Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
List of places on land with elevations below sea level
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This is a list of places on land below mean sea level.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2009) |

Places artificially created such as tunnels, mines, basements, and dug holes, or places under water, or existing temporarily as a result of ebbing of sea tide etc., are not included. Places where seawater and rainwater is pumped away are included. Fully natural places below sea level require a dry climate; otherwise, rain would exceed evaporation and fill the area.
All figures are in meters below mean sea level (as locally defined), arranged by depth, lowest first:
Remove ads
Africa
Remove ads
Antarctica
Asia
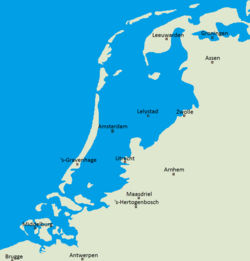
Europe
Remove ads
North America

Remove ads
Oceania
South America
Remove ads
Historic and ice-covered areas
Deeper and larger than any of the trenches in the list above is the Bentley Subglacial Trench in Antarctica, at a depth of 2,540 m (8,330 ft). It is subglacial, covered permanently by the largest glacier in the world. Therefore, it is not included in any list on the page. If the ice melted it would be covered by sea.
The biggest dry land area below sea level that has been known to exist during the geological past, as measured by continuous volume of atmospheric air below sea level, was the dry bed of the Mediterranean Sea of the late Miocene period during the Messinian salinity crisis.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads