DYNLL1
Protein-coding gene in humans From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
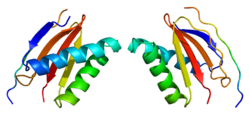
Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNLL1 gene.[5][6][7][8]
Function
Cytoplasmic dyneins are large enzyme complexes with a molecular mass of about 1,200 kD. They contain two force-producing heads formed primarily from dynein heavy chains, and stalks linking the heads to a basal domain, which contains a varying number of accessory intermediate chains. The complex is involved in intracellular transport and motility. The protein described in this record is a light chain and exists as part of this complex but also physically interacts with and inhibits the activity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Binding of this protein destabilizes the neuronal nitric oxide synthase dimer, a conformation necessary for activity, and it may regulate numerous biologic processes through its effects on nitric oxide synthase activity. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized.[8]
Interactions
DYNLL1 has been shown to interact with:
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.