DPD scan
Nuclear medicine scan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A DPD scan is a type of nuclear medicine imaging test which uses radioactive technetium-99m (99mTc) and 3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid (DPD) to diagnose cardiac amyloidosis. The radiopharmaceutical is taken up only in patients with ATTR amyloidosis, making it a useful tool to differentiate from AL amyloidosis.[1]
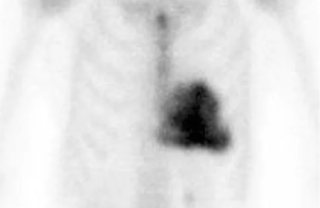
DPD is a diphosphonate and can be used as an alternative to HDP or MDP in nuclear medicine bone scintigraphy.[2]
Procedure
DPD scanning typically uses a gamma camera to obtain SPECT images, with an injection followed by an initial scan after 5 minutes, and a second scan after 3 hours.[3]
Images are often scored using the "Perugini system" whereby:[4][5]
- Grade 0 – no cardiac uptake and normal bone uptake
- Grade 1 – cardiac uptake which is less intense than the bone signal
- Grade 2 – cardiac uptake with intensity similar or greater than bone signal
- Grade 3 – cardiac uptake with much attenuated or absent bone signal
Availability
DPD is not currently available in the United States.[6]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
