Cucurbitane
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
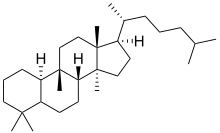
Cucurbitane is a tetracyclic chemical compound with formula C
30H
54. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, specifically triterpene. It is also an isomer of lanostane (specifically 19(10→9β)-abeolanostane), from which it differs by the formal shift of a methyl group (carbon number 19) from the 10 to the 9β position in the standard steroid numbering scheme.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
19-Nor-5ξ,9β,10α-lanostane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,5aΞ,9aR,9bS,11aR)-3a,6,6,9b,11a-Pentamethyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H54 | |
| Molar mass | 414.762 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The name is applied to two stereoisomers, distinguished by the prefixes 5α- and 5β-, which differ by the handedness of the bonds at a particular carbon atom (number 5 in the standard steroid numbering scheme).[1]
- 5α-Cucurbitane
- 5β-Cucurbitane
Cucurbitane is the core chemical structure of a class of derivatives known as cucurbitane-type triterpenoids or simply as cucurbitanes.[3]
Derivatives
Summarize
Perspective
Natural compounds
Compounds with the basic cucurbitane skeleton are found in many plants, and some are important phytopharmaceuticals.[4] Natural cucurbitane-related compounds include:
Named
- Balsaminapentaol, from Momordica balsamina.[5]
- Balsaminol A, from Momordica balsamina.[5]
- Balsaminol B, from Momordica balsamina.[5]
- Brydioside A from Bryonia dioica[4]: 64
- Bryoamaride and derivatives from Bryonia dioica[4]: 65, 66
- Charantin or foetidin, from Momordica charantia[6] and Momordica foetida[7]
- Charantosides I-VIII, from Momordica charantia.[8]
- Cucurbalsaminol B, from Momordica balsamina.[5]
- Cucurbalsaminol A, from Momordica balsamina.[5]
- Cucurbitacins A-L, O-T[4][9][10]: 3–8
- Datiscosides, from Datisca glomerata[4]: 16–19
- Endecaphyllacins A and B, from roots of Hemsleya endecaphylla[10]: 1, 2
- Hemslecins A and B, from roots of H. endecaphylla[10]
- Lepidolide, from the mushroom Russula lepida[11]
- Karavilagenin E, from Momordica balsamina.[5]
- Khekadaengosides A, B, D and K, from Trichosanthes tricuspidata[4]: 57, 58, 67, 68
- Kuguacins A-S, from stems and leaves of Momordica charantia[12][13]
- Kuguaglycosides A-H, from the root of Momordica charantia[14]
- Mogrosides I-V, from the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii[15]
- Momordicin I, II and 28, from Momordica charantia[16][17]
- Momordicines II and IV, from leaves of Momordica charantia[18]
- Momordicosides A-S, from Momordica charantia fruits[8][19][20]
- Neokuguaglucoside, from Momordica charantia fruits[21]
- Neomogroside, from the fruit of Siraitia grosvenorii.[22]
- Pentanorcucurbitacins A and B[23]: 1, 2
- Perseapicroside A, from Persea mexicana[4]: 44
- Scandenoside R9, from Hemsleya panacis-scandens[4]: 45
- Spinosides A and B, from Desfontainia spinosa[4]: 61, 62
Unnamed
- 3β,7β,23ξ-trihydroxycucurbita-5,24-dien-19-al, soluble in chloroform, melts at 123−125 °C, from Momordica charantia, Momordica foetida.[24]: 1
- 3β,7β,25-trihydroxycucurbita-5,23-dien-19-al, soluble in chloroform, melts at 188−191 °C, from Momordica charantia, Momordica foetida[24]: 2
- 3β,7β-dihydroxy-25-methoxycucurbita-5,23-dien-19-al, soluble in chloroform, from Momordica charantia, Momordica foetida[24]: 3
- 5β,19-epoxy-25-methoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3β,19-diol, soluble in chloroform, melts at 182−184 °C, from Momordica foetida[24]: 4
- 5β,19-epoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3β,19,25-triol, soluble in chloroform, from Momordica foetida[24]: 5
- 5β,19-epoxy-19-methoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3β,25-diol, soluble in chloroform, melts at 102−104 °C, from Momordica charantia, Momordica foetida[24]: 6
- 5β,19-epoxy-19,25-dimethoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3β-ol, soluble in chloroform, from Momordica charantia, Momordica foetida[24]: 7
- 5β,19-epoxy-25-methoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3β-ol, soluble in chloroform, melts at 139−141 °C, from Momordica charantia, Momordica foetida[24]: 8
- 19(R)-n-butanoxy-5β,19-epoxycucurbita-6,23-diene-3β,25-diol 3-O-β-glucopyranoside, C
40H
66O
9, white powder soluble in methanol, from Momordica charantia fruit (8 mg/35 kg)[19]: 1 - 23-O-β-allopyranosylecucurbita-5,24-dien-7α,3β,22(R),23(S)-tetraol 3-O-β-allopyranoside,C
42H
69O
14, white powder soluble in methanol, from Momordica charantia fruit (10 mg/35 kg)[19]: 2 - 23(R),24(S),25-trihydroxycucurbit-5-ene 3-O-{[β-glucopyranosyl(1→6)]-O-β-glucopyranosyl}-25-O-β-glucopyranoside, C
48H
82O
19, white powder soluble in methanol, from Momordica charantia fruit (10 mg/35 kg)[19]: 3 - 2,16-dihydroxy-22,23,24,25,26,27-hexanorcucurbit-5-en-11,20-dione 2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, soluble in ethanol, from Cucurbita pepo fruits (25 mg/15 kg)[9]: 3
- 16-hydroxy-22,23,24,25,26,27-hexanorcucurbit-5-en-11,20-dione 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside, white powder, soluble in ethanol, from Cucurbita pepo fruits (12 mg/15 kg)[9]: 4
- 7-methoxycucurbita-5,24-diene-3β,23(R)-diol, from Momordica balsamina[25]
- 25,26,27-trinorcucurbit-5-ene-3,7,23-trione C
27H
40O
3, white powder, soluble in methanol, from stems of Momordica charantia (6 mg/18 kg)[23]: 3
See also
- Goyaglicoside
- Karaviloside
- Momordenol, from Momordica charantia[16]
- 24(R)-stigmastan-3β,5α,6β-triol-25-ene 3-O-β-glucopyranoside, C
35H
60O
8, white powder, from Momordica charantia fruit (15 mg/35 kg)[19]: 4
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.


