Ankistrodesmus
Genus of algae From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae.[2] It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world.[3] The name Ankistrodesmus comes from the Greek roots ankistron, meaning "cross", and desmos, meaning "bond".[4]
| Ankistrodesmus | |
|---|---|
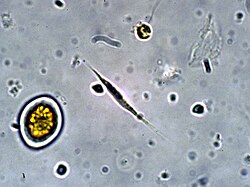 | |
| Ankistrodesmus falcatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | Viridiplantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Chlorophyceae |
| Order: | Sphaeropleales |
| Family: | Selenastraceae |
| Genus: | Ankistrodesmus Corda |
| Type species | |
| Ankistrodesmus fusiformis Corda[1] | |
| Species[2] | |
|
See text | |

Description
Summarize
Perspective
Ankistrodesmus forms colonies of cells, usually found as loose bundles or tufts of cells. Sometimes the cells may twist around each other in the colony. Cells are many times longer than wide, and are variously needle-shaped, sickle-shaped, or sigmoid in outline. They contain a single chloroplast; the chloroplast usually contains a single pyrenoid, but may contain none or several pyrenoids.[3]
Life cycle
Reproduction occurs asexually; sexual reproduction is unknown in Ankistrodesmus. It exclusively forms autospores, and does not appear to have a flagellated stage in its life cycle.[1]
Some strains of Ankistrodesmus have been observed to undergo programmed cell death. The evolutionary role of this process is unknown.[5]
Identification
Ankistrodesmus is chiefly distinguished from the similar genus Monoraphidium in its habit: Ankistrodesmus forms colonies, while Monoraphidium is found as single cells.[6] Meanwhile, Selenastrum differs in having more strongly curved cells.[1] The distinctions between the genera are artificial, since they do not correspond with monophyletic groupings;[7] occasionally, Ankistrodesmus is found as single cells.[6] Other similar genera include Keratococcus and Elakatothrix.[3]
Identification of species chiefly depends on details of the size and shape of cells.[1] However, a molecular phylogenetic study has shown evidence of considerable cryptic diversity.[8]
Uses
Some strains of Ankistrodesmus are promising candidates for biodiesel production, or for producing fatty acids on a commercial scale.[9]
Species
- A. acerosus
- A. acutissimus
- A. amalloides
- A. antarcticus
- A. arcticus
- A. bernardensis
- A. bernardii
- A. caribeum
- A. chlorogonioides
- A. cucumiformis
- A. densus
- A. dulcia
- A. dybowskii
- A. ecsediensis
- A. extensus
- A. falcatus
- A. falciformia
- A. fasciculatus
- A. flexuosus
- A. fractus
- A. fusiformis
- A. gracilis
- A. hindakii
- A. komarekii
- A. lacuster
- A. marinus
- A. minutus
- A. nannoselene
- A. nivalis
- A. pehrii
- A. polymorphus
- A. pseudosabulosum
- A. pyrenogerum
- A. quaternus
- A. rhaphidioides
- A. selenastrum
- A. septatus
- A. sigmoideus
- A. spiralis
- A. spirochromus
- A. stipitatus
- A. tjibodensis
- A. tortus
- A. turneri
- A. viretii
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
