Army Museum (Paris)
Art museum, Historic site, Military museum in rue de Grenelle, Paris From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Musée de l'Armée (French: [myze də laʁme]; "Army Museum") is a national military museum of France located at Les Invalides in the 7th arrondissement of Paris. It is served by Paris Métro stations Invalides, Varenne and La Tour-Maubourg
 Musée de l'Armée, Paris. | |
 | |
| Established | 1905 |
|---|---|
| Location | Hôtel national des Invalides, 129 rue de Grenelle, 75007 Paris |
| Coordinates | 48°51′25″N 2°18′46″E |
| Type | Art museum, Historic site, Military museum |
| Visitors | 1,252,095 (2019), 1,071,072 (2022) |
| Director | Henry de Medlege (since August 2020) |
| Public transit access | Invalides Varenne La Tour-Maubourg Invalides |
| Website | musee-armee |
The Musée de l'Armée was created in 1905 with the merger of the Musée d'Artillerie and the Musée Historique de l'Armée.[1] The museum's seven main spaces and departments contain collections that span the period from antiquity through the 20th century.
History
Summarize
Perspective
The Musée de l'Armée was created in 1905 with the merger of the Musée d'Artillerie and the Musée Historique de l'Armée.[1] The Musée de l'artillerie (Museum of Artillery – "artillerie" meaning all things related to weapons) was founded in 1795 in the aftermath of the French Revolution, and expanded under Napoleon. It was moved into the Hôtel des Invalides in 1871, immediately following the Franco-Prussian War and the proclamation of the Third Republic. Another institution called the Musée historique de l'Armée (Historical Museum of the Army) was created in 1896 following the Paris World Fair. The two institutions merged in 1905 within the space of the former Musée de l'Artillerie. Today, it holds 500,000 artifacts, including weapons, armour, artillery, uniforms, emblems and paintings, exhibited in an area of 12,000 m2. The permanent collections are organised into "historical collections", representing a chronological tour from ancient times through the end of World War II.
In March 1878, the museum hosted an "ethnographic exhibition", as it was called, which represented the main "types" of Oceania, America, Asia and Africa. Dummies representing people from the colonies, along with weapons and equipment, were the main attraction. The exhibit, organised by Colonel Le Clerc, attempted to demonstrate theories of unilineal evolution, putting the European man at the apex of human history.[2] Parts of this collection began to be transferred to the Ethnographic Museum of the Trocadéro in 1910 and in 1917; the last colonial rooms were closed just after the 1931 Paris Colonial Exhibition.[2] All remnants were transferred after the Second World War.[2]
Significant holdings
The Musée de l'Armée has identified 24 aesthetic, technical and symbolic "treasures," which are all closely linked to French military history from the late Middle Ages through to World War II. They include weapons, armour, works of arts and technology.[3]
Main spaces
Summarize
Perspective
The museum consists of six main spaces.
Main Courtyard and artillery collections


The Main Courtyard is the centre of the Hôtel National des Invalides and displays a large part of the artillery collections, gathered during the French Revolution. The collection traces 200 years of the history of French field artillery and enables visitors to discover how the equipment was manufactured, its role and the history of great French artillerymen.[4]
Contains:
- 60 French classical bronze cannons
- A dozen howitzers and mortars
Armour and weapons, 13th–17th centuries


The Musée de l'Armée has a rich ancient collection, which makes it one of the three largest arms museums in the world.[5]
Contains:
- The Royal Room: crown collections
- The Medieval Room: artifacts from the feudal army to the royal army
- The Louis XIII Room: the progress of the royal army)
- A Themed Arsenal Gallery
- An exhibit on Courtly Leisure Activities (late Middle Ages to mid-17th century)
- some rooms of antique and oriental armament
Modern Department, from Louis XIV to Napoleon III, 1643–1870
This department covers the military, political, social and industrial history of France, reliving great battles, exploring the lives of soldiers, and tracing the development of technologies and tactics.[6]
Contains:
- Privates' uniforms
- Luxury weapons and arms
- Equipment of numerous French and foreign regiments
- Illustrious figures, such as Napoleon Bonaparte and his marshals[6]
Contemporary Department, the Two World Wars 1871–1945

The contemporary department tells the story of the French Army from 1871 to 1945, and the two great conflicts of the 20th century.[7]
Contains:
- French and foreign uniforms, including some having belonged to illustrious military leaders (Foch, Joffre, de Lattre, Leclerc, etc.)
- Objects used by soldiers in daily life
- Prestige pieces: marshals' batons and ceremonial swords:
- Emblems, paintings and elements from personal archives: letters, postcards, etc.[7]
The Charles de Gaulle Monument

The Charles de Gaulle Monument (Historial) is an interactive multimedia space dedicated to the work of Charles de Gaulle, the leader of the Free French Forces and founding President of the Fifth Republic.[8]
Contains:
- The Multi-Screen Room
- The Ring: "an overview of the century" projected onto a circular glass ring
- The Permanent Exhibition[8]
Cabinets insolites
Three cabinets are dedicated to special collections.
Contains:
- Artillery models from the 16th to 19th c.
- Military music instruments, selected among the 350 of the collection
- Military figurines, with 5000 toy soldiers displayed of a collection of 140000
The Army museum is associated with four additional spaces:
Musée de l'Ordre de la Libération
The museum is dedicated to the Ordre de la Libération, France's second national order after the Légion d'honneur, which was created in 1940 by General Charles de Gaulle, leader of the Free French Forces.
Contains three galleries:
- Free France
- Interior Resistance
- Deportation
Musée des Plans-Reliefs
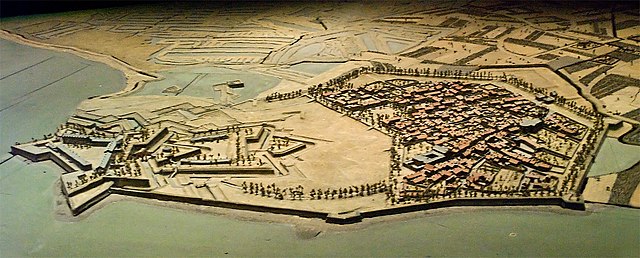
The Musée des Plans-Reliefs is a museum of military models located within the Musée de l'Armée. About 100 models, created between 1668 and 1870, are currently on display in the museum. The construction of models dates to 1668 when the Marquis de Louvois, minister of war to Louis XIV, began a collection of three-dimensional models of fortified cities for military purposes, and kept growing until 1870 with the disappearance of fortifications bastionnées.
Cathedral of Saint-Louis des Invalides

In 1676, the Secretary of State for War, Marquis de Louvois, entrusted the young architect Jules Hardouin-Mansart with the construction of the chapel, which Libéral Bruant had been unable to complete. The architect designed a building which combined a royal chapel, the "Dôme des Invalides", and a veterans' chapel.[9] This way, the King and his soldiers could attend mass simultaneously, while entering the place of worship though different entrances, as prescribed by etiquette. This separation was reinforced in the 19th century with the erection of the tomb of Napoleon I, the creation of the two separate altars and then with the construction of a glass wall between the two chapels.[9]
Contains:
- The Veteran's Chapel[9]
Dôme des Invalides
The Dôme des Invalides is the emblem of the Hôtel National des Invalides and an unmissable monument in the Parisian landscape.[10]
Contains:
- The Dome Church
- The Tomb of Napoleon I[10]
Collection
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Musée de l'Armée.
- The Sword of François I (16th century)
- Olifant carved in an elephant tusk
- Hunting crossbow
- Set of cold weapons
- Powder flask (Mid-16th century)
- Priming flask (Circa. 1600)
- The Saint-Gilles gun (1507)
- Culverin called Wurtembourgeoise (End-16th century)
- Bronze cannon said to be of Cardinal Richelieu, ca. 1600)
- The Qianlong Emperor's armour (18th century)
- 37 mm TRP Mle 1916 rapid-fire infantry cannon
- Taxi de la Marne (1914)
- Renault FT17 tank (1917)
- V-2 missile (1940s)
- Luger pistol used in the (1930s)
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.















