediates with oxocarbenium character of the SN1 mechanism for glycosylation.


Jacobsen and coworkers observed small normal KIEs at C1, C2, and C5 which suggests significant oxocarbenium character in the transition state and an asynchronous reaction mechanism with a large degree of charge separation.
Isotope-ratio mass spectrometry
High precision isotope-ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS) is another method for measuring kinetic fractionation of isotopes for natural abundance KIE measurements. Widlanski and coworkers demonstrated 34S KIE at natural abundance measurements for the hydrolysis of sulfate monoesters. Their observation of a large KIE suggests S-O bond cleavage is rate controlling and likely rules out an associate reaction mechanism.[46]

The major limitation for determining KIEs at natural abundance using IRMS is the required site selective degradation without isotopic fractionation into an analyzable small molecule, a non-trivial task.[37]
Remove ads
Case studies
Summarize
Perspective
Primary hydrogen isotope effects
Primary hydrogen KIEs refer to cases in which a bond to the isotopically labeled hydrogen is formed or broken at a rate- and/or product-determining step of a reaction.[5] These are the most commonly measured KIEs, and much of the previously covered theory refers to primary KIEs. When there is adequate evidence that transfer of the labeled hydrogen occurs in the rate-determining step of a reaction, if a fairly large KIE is observed, e.g. kH/kD of at least 5-6 or kH/kT about 10–13 at room temperature, it is quite likely that the hydrogen transfer is linear and that the hydrogen is fairly symmetrically located in the transition state. It is usually not possible to make comments about tunneling contributions to the observed isotope effect unless the effect is very large. If the primary KIE is not as large, it is generally considered to be indicative of a significant contribution from heavy-atom motion to the reaction coordinate, though it may also mean that hydrogen transfer follows a nonlinear pathway.[8]
Secondary hydrogen isotope effects
Secondary hydrogen isotope effects or secondary KIE (SKIE) arise in cases where the isotopic substitution is remote from the bond being broken. The remote atom nonetheless influences the internal vibrations of the system, which via changes in zero-point energy (ZPE) affect the rates of chemical reactions.[47] Such effects are expressed as ratios of rate for the light isotope to that of the heavy isotope and can be "normal" (ratio ≥ 1) or "inverse" (ratio < 1) effects.[48] SKIEs are defined as α,β (etc.) secondary isotope effects where such prefixes refer to the position of the isotopic substitution relative to the reaction center (see alpha and beta carbon).[49] The prefix α refers to the isotope associated with the reaction center and the prefix β refers to the isotope associated with an atom neighboring the reaction center and so on.
In physical organic chemistry, SKIE is discussed in terms of electronic effects such as induction, bond hybridization, or hyperconjugation.[50] These properties are determined by electron distribution, and depend upon vibrationally averaged bond length and angles that are not greatly affected by isotopic substitution. Thus, the use of the term "electronic isotope effect" while legitimate is discouraged from use as it can be misinterpreted to suggest that the isotope effect is electronic in nature rather than vibrational.[49]
SKIEs can be explained in terms of changes in orbital hybridization. When the hybridization of a carbon atom changes from sp3 to sp2, a number of vibrational modes (stretches, in-plane and out-of-plane bending) are affected. The in-plane and out-of-plane bending in an sp3 hybridized carbon are similar in frequency due to the symmetry of an sp3 hybridized carbon. In an sp2 hybridized carbon the in-plane bend is much stiffer than the out-of-plane bending resulting in a large difference in the frequency, the ZPE and thus the SKIE (which exists when there is a difference in the ZPE of the reactant and transition state).[19] The theoretical maximum change caused by the bending frequency difference has been calculated as 1.4.[19]
When carbon undergoes a reaction that changes its hybridization from sp3 to sp2, the out-of-plane bending force constant at the transition state is weaker as it is developing sp2 character and a "normal" SKIE is observed with typical values of 1.1 to 1.2.[19] Conversely, when carbon's hybridization changes from sp2 to sp3, the out of plane bending force constants at the transition state increase and an inverse SKIE is observed with typical values of 0.8 to 0.9.[19]
More generally the SKIE for reversible reactions can be "normal" one way and "inverse" the other if bonding in the transition state is midway in stiffness between substrate and product, or they can be "normal" both ways if bonding is weaker in the transition state, or "inverse" both ways if bonding is stronger in the transition state than in either reactant.[48]
An example of an "inverse" α SKIE can be seen in the work of Fitzpatrick and Kurtz who used such an effect to distinguish between two proposed pathways for the reaction of d-amino acid oxidase with nitroalkane anions.[51] Path A involved a nucleophilic attack on the coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), while path B involves a free-radical intermediate. As path A results in the intermediate carbon changing hybridization from sp2 to sp3 an "inverse" SKIE is expected. If path B occurs then no SKIE should be observed as the free radical intermediate does not change hybridization. An SKIE of 0.84 was observed and Path A verified as shown in the scheme below.
Another example of SKIE is oxidation of benzyl alcohols by dimethyldioxirane, where three transition states for different mechanisms were proposed. Again, by considering how and if the hydrogen atoms were involved in each, researchers predicted whether or not they would expect an effect of isotopic substitution of them. Then, analysis of the experimental data for the reaction allowed them to choose which pathway was most likely based on the observed isotope effect.[52]
Secondary hydrogen isotope effects from the methylene hydrogens were also used to show that Cope rearrangement in 1,5-hexadiene follow a concerted bond rearrangement pathway, and not one of the alternatively proposed allyl radical or 1,4-diyl pathways, all of which are presented in the following scheme.[53]

Alternative mechanisms for the Cope rearrangement of 1,5-hexadiene: (from top to bottom), allyl radical, synchronous concerted, and 1,4-dyil pathways. The predominant pathway is found to be the middle one, which has six delocalized π electrons corresponding to an aromatic intermediate.[53]
Steric isotope effects
 |
The steric isotope effect (SIE) is a SKIE that does not involve bond breaking or formation. This effect is attributed to the different vibrational amplitudes of isotopologues.[54] An example of such an effect is the racemization of 9,10-dihydro-4,5-dimethylphenanthrene.[55] The smaller amplitude of vibration for 2H than for 1H in C–1H, C–2H bonds, results in a smaller van der Waals radius or effective size in addition to a difference in the ZPE between the two. When there is a greater effective bulk of molecules containing one over the other this may be manifested by a steric effect on the rate constant. For the example above, 2H racemizes faster than 1H resulting in a SIE. A model for the SIE was developed by Bartell.[56] A SIE is usually small, unless the transformations passes through a transition state with severe steric encumbrance, as in the racemization process shown above.
Another example of the SIE is in the deslipping reaction of rotaxanes. 2H, due to its smaller effective size, allows easier passage of the stoppers through the macrocycle, resulting in faster deslipping for the deuterated rotaxanes.[57]
Inverse kinetic isotope effects
Reactions are known where the deuterated species reacts faster than the undeuterated one, and these cases are said to exhibit inverse KIEs (IKIE). IKIEs are often observed in the reductive elimination of alkyl metal hydrides, e.g. ((Me2NCH2)2)PtMe(H).[b] In such cases the C-D bond in the transition state, an agostic species, is highly stabilized relative to the C–H bond.[58]
An inverse effect can also occur in a multistep reaction if the overall rate constant depends on a pre-equilibrium prior to the rate-determining step which has an inverse equilibrium isotope effect. For example, the rates of acid-catalyzed reactions are usually 2-3 times greater for reactions in D2O catalyzed by D3O+ than for the analogous reactions in H2O catalyzed by H3O+[4]: 433 This can be explained for a mechanism of specific hydrogen-ion catalysis of a reactant R by H3O+ (or D3O+).
- H3O+ + R ⇌ RH+ + H2O
- RH+ + H2O → H3O+ + P
The rate of formation of products is then d[P]/dt = k2[RH+] = k2K1[H3O+][R] = kobs[H3O+][R]. In the first step, H3O+ is usually a stronger acid than RH+. Deuteration shifts the equilibrium toward the more strongly bound acid species RD+ in which the effect of deuteration on zero-point vibrational energy is greater, so that the deuterated equilibrium constant K1D is greater than K1H. This equilibrium isotope effect in the first step usually outweighs the kinetic isotope effect in the second step, so that there is an apparent inverse isotope effect and the observed overall rate constant kobs = k2K1 decreases.[4]: 433
Solvent hydrogen kinetic isotope effects
For the solvent isotope effects to be measurable, a fraction of the solvent must have a different isotopic composition than the rest. Therefore, large amounts of the less common isotopic species must be available, limiting observable solvent isotope effects to isotopic substitutions involving hydrogen. Detectable KIEs occur only when solutes exchange hydrogen with the solvent or when there is a specific solute-solvent interaction near the reaction site. Both such phenomena are common for protic solvents, in which the hydrogen is exchangeable, and they may form dipole-dipole interactions or hydrogen bonds with polar molecules.[8]
Carbon-13 isotope effects
Most organic reactions involve breaking and making bonds to carbon; thus, it is reasonable to expect detectable carbon isotope effects. When 13C is used as the label, the change in mass of the isotope is only ~8%, though, which limits the observable KIEs to much smaller values than the ones observable with hydrogen isotope effects.
Compensating for variations in 13C natural abundance
Often, the largest source of error in a study that depends on the natural abundance of carbon is the slight variation in natural 13C abundance itself. Such variations arise; because the starting materials in the reaction, are themselves products of other reactions that have KIEs and thus isotopically enrich the products. To compensate for this error when NMR spectroscopy is used to determine the KIE, the following guidelines have been proposed:[38]
- Choose a carbon that is remote from the reaction center that will serve as a reference and assume it does not have a KIE in the reaction.
- In the starting material that has not undergone any reaction, determine the ratios of the other carbon NMR peak integrals to that of the reference carbon.
- Obtain the same ratios for the carbons in a sample of the starting material after it has undergone some reaction.
- The ratios of the latter ratios to the former ratios yields R/R0.
If these as well as some other precautions listed by Jankowski are followed, KIEs with precisions of three decimal places can be achieved.[38]
Isotope effects with elements heavier than carbon
Interpretation of carbon isotope effects is usually complicated by simultaneously forming and breaking bonds to carbon. Even reactions that involve only bond cleavage from the carbon, such as SN1 reactions, involve strengthening of the remaining bonds to carbon. In many such reactions, leaving group isotope effects tend to be easier to interpret. For example, substitution and elimination reactions in which chlorine acts as a leaving group are convenient to interpret, especially since chlorine acts as a monatomic species with no internal bonding to complicate the reaction coordinate, and it has two stable isotopes, 35Cl and 37Cl, both with high abundance. The major challenge to the interpretation of such isotope affects is the solvation of the leaving group.[8]
Owing to experimental uncertainties, measurement of isotope effect may entail significant uncertainty. Often isotope effects are determined through complementary studies on a series of isotopomers. Accordingly, it is quite useful to combine hydrogen isotope effects with heavy-atom isotope effects. For instance, determining nitrogen isotope effect along with hydrogen isotope effect was used to show that the reaction of 2-phenylethyltrimethylammonium ion with ethoxide in ethanol at 40°C follows an E2 mechanism, as opposed to alternative non-concerted mechanisms. This conclusion was reached upon showing that this reaction yields a nitrogen isotope effect, k14/k15, of 1.0133±0.0002 along with a hydrogen KIE of 3.2 at the leaving hydrogen.[8]
Similarly, combining nitrogen and hydrogen isotope effects was used to show that syn eliminations of simple ammonium salts also follow a concerted mechanism, which was a question of debate before. In the following two reactions of 2-phenylcyclopentyltrimethylammonium ion with ethoxide, both of which yield 1-phenylcyclopentene, both isomers exhibited a nitrogen isotope effect k14/k15 at 60°C. Though the reaction of the trans isomer, which follows syn elimination, has a smaller nitrogen KIE (1.0064) than the cis isomer which undergoes anti elimination (1.0108); both results are large enough to be indicative of weakening of the C-N bond in the transition state that would occur in a concerted process.[c]

Other examples
Since KIEs arise from differences in isotopic mass, the largest observable KIEs are associated with substitution of 1H with 2H (2× increase in mass) or 3H (3× increase in mass). KIEs from isotopic mass ratios can be as large as 36.4 using muons. They have produced the lightest "hydrogen" atom, 0.11H (0.113 amu), in which an electron orbits a positive muon (μ+) "nucleus" that has a mass of 206 electrons. They have also prepared the heaviest "hydrogen" atom by replacing one electron in helium with a negative muon μ− to form Heμ (mass 4.116 amu). Since μ− is much heavier than an electron, it orbits much closer to the nucleus, effectively shielding one proton, making Heμ behave as 4.1H. With these exotic atoms, the reaction of H with 1H2 was investigated. Rate constants from reacting the lightest and the heaviest hydrogen analogs with 1H2 were then used to calculate k0.11/k4.1, in which there is a 36.4× difference in isotopic mass. For this reaction, isotopic substitution happens to produce an IKIE, and the authors report a KIE as low as 1.74×10−4, the smallest KIE ever reported.[59]
The KIE leads to a specific distribution of 2H in natural products, depending on the route they were synthesized in nature. By NMR spectroscopy, it is therefore easy to detect whether the alcohol in wine was fermented from glucose, or from illicitly added saccharose.
Another reaction mechanism that was elucidated using the KIE is halogenation of toluene:[60]
In this particular "intramolecular KIE" study, a benzylic hydrogen undergoes radical substitution by bromine using N-bromosuccinimide as the brominating agent. It was found that PhCH3 brominates 4.86x faster than PhC2H3 (PhCD3). A large KIE of 5.56 is associated with the reaction of ketones with bromine and sodium hydroxide.[61]
In this reaction the rate-limiting step is formation of the enolate by deprotonation of the ketone. In this study the KIE is calculated from the reaction rate constants for regular 2,4-dimethyl-3-pentanone and its deuterated isomer by optical density measurements.
In asymmetric catalysis, there are rare cases where a KIE manifests as a significant difference in the enantioselectivity observed for a deuterated substrate compared to a non-deuterated one. One example was reported by Toste and coworkers, in which a deuterated substrate produced an enantioselectivity of 83% ee, compared to 93% ee for the undeuterated substrate. The effect was taken to corroborate additional inter- and intramolecular competition KIE data that suggested cleavage of the C-H/D bond in the enantiodetermining step.[62]
Remove ads
Notes
- This convention exists for both convenience in nomenclature and as a reflection of how 2H KIEs are generally studied experimentally: Though deuterium (2H) has the IUPAC-sanctioned symbol D, there is no common symbol that specifically refers to protium (1H). Still, it has proven useful to have labels to refer to the respective rate constants of protium- or deuterium-containing isotopologues, so kH and kD, respectively, have typically been used. Moreover, the magnitude of a KIE can then be expressed as kH/kD. This notation is consistent with the fact that, experimentally, 2H KIEs are measured by comparing the reaction rate of a 2H-enriched starting material to that of an unenriched starting material containing hydrogen at natural abundance. This is almost always valid, since protium accounts for ~99.985% of natural hydrogen, so there is usually no need to further deplete the deuterium in the starting material to obtain a "protium-enriched" sample. Combined, the notation and experimental setup led to the common conceptualization of deuterium as a "substituent" that takes the place of normal hydrogen in an isotope effect study.
- "Me" means methyl, CH3.
Remove ads
See also
- Crossover experiment (chemistry)
- Equilibrium constant#Effect of isotopic substitution
- Isotope effect on lipid peroxidation
- Kinetic isotope effects of RuBisCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase)
- Magnetic isotope effect
- Reaction mechanism
- Transient kinetic isotope fractionation
- Urey–Bigeleisen–Mayer equation
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
![{\displaystyle {\begin{matrix}\\{\ce {{CN^{-}}+{^{12}CH3-Br}->[k_{12}]{^{12}CH3-CN}+Br^{-}}}\\{\ce {{CN^{-}}+{^{13}CH3-Br}->[k_{13}]{^{13}CH3-CN}+Br^{-}}}\\{}\end{matrix}}\qquad {\text{KIE}}={\frac {k_{12}}{k_{13}}}=1.082\pm 0.008}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/438109ea220fd190ccc57f3e2c3726c47c24aae0)

![{\displaystyle {\frac {k_{{\ce {H}}}}{k_{{\ce {D}}}}}=\left({\frac {\sigma _{{\ce {H}}}\sigma _{{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger }}{\sigma _{{\ce {D}}}\sigma _{{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }}}\right)\left({\frac {M_{{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }M_{{\ce {D}}}}{M_{{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger }M_{{\ce {H}}}}}\right)^{\frac {3}{2}}\left({\frac {I_{x{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }I_{y{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }I_{z{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }}{I_{x{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger }I_{y{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger }I_{z{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger }}}{\frac {I_{x{\ce {D}}}I_{y{\ce {D}}}I_{z{\ce {D}}}}{I_{x{\ce {H}}}I_{y{\ce {H}}}I_{z{\ce {H}}}}}\right)^{\frac {1}{2}}\left({\frac {\prod \limits _{i=1}^{3N^{\ddagger }-7}{\frac {1-e^{-u_{i{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger }}}{1-e^{-u_{i{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }}}}}{\prod \limits _{i=1}^{3N-6}{\frac {1-e^{-u_{i{\ce {D}}}}}{1-e^{-u_{i{\ce {H}}}}}}}}\right)e^{-{\frac {1}{2}}\left[\sum \limits _{i=1}^{3N^{\ddagger }-7}(u_{i{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }-u_{i{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger })-\sum \limits _{i=1}^{3N-6}(u_{i{\ce {H}}}-u_{i{\ce {D}}})\right]}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/93f26faede9d0fba35d6f675e641c716e7284c0d)




![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {k_{{\ce {H}}}}{k_{{\ce {D}}}}}&\cong \exp \left\{-{\frac {1}{2}}\left[\sum \limits _{i=1}^{3N^{\ddagger }-7}(u_{i{\ce {H}}}^{\ddagger }-u_{i{\ce {D}}}^{\ddagger })-\sum \limits _{i=1}^{3N-6}(u_{i{\ce {H}}}-u_{i{\ce {D}}})\right]\right\}\\&\cong \exp \left[\sum _{i}^{\mathrm {(react.)} }{\frac {1}{2}}\Delta u_{i}-\sum _{i}^{\mathrm {(TS)} }{\frac {1}{2}}\Delta u_{i}^{\ddagger }\right]\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/20d669d624e10fcb89d116442c5543998ea4fbf8)

















![{\displaystyle {\frac {d[A]}{dt}}={\frac {k_{1}k_{3}[ABCD]}{k_{2}[D]+k_{3}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f71c52221df559ae3b305086cf125e2cfbfa62c4)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {d[A]}{dt}}=k_{1}[ABCD]}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6cfaea2beb4c13e320a49b4f66ede1c5a85d0fba)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {d[A]}{dt}}={\frac {k_{1}k_{3}[ABCD]}{k_{2}[D]}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ea50a8acf1a1307f4d9c2b4605f62578e2f79771)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\ce {{A1}+{B}+{C}+\cdots }}\ &{\ce {->[k_{1}]P1}}\\{\ce {{A2}+{B}+{C}+\cdots }}\ &{\ce {->[k_{2}]P2}}\end{aligned}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8a3e1c66994bddc0e6b39e89f23e4e0ec7a47b5c)

![{\displaystyle {\text{rate}}={-d[{\ce {A}}_{n}] \over dt}=k_{n}\times [{\ce {A}}_{n}]\times f([{\ce {B}}],[{\ce {C}}],\cdots ){\text{ where }}n=1{\text{ or }}2}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/26ca6ed80abd2295998fb23de5de165477f2848e)
![{\displaystyle {1 \over k_{1}}\times {\ce {{\mathit {d}}[A1] \over [A1]}}={1 \over k_{2}}\times {\ce {{\mathit {d}}[A2] \over [A2]}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ec95ce0a836f8db29e8a86da2d3a2390214f462c)
![{\displaystyle {1 \over k_{1}}\times \int \limits _{\ce {[A1]^{0}}}^{\ce {[A1]}}{d[{\ce {A}}'_{1}] \over [{\ce {A}}'_{1}]}={1 \over k_{2}}\times \int \limits _{\ce {[A2]^{0}}}^{\ce {[A2]}}{d[{\ce {A}}'_{2}] \over [{\ce {A}}'_{2}]}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8b3f5c1311b00398d60afa93ae27d58ac423fd32)
![{\displaystyle {k_{1} \over k_{2}}={\frac {\ce {\ln([A1]/[A1]^{0})}}{\ce {\ln([A2]/[A2]^{0})}}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a4f8b9f334d8799e9e6fc51d105e53d0148086f1)

![{\displaystyle {\text{KIE}}={\frac {k_{1}}{k_{2}}}={\frac {\ln(1-F_{1})}{\ln[(1-F_{1})R/R_{0}]}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9f819291ca2e6641dfaf1a2d31025c40927bdd7a)
![{\displaystyle {R \over R_{0}}={\ce {{\frac {[A2]/[A1]}{[A2]^0/[A1]^0}}}}={\ce {{\frac {[A2]/[A2]^0}{[A1]/[A1]^0}}}}={\frac {1-F_{2}}{1-F_{1}}}=(1-F_{1})^{(k_{2}/k_{1})-1}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/61529d236e7c75ed167c0a1e43f996134b54b908)
![{\displaystyle {k_{1} \over k_{2}}={\frac {\ln(1-F_{1})}{\ln[1-(F_{1}R_{P}/R_{0})]}}}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/37f721659b133bfa69404286f90a8309fea92944)






