Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Butalbital
Barbiturate drug used for headaches From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
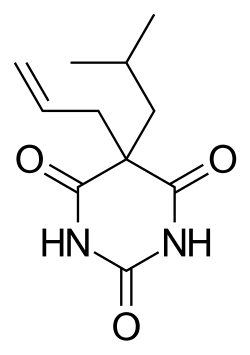
Butalbital is a barbiturate with an intermediate duration of action. Butalbital is often combined with other medications, such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) (as butalbital/acetaminophen) or aspirin, for the treatment of pain and headache. The various formulations combined with codeine are FDA-approved for the treatment of tension headaches. Butalbital has the same chemical formula as talbutal but a different structure—namely, 5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid.[3]
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2025) |
Remove ads
Available forms
This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2025) |
Combinations include:[citation needed]
- Butalbital/acetaminophen, Butalbital and acetaminophen (paracetamol), (trade names: Axocet, Bucet, Bupap, Cephadyn, Dolgic, Phrenilin, Forte, Sedapap)
- Butalbital/paracetamol/caffeine (trade names: Fioricet, Esgic, Esgic-Plus, Orbivan, Fiormor, Fiortal, Fortabs, Laniroif)
- Butalbital/caffeine/codeine (trade name: Fioricet#3 with Codeine)
- Butalbital/aspirin (trade name: Axotal)
- Butalbital/aspirin/caffeine (trade name: Fiorinal)
- Butalbital/aspirin/caffeine/codeine (trade name: Fiorinal#3 with Codeine)
- Ergotamine/caffeine/butalbital/belladonna alkaloids (trade name: Cafergot-PB)
Remove ads
Contraindications
There are specific treatments which are appropriate for targeting migraines and headaches.[4] Butalbital is not recommended as a first-line treatment because it impairs alertness, brings risk of dependence and addiction, and increases the risk that episodic headaches will become chronic.[5] When other treatments are unavailable or ineffective, butalbital may be appropriate if the patient can be monitored to prevent the development of chronic headache.[5]
Remove ads
Side effects
This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2025) |
Side effects for butalbital is usually well tolerated. Commonly reported side effects for butalbital, some of which tend to subside with continued use, include:[citation needed]
- Dizziness
- Respiratory depression
- Drowsiness
- Intoxicated feeling
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Sedation
- Euphoria
- Severe impairment of judgment
- Diarrhea
- Memory Loss
- Constipation
Rare side effects include Stevens–Johnson syndrome, an adverse reaction to barbiturates, and anaphylaxis.
The risk and severity of all side effects is greatly increased when butalbital are combined with other sedatives (e.g., alcohol, opioids, benzodiazepines, antihistamines). Butalbital when taken with sedatives can cause life-threatening respiratory depression and death. Inhibitors of the hepatic enzyme CYP3A4 may also increase the risk, severity, and duration of side effects, many drugs inhibit this enzyme as do some foods such as grapefruit and the blood orange.[citation needed]
Butalbital can cause dependence or addiction.[citation needed]
Interactions
This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2025) |
Mixing with alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other depressants increases the risk of intoxication, increases respiratory depression, and increases liver toxicity when in combination with paracetamol (acetaminophen). Use of butalbital and alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other depressants can contribute to coma, and in extreme cases, fatality.[citation needed]
Remove ads
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads