Bezafibrate
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Bezafibrate (marketed as Bezalip and various other brand names) is a fibrate drug used as a lipid-lowering agent to treat hyperlipidaemia. It helps to lower LDL cholesterol and triglyceride in the blood, and increase HDL.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a682711 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.498 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H20ClNO4 |
| Molar mass | 361.82 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
It was patented in 1971 and approved for medical use in 1978.[1]
Medical uses
Bezafibrate improves markers of combined hyperlipidemia, effectively reducing LDL and triglycerides and improving HDL levels.[2] The main effect on cardiovascular morbidity is in patients with the metabolic syndrome, the features of which are attenuated by bezafibrate.[3] Studies show that in patients with impaired glucose tolerance, bezafibrate may delay progress to diabetes,[4] and in those with insulin resistance it slowed progress in the HOMA severity marker.[5] In addition, a prospective observational study of dyslipidemic patients with diabetes or hyperglycemia showed that bezafibrate significantly reduces haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) concentration as a function of baseline HbA1c levels, regardless of concurrent use of antidiabetic drugs.[6]
Side-effects
The main toxicity is hepatic (abnormal liver enzymes); myopathy and on rare occasions rhabdomyolysis have been reported.
Other uses
The Australian biotech company Giaconda combines bezafibrate with chenodeoxycholic acid in an anti-hepatitis C drug combination called Hepaconda.
Bezafibrate has been shown to reduce tau protein hyperphosphorylation and other signs of tauopathy in transgenic mice having human tau mutation.[7]
The combination of a cholesterol-lowering drug, bezafibrate, and a contraceptive steroid, medroxyprogesterone acetate, could be an effective, non-toxic treatment for a range of cancers, researchers at the University of Birmingham have found.[8]
Mode of action
Like the other fibrates, bezafibrate is an agonist of PPARα; some studies suggest it may have some activity on PPARγ and PPARδ as well.[9]
Synthesis
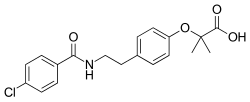
Further evidence that substantial bulk tolerance is available in the para position is given by the lipid lowering agent bezafibrate.

The p-chlorobenzamide of tyramine undergoes a Williamson ether synthesis with ethyl 2-bromo-2-methylpropionate to complete the synthesis. The ester group is hydrolyzed in the alkaline reaction medium.
History
Bezafibrate was first introduced by Boehringer Mannheim in 1977.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
