Antoinette military monoplane
1910s French military aircraft prototype From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
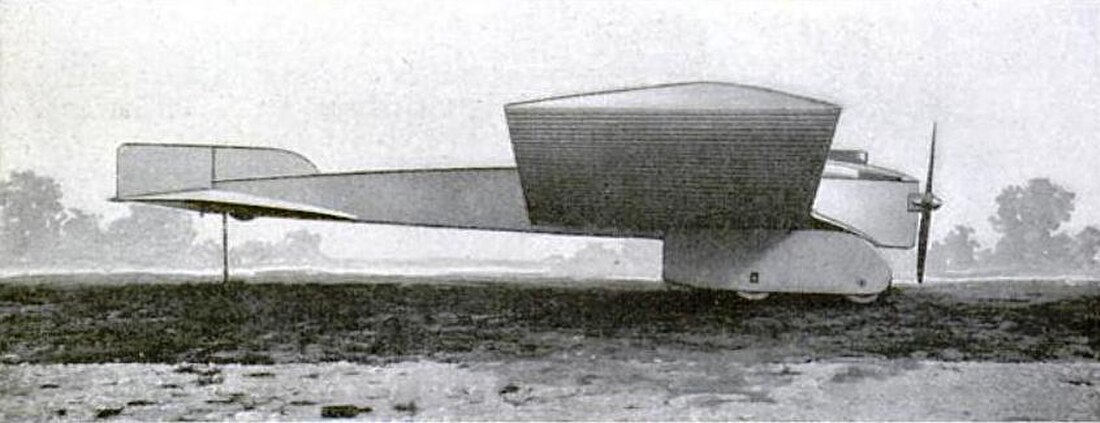
The Antoinette military monoplane, also known as the Antoinette Monobloc or the Antoinette-Latham was an early 3-seat monoplane built in France in 1911 by the Antoinette company in the hope of attracting orders from the French military. It featured a futuristic and aerodynamic design with innovative elements that were ahead of its time, including unbraced cantilever wings, an enclosed fuselage and wheel fairings, and an engine with steam cooling and direct fuel injection. However, due to an under-powered engine, it was barely able to fly and failed to attract orders.
| "Military monoplane" | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General information | |
| Type | Prototype military aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Antoinette |
| Designer | Léon Levavasseur and Jules Gastambide |
| Number built | 1 |
| History | |
| First flight | 1911 |
Design
Summarize
Perspective
Aerodynamic streamlining
Designed by Léon Levavasseur and Jules Gastambide, and baptized with the name "Monobloc", the aircraft featured a number of innovative aerodynamic refinements for its time. The design was characterized by an enclosed and streamlined body and wings. The design reduced air resistance by the absence of any external bracing wires, and by having its control cables totally enclosed within its quadrangular-section fuselage and large wooden cantilever wings.[1]
Wings
The wooden wings were 70 cm thick at the base and 25 cm at the ends, with internal bracing and built around four square steel spars. The main spar was 70 cm high and fixed at the front third of the wing; the others (i fore, 2 aft) hinged in the middle of their axes, allowing the wings to 'warp' to provide lateral control of the machine. These were controlled by the pilot by a distortable frame which could be pushed for-and-aft or side-to-side for controlling the wing warping.[1][2]
The spars were supported by ribs spaced 40 cm apart; the wings, fully loaded, were designed to bear about 25 kg per m2 — when the current aircraft of the time only were designed to bear 15 kg/m2. The chord of each wing was 4 metres at the junction with the fuselage, and decreased to 3 metres at the wing tip. The upper side of the wing's airfoil was cambered, while the under side was very flat, with the leading and trailing edges being quite sharp.[2][3][4] The tailplane included a long, low fin and a large rectangular rudder that could be enlarged by an extension.[5]

Fuselage
The streamlined fuselage was decked over with wood frames and tight canvas, with only the cylinder-head of the engine exposed. The fuselage terminated at the front by a bow shaped like that of a boat. The crew compartment had three seats lined up and was closed, so access was through a door under the fuselage. Seated at the front was the mechanic, who had easy direct access to the engine at the front. Behind him, the pilot had a good range of vision, with windows in the floor enabling him to see beneath him. An observer sat behind the pilot in the rear.[2][4][5][6]
Wheel fairings
The enclosure of the aircraft's fixed landing gear by streamlined fairings or "spats" was viewed as a remarkable innovation in 1911.[7] Each fairing consisted of a canvas-covered structure containing a large double main wheel on a flexibly sprung axle, and a smaller wheel placed forward to avoid nose-overs on landing.[1][3][5][7] A similar arrangement was used by the Coandă 1911 twin-Gnôme engine monoplane.[7]
Engine
Acting as a radiator, a network of copper tubes running along the fuselage cooled the Antoinette 8V engine of 50 to 60 hp (according to different sources).[3][5][6] For the 1911 military contest at Reims in September-October 1911 a larger V12 engine of 100 hp was fitted. This was cooled by steam — heated water evaporated in the cylinder jackets and then condensed in copper tubing attached to the outside of the aircraft. The engine had two valves per cylinder, a mechanically operated exhaust valve and an automatic inlet valve. Instead of a carburetor, two fuel pumps delivered fuel to the inlet valve chambers.[8]
A larger engine of V16 configuration and 120 hp was planned,[2] but this may not have been possible due to limited space between the engine and the crew's entry hatch located underneath the fuselage.[9]
Reims French Army military trials 1911
The aircraft was exhibited at Le Grand Concours d'Aviation Militaire at Reims in September 1911 in the hope of attracting orders from the French military. Organized by the French Army, this competition required that the aircraft and engines be fully built in France, and be able to fly without stop on a closed circuit of 300 km with a 300 kg load (not including oil, water and fuel) at a speed of more than 60 km/h. Additionally, they were to be 3-seaters, and be able to take-off and land from unprepared surfaces. The first prize was 700,000 francs plus additional sums for increases in speed over 60 km/h, as well as a commitment by the military to purchase 10 aircraft. The competition attracted the major French aircraft manufacturers of the time, including Blériot, Farman, Deperdussin and Nieuport.[2]
Despite the fitting of a more powerful V12 engine of 100 hp[8] and a smaller 16 litre fuel tank, Antoinette's Monobloc entry was under-powered and, though it may have managed a short hop of several metres, it was unable to successfully fly. It failed to attract any orders, and following this setback, the Antoinette company soon went into bankruptcy.[5]
Specifications
Data from collated from various sources listed below
General characteristics
- Crew: Three: pilot, observer and mechanic
- Capacity: 500 kgs
- Length: 11.5 m (37 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 15.9 m (52 ft 2 in)
- Height: 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in)
- Wing area: 56 m2 (600 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 850–935 kg (1,874–2,061 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,250 kg (2,756 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Antoinette 8V V-8 water-cooled piston engine, 37–75 kW (50–100 hp) (hp varies according to different sources)
- Propellers: Antoinette
- Maximum speed: 150 km/h (93 mph, 81 kn) projected
- Cruise speed: 80 km/h (50 mph, 43 kn)
- Wing loading: 25 kg/m2 (5.1 lb/sq ft)
See also
- Gastambide-Mengin monoplane
- Antoinette III
- Antoinette IV
- Antoinette V
- Antoinette VI
- Antoinette VII
- Fedor Ivanovich Bylinkin, designer of a similar aircraft, 1910
Related lists List of aircraft (pre-1914)
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.