Cribriform fascia
Portion of fascia covering the saphenous opening in the thigh From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The cribriform fascia (also known as the fascia cribrosa, or Hesselbach's fascia) is the portion of the superficial layer of the deep fascia of leg which extends between the sartorius muscle, adductor longus muscle, and inguinal ligament to form the anterior portion of the femoral canal.[1]
| Cribriform fascia | |
|---|---|
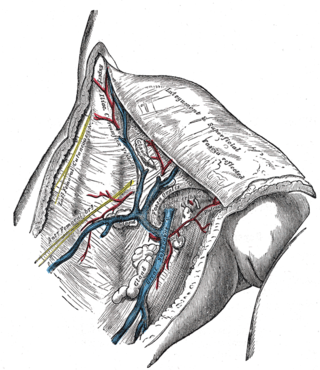
 The great saphenous vein and its tributaries at the saphenous opening | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia cribrosa |
| TA98 | A04.7.03.020 |
| TA2 | 2706 |
| FMA | 58735 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The cribriform fascia forms numerous openings to allow the passage of vessels and nerves, the most prominent of these being the saphenous opening (saphenous hiatus) (which gives passage to the great saphenous vein).[1]
Anatomy
Structure
An inferior aponeurotic thickening of the cribriform fascia - the falciform margin of sphenous opening - forms the inferior margin of the sapnenous opening, embracing the arch of the great saphenous vein.[2]
Clinical significance
The cribriform fascia has been proposed for use in preventing new vascularization when surgery is performed at the join between the great saphenous vein and the femoral vein.[3]
Eponym
When the eponym is used, it is named for Franz Kaspar Hesselbach.[4][5]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.