Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Bucharest Henri Coandă International Airport
Airport in Romania From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
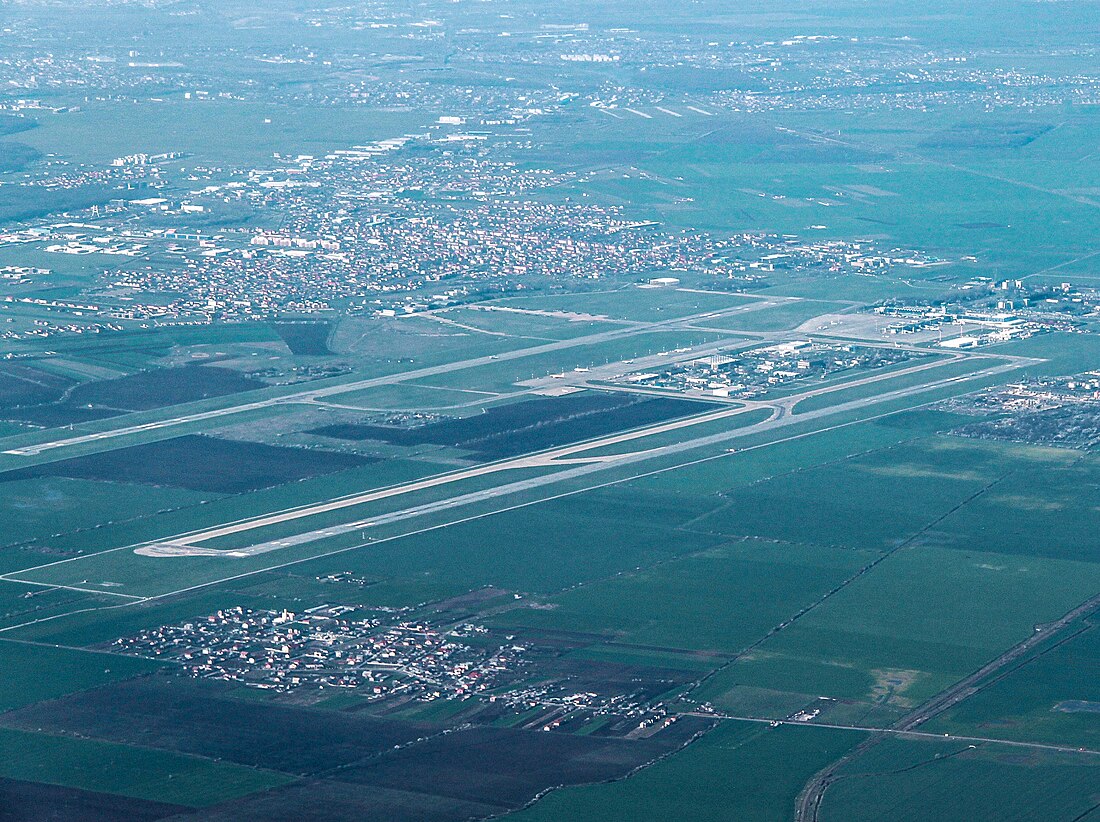
Bucharest Henri Coandă International Airport (Romanian: Aeroportul Internațional Henri Coandă București) (IATA: OTP, ICAO: LROP) is Romania's busiest international airport, located in Otopeni, 16.5 km (10.3 mi) north of Bucharest's city centre.[1] It is currently one of the two airports serving the capital of Romania. The other is the smaller Aurel Vlaicu Airport, used mostly for private flights. The airport covers 605 hectares (1,495 acres) of land and contains two parallel runways, both 3,500 meters long.[3]
Remove ads
The airport is named after Romanian flight pioneer Henri Coandă, builder of Coandă-1910 aircraft and discoverer of the Coandă effect of fluidics. Prior to May 2004, the official name was Bucharest Otopeni International Airport (Romanian: Aeroportul Internațional București Otopeni). Henri Coandă International Airport serves as headquarters for TAROM, the country's national airline.[4] It also serves as a base of operations for low-cost airlines Animawings, HiSky, Ryanair and Wizz Air. It is managed by The National Company Bucharest Airports S.A. (Compania Națională Aeroporturi București S.A.).[5] The military section of the airport is used as the 90th Airlift Base of the Romanian Air Force.
Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Early years

Originally, the airport in Otopeni was intended to be used as a Romanian civil aviation and military training center. During World War II, it was used as an airbase by the Luftwaffe. It was further developed in 1943, becoming one of the principal Luftwaffe bases around Bucharest. By 1944, it featured a beam approach system and two concrete runways, one of 1,370 metres (4,490 ft) aligned North-South and one of 1,190 metres (3,900 ft) aligned East-West.[6] After 23 August 1944, the airport was used to launch air raids on Bucharest in support of the German efforts to overthrow the new government.[7] It was bombed by the USAAF on 26 August and taken over by the Romanian military in the aftermath.[8][9]
Until 1965, it was a major airfield for the Romanian Air Force, with Băneasa Airport serving as Bucharest's commercial airport. In 1965, with the growth of air traffic, the Otopeni airbase was converted to a commercial airport. The runway was modernized and extended to 3,500 metres (11,500 ft) from the previous 1,200 metres (3,900 ft), making it one of the longest in Europe at that time.[10]
In August 1969, when United States President Richard Nixon visited Romania, a VIP lounge was inaugurated. A new passenger terminal (designed by Cezar Lăzărescu), with a capacity of 1,200,000 passengers per year, was opened on 13 April 1970, for domestic and international flights.[10] An improvement program added a second runway in 1986, expanding capacity to 35 aircraft movements per hour.[10]
In 1992, Otopeni Airport became a regular member of Airports Council International (ACI).
Expansion since the 1990s
The first stage of the plan (Phase I), taking place between 1994 and 1998, involved the construction of a new departures terminal and of a new airside concourse with five jetways and nine gates (referred to as 'the Finger') as well as the extension of airport ramps and of their associated taxiways.[11]
The second phase (labeled Phase II/IIe) of the plan led to the construction of a terminal dedicated to domestic flights and of a multi-story car park (2003), the complete overhaul of the control tower (between 2005 and 2007) as well as the transformation of the old terminal building into a dedicated arrivals hall (in 2000). During the same phase, two high-speed taxiways (Victor and Whiskey) were constructed. Phase II was completed in 2007.[11]
TAROM ended its unprofitable service to New York City in November 2003.[12][13][14] In June 2007, Delta Air Lines began flying the same route with Boeing 767s.[15] The company made the link seasonal in 2008.[16] Delta terminated it in September 2009 due to the recession and difficulty competing with other airlines.[17] HiSky has commenced service to New York in June 2024, reconnecting Bucharest to the United States.[18]
The third stage of the plan (Phase III), which started in 2009, involved the extension of the airside concourse ('the Finger') with 15 new gates (nine of which have jetways), as well as the expansion of the Departure Hall (with 8 new gates). The airside concourse extension, designed by Studio Capelli Architettura & Associati, and measuring 17,000 square metres (200,000 sq ft), was inaugurated on 29 March 2011.[11][19] It was followed, in November 2012, by the extension of the Departure Hall to a total area of 38,600 square metres (400,000 sq ft).[20][21]
In March 2012, all air traffic except for business air traffic was transferred from Aurel Vlaicu International Airport (at that time Bucharest's low-cost hub) to Henri Coandă International Airport.[citation needed] Air Canada Rouge introduced seasonal routes to Toronto and Montreal in June 2018. The carrier operated the flights with Boeing 767s.[22][23]
Future development
Beyond Phase III, a new terminal building (Henri Coandă 2) at the eastern end of the current location is envisaged. The new building is expected to include a large commercial space.[24] Henri Coandă 2 will be of a modular design, consisting of four separate buildings, each capable of handling 5 million passengers annually. Each module will be built as traffic demands dictate. By 2030, Terminal 2 alone should be able to handle the expected volume of 20 million passengers per year. The terminal will be directly connected to the A3 motorway and to the railway system. However, the plans might get delayed due to funding problems.
On 18 January 2021, it has been announced that the airport purchased all the land it needs in order to begin the expansion.[25][26] However, on 15 May 2023, the Minister of Transport and Infrastructure declared that a new terminal will not be built in the near future, because it is not necessary,[27] a declaration which sparked criticism.[28]
Remove ads
Terminals
The airport's facilities consist of a single terminal with three main facilities (colloquially referred to as "Terminals"): the Departures Hall/Terminal, the Arrivals Hall/Terminal, and the Finger Terminal (the airside concourse).[29] A walkway with shops connects the departures and arrivals buildings. The airside concourse is organized in two (domestic and international) passengers flows.[30] The entire terminal has 104 check-in desks, 38 gates (of which 14 are equipped with jetways),[20] and a total floor area of 86,000 square metres (930,000 sq ft).[10][19][21]
Remove ads
Airlines and destinations
Summarize
Perspective
Passenger
The following airlines operate regular scheduled and charter flights at Bucharest Henri Coandă Airport:
Cargo
Remove ads
Statistics
Summarize
Perspective



Passengers
In 2018, 13,824,830 passengers passed through the airport, an increase of 7.95% compared to 2017.[140] In 2018, the airport handled 13.8 million passengers (63.3% of the total number of passengers carried by Romanian airports) and 39,534 tons of cargo (81.4% of the total amount of cargo handled by Romanian airports).[141]
Busiest routes
Busiest Airlines
Remove ads
Ground transportation
Summarize
Perspective
Rail

An airport rail link service to the main railway station, Gara de Nord (Bucharest North), runs from the Airport railway station located near the parking lot of the Arrivals hall.[147] As of August 2021, the trains, alternately operated by CFR and TFC depart every 40 minutes, seven days a week. A one-way trip takes 15–20 minutes.[147]
A new Metro Line M6 is also planned, connecting the airport to the Gara de Nord train station, and integrating the airport into the Bucharest Metro network.[148]

Bus
Henri Coandă Airport is connected to the public transport company STB system. The 100 route provides 24/7 express bus service to the city center (Piața Unirii).[149]
Car
The airport is 16.5 km (10.3 mi) north of central Bucharest, to which it is connected by the DN1 national road. The DN1 also connects the airport with the nearby A0 motorway. The A3 motorway will connect the future terminal 2 and the city.
Taxi and ride-share
As of May 2013, taxis serving Henri Coandă Airport can be ordered using a touch screen system in the arrivals terminal, allowing the taxi drivers to enter the pick-up area. This measure was taken after many complaints from passengers who were being overcharged when using illegal, high-price taxis.[150] Uber and Bolt are also available at the airport.
Remove ads
Incidents and accidents
- On 9 February 1989, a TAROM Tupolev TU-154 crashed during a training flight following a simulated engine failure when a flight crew member raised the flaps too soon. All 5 occupants were killed.[151]
- On 31 March 1995, TAROM Flight 371, an Airbus A310-324 registered as YR-LCC, simultaneously experienced asymmetric thrust during climb and one of the pilots being incapacitated. The plane crashed near Balotești just two minutes after takeoff. All 60 people aboard were killed.[152]
- On 30 December 2007, a TAROM Boeing 737-300 (YR-BGC "Constanța"), flying Flight 3107 hit a car on the runway while taking off for Sharm-el-Sheikh. The aircraft stopped beside the runway and was severely damaged.[153]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads