Colonial colleges
Nine oldest institutions of higher education in the United States From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The colonial colleges are nine institutions of higher education founded in the Thirteen Colonies, predating the United States. As the only American universities old enough to have alumni that participated in the American Revolution and the founding of the United States, these schools have been identified as a group for their influence on U.S. history.[1][2]
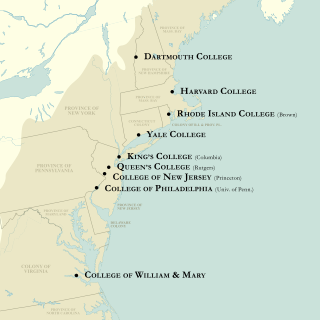
While all nine colonial colleges were founded as private institutions, two later became public universities: the College of William & Mary in 1906, and Rutgers University in 1945. The remaining seven are all members of the Ivy League and remain private to the present day: Harvard, Yale, Princeton, Columbia, Penn, Brown, and Dartmouth.
Nine colonial colleges
Summarize
Perspective
Seven of the nine colonial colleges began their histories as institutions of higher learning. The other two developed out of existing preparatory schools. The University of Pennsylvania, an Ivy League university in Philadelphia, began operating in 1751 as the Academy of Philadelphia, a secondary school founded by Benjamin Franklin, and later added an institution of higher education in 1755 following the granting of a charter to the College of Philadelphia. Dartmouth College, an Ivy League college in Hanover, New Hampshire, began operating in 1768 as the collegiate department of Moor's Charity School, a secondary school founded in 1754 by Eleazar Wheelock, the college's founder. Dartmouth considers its founding date to be 1769, when it was granted a collegiate charter.
| Image | Colonial college (present name, if different) |
Colony | Founded | Chartered | First instruction | First degrees | Primary religious influence | Ivy League |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Harvard College[nb 1] (Harvard University) |
Massachusetts Bay Colony | 1636 | 1650[3] | 1642 | 1642 | Puritan (Congregational)/Unitarian | Yes |
 |
College of William & Mary | Colony of Virginia | 1693[nb 2] | 1693[6] | 1694[7] | 1694 | Church of England[nb 3] (Episcopalian) |
No |
 |
Collegiate School (Yale University) |
Connecticut Colony | 1701 | 1701[8] | 1702 | 1702 honorary MA
1703 BA[9] |
Puritan (Congregational) | Yes |
 |
College of New Jersey (Princeton University) |
Province of New Jersey | 1746 | 1746[10] | 1747 | 1748 | Presbyterian but officially nonsectarian | Yes |
 |
King's College (Columbia University) |
Province of New York | 1754 | 1754[11] | 1754 | 1758[12] | Church of England with a commitment to "religious liberty."[13] | Yes |
 |
College of Philadelphia (University of Pennsylvania) |
Province of Pennsylvania | 1740 (college)[nb 4] | 1755[18] | 1755 | 1757 | Church of England but officially nonsectarian [19][nb 5] | Yes |
 |
College of Rhode Island[24] (Brown University) |
Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations | 1764 | 1764[25] | 1765[26] | 1765 | Baptist (but no religious requirement for admissions)[nb 6] | Yes |
 |
Queen's College (Rutgers University) |
Province of New Jersey | 1766 | 1766[27] | 1771 | 1774 | Dutch Reformed (Calvinist) | No |
 |
Dartmouth College | Province of New Hampshire | 1769 | 1769[28] | 1768 | 1771[nb 7] | Puritan (Congregational) | Yes |
Other colonial-era colleges and universities
Summarize
Perspective
Several other colleges and universities trace their founding to colonial-era academies or schools, but are not considered colonial colleges because they were not formally chartered as colleges with degree-granting powers until after the nation's founding in 1776. These include:
| Institution (present name, where different) | Colony or state | Founded | Chartered | Religious influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| King William's School (absorbed by St. John's College when the latter was founded) |
Province of Maryland | 1696 | 1784 | Church of England |
| Kent County Free School (absorbed by Washington College when the latter was founded) |
Province of Maryland | 1723 | 1782 | Nonsectarian |
| Bethlehem Female Seminary (Moravian University) |
Province of Pennsylvania | 1742 | 1863 | Moravian Church |
| Newark Academy (University of Delaware) |
Delaware Colony | 1743 | 1833 | Presbyterian, but officially nonsectarian after 1769 |
| Augusta Academy (Washington and Lee University) |
Colony of Virginia | 1749 | 1782 | Presbyterian, but officially non-sectarian |
| College of Charleston | Province of South Carolina | 1770 | 1785 | Church of England |
| Pittsburgh Academy (University of Pittsburgh) |
Province of Pennsylvania[nb 8] | 1770?[29] | 1787 | Nonsectarian |
| Little Girls' School (Salem College) |
Province of North Carolina | 1772 | 1866 | Moravian Church |
| Dickinson College | Province of Pennsylvania | 1773 | 1783 | Presbyterian |
| Hampden–Sydney College | Colony of Virginia | 1775 | 1783 | Presbyterian |
See also
- First university in the United States
- List of oldest universities in continuous operation
- Ancient universities, oldest universities in Great Britain and Ireland
- Ancient universities of Scotland, oldest universities in Scotland
- Imperial Universities, oldest universities founded during the Empire of Japan
- Sandstone universities, oldest universities in Australia
Notes
- The institution was founded in 1636 by a vote of the legislature of the colony to provide money for "a school or college" at Newtowne (the present Cambridge). Nothing further was done about creating a school until 1638, when John Harvard bequeathed money and books to the yet-uncreated college in his will. Construction began shortly thereafter on a school that was given the name of its first benefactor.
- The College of William & Mary sometimes asserts a connection with an attempt to found a "University of Henrico" at Henricopolis (also known as Henricus) in the Colony of Virginia, which received a charter in 1618; but only a small school for Native Americans had begun operation by 1622 when the town was destroyed in a Native American raid. A page on their website says, "The College of William & Mary [...] was the first college planned for the United States. Its roots go back to the College proposed at Henrico in 1619." However, it immediately notes, "The College is second only to Harvard University in actual operation."[4] Since William & Mary describes itself as "America's second-oldest college" and gives its year of founding as 1693, it does not seem to be suggesting institutional continuity with the University of Henrico, rather, W&M is providing historical perspective.[original research?] However, this depends upon the orientation and competitiveness of the administration at any given time; for instance, when a Harvard grad is President, Wm & M is presented as "second college", but when Va grad is president, it is "the first college in its roots"..[original research?] (This original college has been revived, in 1992, as "Henricus Colledge (1619), America's 1st College.".[5][failed verification]) William & Mary has a published list of its early graduates by its Swem Library.
- In the wake of the American Civil War, the College ceased to enroll students in 1882 due to attendant financial pressures. Students returned in 1888 after the Commonwealth of Virginia authorized $10,000 for it to become a state normal school for men. In 1906, it became a public, nonsectarian school with the college's royal charter still in effect, except where superseded by state or federal laws.
- There is some disagreement about Penn's date of founding as the university has never used its legal charter date for this purpose and, in addition, took the unusual step of changing its official founding date to approximately 150 years after the fact. The first meeting of the secondary school's founding trustees, which eventually became the University of Pennsylvania, took place in November 1749. Secondary instruction for boys at the Academy of Philadelphia began in August 1751. Undergraduate education for men began after a collegiate charter for the College of Philadelphia was granted in 1755. Penn initially designated 1750 as its founding date. Sometime later in its early history, Penn began to refer to 1749 instead. The school considered 1749 its founding date for more than a century until, in 1895, elite universities in the United States agreed that formal academic processions would place visiting dignitaries and other officials in the order of their institution's founding dates. Four years later, in 1899, Penn's board of trustees voted to retroactively revise the university's founding date from 1749 to 1740 to become older than Princeton, chartered in 1746. The premise for this revised founding date was that the Academy of Philadelphia purchased the building and assumed the educational mandate of an inactive trust which had originally hoped to open a charity school for indigent children. This was part of a 1740 project planned to comprise both a church and school, though, due to insufficient funding, only the church was built, and even it was never put into use. The dormant church building was conveyed to the Academy of Philadelphia in 1750.[14][15][16] To further complicate the comparison of founding dates, Princeton University has historical ties to an older college. Five of the twelve members of Princeton's first board of trustees were very closely associated with a "Log College" operated by Presbyterian minister William Tennent and his son Gilbert in Bucks County, Pennsylvania from 1726 until 1746.[17] Because the College of New Jersey and the Log College shared the same religious affiliation (a moderate element within the "New Side" or "New Light" wing of the Presbyterian Church) and there was a considerable overlap in their boards of trustees, some historians suggest that there is sufficient connection between this school and the College of New Jersey which would enable Princeton to claim a founding date of 1726. However, Princeton does not officially do so, and a university historian says that the "facts do not warrant" such a claim.[17]
- Penn's website, like other sources, makes an important point of Penn's heritage being nonsectarian, associated with Benjamin Franklin and the Academy of Philadelphia's nonsectarian board of trustees: "The goal of Franklin's nonsectarian, practical plan would be the education of a business and governing class rather than of clergymen.".[20] Jencks and Riesman (2001) write: "The Anglicans who founded the University of Pennsylvania, however, were evidently anxious not to alienate Philadelphia's Quakers, and they made their new college officially nonsectarian." Franklin himself was a self-described "thorough Deist." Starting in 1751, the same trustees also operated a Charity School for Boys, whose curriculum combined "general principles of Christianity" with practical instruction leading toward careers in business and the "mechanical arts",[21] and thus might be described as "non-denominational Christian." The charity school was originally planned and a trust was organized on paper in 1740 by followers of traveling evangelist George Whitefield. The school intended to operate inside a church supported by the same adherents. However, the organizers ran short of financing, and although the frame of the building was raised, the interior was left unfinished. The founders of the Academy of Philadelphia purchased the unused building in 1750 for their new venture and, in the process, assumed the original trust. Since 1899, Penn has claimed a founding date of 1740, based on the organizational date of the charity school and the premise that it had institutional identity with the Academy of Philadelphia. Whitefield was a firebrand Methodist associated with the Great Awakening; since the Methodists did not formally break from the Church of England until 1784, Whitefield in 1740 would be labelled Episcopalian, and in fact Brown University, emphasizing its own pioneering nonsectarianism, refers to Penn's origin as "Episcopalian".[22] Penn is sometimes assumed to have Quaker ties (its athletic teams are called "Quakers," and the cross-registration alliance between Penn, Haverford, Swarthmore and Bryn Mawr is known as the "Quaker Consortium.") But Penn's website does not assert any formal affiliation with Quakerism, historical or otherwise, and Haverford College implicitly asserts a non-Quaker origin for Penn when it states that "Founded in 1833, Haverford is the oldest institution of higher learning with Quaker roots in North America."[23]
- Brown's website characterizes it as "the Baptist answer to Congregationalist Yale and Harvard; Presbyterian Princeton; and Episcopalian Penn and Columbia," but adds that at the time it was "the only one that welcomed students of all religious persuasions."[22] Brown's charter stated that "into this liberal and catholic institution shall never be admitted any religious tests, but on the contrary, all the members hereof shall forever enjoy full, free, absolute, and uninterrupted liberty of conscience." The charter further required that its president and twenty-two of the thirty-six trustees be Baptists and that the remainder consist of "five Friends, four Congregationalists, and five Episcopalians"[citation needed]
- Dartmouth College began operating during 1768 as the collegiate department of Moor's School (1754) in Columbia, Connecticut. The collegiate department was being described in writing as "Dartmouth College" by January of 1769 when the Township of Hanover, New Hampshire voted to offer it a grant of land. The institution received a royal charter on December 13, 1769, and its students moved from Columbia to Hanover in October 1770. The first degrees were awarded in August 1771. Queen's College, although granted a charter earlier, began operation in 1771 after Dartmouth College began awarding degrees.
- Although most early records of the university were destroyed in the Great Fire of 1845 as well as a subsequent fire in 1849, it is known that the school began its life as a preparatory academy, possibly as early as 1770,[29] or at some point in the 1780s.[30][31] Presumably starting its life in a log cabin[32] on what was then the nation's frontier, Hugh Henry Brackenridge sought and obtained a charter for the school from the state legislature of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania that was passed by the assembly on February 28, 1787. The school's charter was altered in 1819 to grant it university status and confer the name of the Western University of Pennsylvania. The university received its current name, the University of Pittsburgh, with a subsequent alteration to its charter in 1908.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
