Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Conjunctiva
Part of the eye; protective outer layer covering the sclera From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
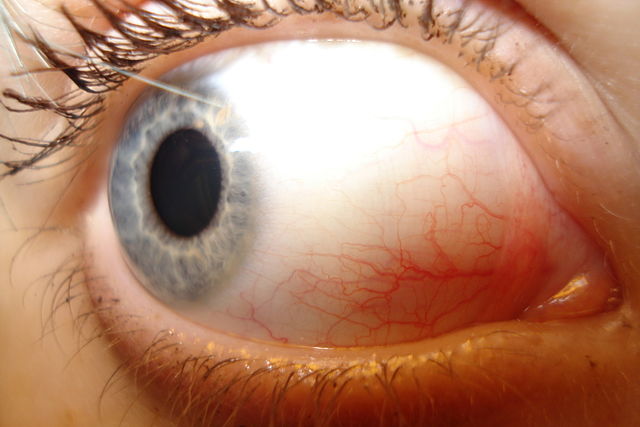
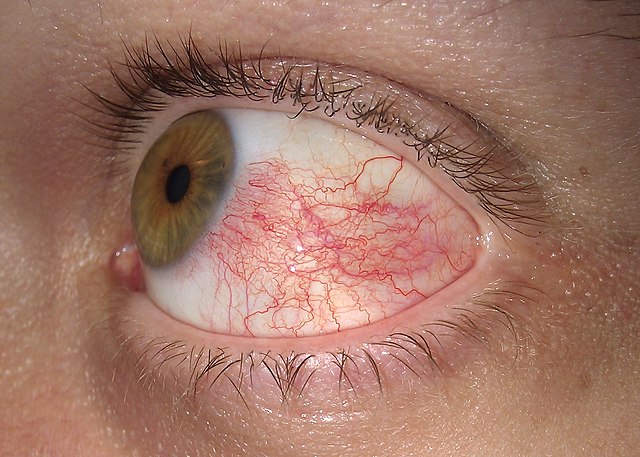
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (pl.: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye).[1] It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies.
Remove ads
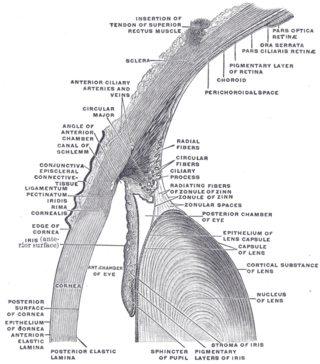
Structure
Summarize
Perspective
The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts:
Blood supply
Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents.[4]
Nerve supply
Sensory innervation of the conjunctiva is divided into four parts:[5]
Microanatomy
The conjunctiva consists of unkeratinized, both stratified squamous and stratified columnar epithelium, with interspersed goblet cells.[6] The epithelial layer contains blood vessels, fibrous tissue, and lymphatic channels.[6] Accessory lacrimal glands in the conjunctiva constantly produce the aqueous portion of tears.[6] Additional cells present in the conjunctival epithelium include melanocytes, T and B cell lymphocytes.[6]
Remove ads
Function
The conjunctiva helps lubricate the eye by producing mucus and tears, although a smaller volume of tears than the lacrimal gland.[7] It also contributes to immune surveillance and helps to prevent the entrance of microbes into the eye.
Clinical significance
Summarize
Perspective
Disorders of the conjunctiva and cornea are common sources of eye complaints, in particular because the surface of the eye is exposed to various external influences and is especially susceptible to trauma, infections, chemical irritation, allergic reactions, and dryness.
- The conjunctival microvascular hemodynamics are affected by diabetic retinopathy (DR), hence can be useful for DR diagnosis and monitoring,[8] and discriminating stages of DR.[9]
- Type II diabetes is associated with conjunctival hypoxia,[10] increased average blood vessel diameter, and capillary loss.[11][12][13]
- Sickle-cell anemia is associated with blood vessel sludging, altered blood flow and blood vessel diameter, and capillary micro-haemorrhages.[14][15][16]
- Hypertension is associated with an increase in the tortuosity of bulbar conjunctival blood vessels and capillary and arteriole loss.[17][18]
- Carotid artery occlusion is associated with slower conjunctival blood flow and apparent capillary loss.[4]
- With age, the conjunctiva can stretch and loosen from the underlying sclera, leading to the formation of conjunctival folds, a condition known as conjunctivochalasis.[19][20]
- The conjunctiva can be affected by tumors which can be benign, pre-malignant or malignant.[21]
- Leptospirosis, an infection with Leptospira, can cause conjunctival suffusion, which is characterized by chemosis, and redness without exudates.
Bulbar conjunctival microvasculature
Summarize
Perspective
Vessel morphology
The bulbar conjunctival microvasculature contains arterioles, meta-arterioles, venules, capillaries, and communicating vessels. Vessel morphology varies greatly between subjects and even between regions of the individual eyes. In some subjects, arterioles and venules can be seen to run parallel with each other. Paired arterioles are generally smaller than corresponding venules.[22] The average bulbar conjunctival vessel has been reported to be 15.1 microns, which reflects the high number of small capillaries, which are typically <10 microns in diameter.[23]
Blood oxygen dynamics
The bulbar conjunctival microvasculature is in close proximity to ambient air, thus oxygen diffusion from ambient air strongly influences their blood oxygen saturation. Because of oxygen diffusion, hypoxic bulbar conjunctival vessels will rapidly reoxygenate (in under 10 seconds) when exposed to ambient air (i.e. when the eyelid is open). Closing the eyelid stops this oxygen diffusion by placing a barrier between the bulbar conjunctival microvessels and ambient air.[24]
Blood vessel imaging methods
The bulbar conjunctival microvessels are typically imaged with a high-magnification slit lamp with green filters.[25][26][27] With such high-magnification imaging systems, it is possible to see groups of individual red blood cells flowing in vivo.[25] Fundus cameras may also be used for low-magnification wide field-of-view imaging of the bulbar conjunctival microvasculature. Modified fundus cameras have been used to measure conjunctival blood flow [28] and to measure blood oxygen saturation.[24] Fluorescein angiography has been used to study the blood flow of the bulbar conjunctiva and to differentiate the bulbar conjunctival and episcleral microcirculation.[29][30][31]
Vasodilation
The bulbar conjunctival microvasculature is known to dilate in response to several stimuli and external conditions, including allergens (e.g. pollen),[32] temperature,[33] time-of-day,[33] contact-lens wear,[13] and acute mild hypoxia.[24] Bulbar conjunctival vasodilation has also been shown to correlate changes in emotional state.[34]
Type 2 diabetes is associated with an increase in average bulbar conjunctival vessel diameter and capillary loss.[11][12] Sickle-cell anemia is associated with altered average vessel diameter.[14]
Remove ads
See also
Additional images
- Sagittal section through the upper eyelid
- Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads