Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
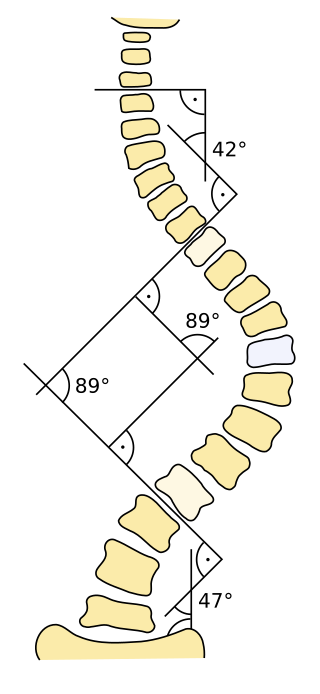
Cobb angle
Measurement of scoliosis From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Cobb angle is a measurement of bending disorders of the vertebral column such as scoliosis and traumatic deformities.

Definition and method
It is defined as the greatest angle at a particular region of the vertebral column, when measured from the superior endplate of a superior vertebra to the inferior endplate of an inferior vertebra.[1] However, the endplates are generally parallel for each vertebra, so not all sources include usage of a superior versus inferior endplate in the definition.[2]
Unless otherwise specified it is generally presumed to refer to angles in the coronal plane, such as projectional radiography in posteroanterior view. In contrast, a sagittal Cobb angle is one measured in the sagittal plane such as on lateral radiographs.[3]
Cobb angles are preferably measured while standing, since laying down decreases Cobb angles by around 7–10°.[4]
Remove ads
Uses
It is a common measurement of scoliosis.
The Cobb angle is also the preferred method of measuring post-traumatic kyphosis in a recent meta-analysis of traumatic spine fracture classifications.[5]
Severity
Those with Cobb angle of more than 60° usually have respiratory complications.[7]
Scoliosis cases with Cobb angles between 40 and 50 degrees at skeletal maturity progress at an average of 10 to 15 degrees during a normal lifetime. Cobb angles of more than 50 degrees at skeletal maturity progress at about 1 to 2 degrees per year.[8]
History
The Cobb angle is named after the American orthopedic surgeon John Robert Cobb (1903–1967). It was originally used to measure coronal plane deformity on radiographs with antero-posterior projection for the classification of scoliosis.[9] It has subsequently been adapted to classify sagittal plane deformity, especially in the setting of traumatic thoracolumbar spine fractures.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads