Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
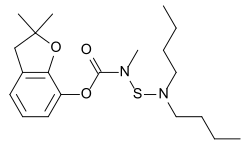
Carbosulfan
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Carbosulfan is an organic compound adherent to the carbamate class. At normal conditions, it is brown viscous liquid. It is not very stable; it decomposes slowly at room temperature. Its solubility in water is low but it is miscible with xylene, hexane, chloroform, dichloromethane, methanol and acetone. Carbosulfan is used as an insecticide.[1] The European Union banned use of carbosulfan in 2007.[2]
Its oral LD50 for rats is 90 to 250 mg/kg bw, inhalation LC50 is 0.61 mg/L. Carbosulfan is only slightly absorbed through skin (LD50 >2000 mg/kg for rabbits). The mechanism of toxicity is based on reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (as for carbamates generally).[3] Carbosulfan has very low maximum residue limits for use in the EU and UK examples of this can be seen in apples and oranges, where it is 0.05 mg/kg.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads