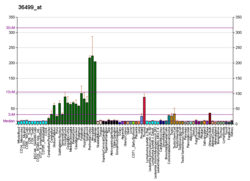
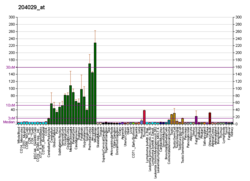
CELSR2
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CELSR2 gene.[5][6]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. The flamingo subfamily consists of nonclassic-type cadherins; a subpopulation that does not interact with catenins. The flamingo cadherins are located at the plasma membrane and have nine cadherin domains, seven epidermal growth factor-like repeats and two laminin A G-type repeats in their ectodomain. They also have seven transmembrane domains, a characteristic unique to this subfamily. It is postulated that these proteins are receptors involved in contact-mediated communication, with cadherin domains acting as homophilic binding regions and the EGF-like domains involved in cell adhesion and receptor-ligand interactions. The specific function of this particular member has not been determined.[6]
See also
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.