Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Accommodation (vertebrate eye)
Focusing ability of eye From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point—the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a reflex, including part of the accommodation-convergence reflex, but it can also be consciously controlled.
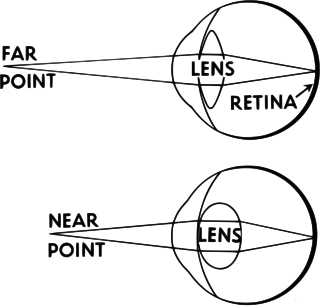

The main ways animals may change focus are:
- Changing the shape of the lens.
- Changing the position of the lens relative to the retina.
- Changing the axial length of the eyeball.
- Changing the shape of the cornea.
Remove ads
Focusing mechanisms
Summarize
Perspective

Focusing the light scattered by objects in a three dimensional environment into a two dimensional collection of individual bright points of light requires the light to be bent. To get a good image of these points of light on a defined area requires a precise systematic bending of light called refraction. The real image formed from millions of these points of light is what animals see using their retinas. Very even systematic curvature of parts of the cornea and lens produces this systematic bending of light onto the retina.

Due to the nature of optics the focused image on the retina is always inverted relative to the object. Different animals live in different environments having different refractive indices involving water, air and often both. The eyes are therefore required to bend light by different amounts leading to different mechanisms of focus being used in different environments. The air/cornea interface involves a larger difference in refractive index than hydrated structures within the eye. As a result, animals living in air have most of the bending of light achieved at the air/cornea interface with the lens being involved in finer focus of the image.
Generally mammals, birds and reptiles living in air vary their eyes' optical power by subtly and precisely changing the shape of the elastic lens using the ciliary body.
The small difference in refractive index between water and the hydrated cornea means fish and amphibians need to bend the light more using the internal structures of the eye. Therefore, eyes evolved in water have a mechanism involving changing the distance between a rigid rounder more refractive lens and the retina using less uniform muscles rather than subtly changing the shape of the lens itself using circularly arranged muscles.[1]
Land based animals and the shape changing lens
Varying forms of direct experimental proof outlined in this article show that most non-aquatic vertebrates achieve focus, at least in part, by changing the shapes of their lenses.
What is less well understood is how the subtle, precise and very quick changes in lens shape are made. Direct experimental proof of any lens model is necessarily difficult as the vertebrate lens is transparent and only functions well in the living animal. When considering vertebrates, aspects of all models may play varying roles in lens focus. The models can be broadly divided into two camps: those models that stress the importance of external forces acting on a more passively elastic lens and other models that include forces that may be generated by the lens internally.
External forces
The model of a shape changing lens of humans was proposed by Thomas Young in a lecture on the 27th Nov 1800.[2] Others such as Hermann von Helmholtz and Thomas Henry Huxley refined the model in the mid-1800s explaining how the ciliary muscle contracts, rounding the lens to focus near.[3][4][5] The model may be summarized like this: normally the lens is held under tension by its suspending ligaments and capsule being pulled tight by the pressure of the eyeball. At short focal distance the ciliary muscle contracts, stretching the ciliary body and relieving some of the tension on the suspensory ligaments, allowing the elastic lens to become more spherical, increasing refractive power. Changing focus to an object at a greater distance requires a thinner less curved lens. This is achieved by relaxing some of the sphincter-like ciliary muscles allowing the ciliarly body to spring back, pulling harder on the lens making it less curved and thinner, so increasing the focal distance. There is a problem with the Helmholtz model in that despite mathematical models being tried, none has come close enough to working using only the Helmholtz mechanisms.[6]

In 1992, Ronald Schachar proposed a model for land based vertebrates that was not well received.[7] The theory allows mathematical modeling to more accurately reflect the way the lens focuses while also taking into account the complexities in the suspensory ligaments and the presence of radial as well as circular muscles in the ciliary body.[8][9] In this model the ligaments may pull to varying degrees on the lens at the equator using the radial muscles, while the ligaments offset from the equator to the front and back[10] are relaxed to varying degrees by contracting the circular muscles.[11] These multiple actions[12] operating on the elastic lens allows it to change lens shape at the front more subtly. Not only changing focus, but also correcting for lens aberrations that might otherwise result from the changing shape while better fitting mathematical modeling.[6]
The "catenary" model of lens focus proposed by Coleman[13] demands less tension on the ligaments suspending the lens. Rather than the lens as a whole being stretched thinner for distance vision and allowed to relax for near focus, contraction of the circular ciliary muscles results in the lens having less hydrostatic pressure against its front. The lens front can then reform its shape between the suspensory ligaments in a similar way to a slack chain hanging between two poles might change its curve when the poles are moved closer together. This model requires precise fluid movement of the lens front only rather than trying to change the shape of the lens as a whole. While this concept may be involved in the focusing it has been shown by Scheimpflug photography that the rear of the lens also changes shape in the living eye.[14]
Internal forces


When Thomas Young proposed the changing of the human lens' shape as the mechanism for focal accommodation in 1801, he thought the lens may be a muscle capable of contraction. This type of model is termed intracapsular accommodation as it relies on activity within the lens. In a 1911 Nobel lecture Allvar Gullstrand spoke on "How I found the intracapsular mechanism of accommodation" and this aspect of lens focusing continues to be investigated.[15][16][17] Young spent time searching for the nerves that could stimulate the lens to contract without success. Since that time it has become clear the lens is not a simple muscle stimulated by a nerve so the 1909 Helmholtz model took precedence. Pre-twentieth century investigators did not have the benefit of many later discoveries and techniques. Membrane proteins such as aquaporins which allow water to flow into and out of cells are the most abundant membrane protein in the lens.[18][19] Connexins which allow electrical coupling of cells are also prevalent. Electron microscopy and immunofluorescent microscopy show fiber cells to be highly variable in structure and composition.[20][21][22] Magnetic resonance imaging confirms a layering in the lens that may allow for different refractive plans within it.[23] The refractive index of human lens varies from approximately 1.406 in the central layers down to 1.386 in less dense layers of the lens.[24] This index gradient enhances the optical power of the lens. As more is learned about mammalian lens structure from in situ Scheimpflug photography, MRI[14][25] and physiological investigations, it is becoming apparent the lens itself is not responding entirely passively to the surrounding ciliary muscle, but may be able to change its overall refractive index through mechanisms involving water dynamics in the lens still to be clarified.[26][27][28] The accompanying micrograph shows wrinkled fibers from a relaxed sheep lens after it is removed from the animal indicating shortening of the lens fibers during near focus accommodation. The age related changes in the human lens may also be related to changes in the water dynamics in the lens.[29][30]
Human eyes

The young human eye can change focus from distance (infinity) to as near as 6.5 cm from the eye.[32][33] This dramatic change in focal power of the eye of approximately 15 dioptres (the reciprocal of focal length in metres) occurs as a consequence of a reduction in zonular tension induced by ciliary muscle contraction. This process can occur in as little as 224 ± 30 milliseconds in bright light.[34] The amplitude of accommodation declines with age. By the fifth decade of life the accommodative amplitude can decline so that the near point of the eye is more remote than the reading distance. When this occurs the patient is presbyopic. Once presbyopia occurs, those who are emmetropic (i.e., do not require optical correction for distance vision) will need an optical aid for near vision; those who are myopic (nearsighted and require an optical correction for distance or far vision), will find that they see better at near without their distance correction; and those who are hyperopic (farsighted) will find that they may need a correction for both distance and near vision. Note that these effects are most noticeable when the pupil is large; i.e. in dim light. The age-related decline in accommodation occurs almost universally to less than 2 dioptres by the time a person reaches 45 to 50 years, by which time most of the population will have noticed a decrease in their ability to focus on close objects and hence require glasses for reading or bifocal lenses. Accommodation decreases to about 1 dioptre at the age of 70 years. The dependency of accommodation amplitude on age is graphically summarized by Duane's classical curves.[31]
Amplitude of accommodation
The amplitude of accommodation is a clinical measurement that describes the maximum potential increase in optical power that an eye can achieve in adjusting its focus. It refers to a certain range of object distances for which the retinal image is as sharply focused as possible. Amplitude of accommodation is measured during routine eye-examination. The closest that a normal eye can focus is typically about 10 cm for a child or young adult. Accommodation then decreases gradually with age, effectively finishing just after age fifty.[35][36][37] The average amplitude of accommodation, in diopters, for a patient of a given age was estimated by Hofstetter in 1950 to be 18.5 − (0.30 × patient age in years) with the minimum amplitude of accommodation as 15 − (0.25 × age in years), and the maximum as 25 − (0.40 × age in years). However, Hofstetter's work was based on data from two early surveys[38][39] which, although widely cited, used methodology with considerable inherent error. (Donders, Sheard, Duane, Turner for reference)
Theories on how humans focus
- Helmholtz—The most widely held[40] theory of accommodation is that proposed by Hermann von Helmholtz in 1855. When viewing a far object, the circularly arranged ciliary muscle relaxes allowing the lens zonules and suspensory ligaments to pull on the lens, flattening it. The source of the tension is the pressure that the vitreous and aqueous humours exert outwards onto the sclera. When viewing a near object, the ciliary muscles contract (resisting the outward pressure on the sclera) causing the lens zonules to slacken which allows the lens to spring back into a thicker, more convex, form.
- Schachar—Ronald A. Schachar proposed in 1992 what has been called a "rather bizarre geometric theory"[41] which claims that focus by the human lens is associated with increased tension on the lens via the equatorial zonules; that when the ciliary muscle contracts, equatorial zonular tension is increased, causing the central surfaces of the crystalline lens to steepen, the central thickness of the lens to increase (anterior-posterior diameter), and the peripheral surfaces of the lens to flatten. While the tension on equatorial zonules is increased during accommodation, the anterior and posterior zonules are simultaneously relaxing. The increased equatorial zonular tension keeps the lens stable and flattens the peripheral lens surface during accommodation. As a consequence, gravity does not affect the amplitude of accommodation and primary spherical aberration shifts in the negative direction during accommodation.[42][43] The theory has not found much independent support.[citation needed]
- Catenary—D. Jackson Coleman proposes that the lens, zonule and anterior vitreous comprise a diaphragm between the anterior and vitreous chambers of the eye.[44] Ciliary muscle contraction initiates a pressure gradient between the vitreous and aqueous compartments that support the anterior lens shape. It is in this lens shape that the mechanically reproducible state of a steep radius of curvature in the center of the lens with slight flattening of the peripheral anterior lens, i.e. the shape, in cross section, of a catenary occurs. The anterior capsule and the zonule form a trampoline shape or hammock shaped surface that is totally reproducible depending on the circular dimensions, i.e. the diameter of the ciliary body (Müeller's muscle). The ciliary body thus directs the shape like the pylons of a suspension bridge, but does not need to support an equatorial traction force to flatten the lens.[45][46]
Induced effects of accommodation
When humans accommodate to a near object, they also converge their eyes and constrict their pupils. The combination of these three movements (accommodation, convergence and miosis) is under the control of the Edinger-Westphal nucleus and is referred to as the near triad, or accommodation reflex.[47] While it is well understood that proper convergence is necessary to prevent diplopia, the functional role of the pupillary constriction remains less clear. Arguably, it may increase the depth of field by reducing the aperture of the eye, and thus reduce the amount of accommodation needed to bring the image in focus on the retina.[48]
There is a measurable ratio (Matthiessen's ratio) between how much convergence takes place because of accommodation (AC/A ratio, CA/C ratio). Abnormalities with this can lead to binocular vision problems.[49]
Anomalies of accommodation described in humans
There are many types of accommodation anomalies. It can be broadly classified into two, decreased accommodation and increased accommodation.[50] Decreased accommodation may occur due to physiological (presbyopia), pharmacological (cycloplegia) or pathological.[50] Excessive accommodation and spasm of accommodation are types of increased accommodation.[citation needed]
Presbyopia
Presbyopia, physiological insufficiency of accommodation due to age related changes in lens (decreased elasticity and increased hardness) and ciliary muscle power is the commonest form of accommodative dysfunction.[50] It will cause gradual decrease in near vision.
Accommodative insufficiency
Accommodative insufficiency is the condition where amplitude of accommodation of a person is lesser compared to physiological limits for their age.[50] Premature sclerosis of lens or ciliary muscle weaknesses due to systemic or local cases may cause accommodative insufficiency.[50] Accommodative insufficiency is further categorised into different categories.[citation needed]
Ill-sustained accommodation
Ill-sustained accommodation is a condition similar to accommodative insufficiency. In this, range of accommodation will be normal, but after excessive near work accommodative power will decrease.[51]
Paralysis of accommodation
In paralysis of accommodation, amplitude of accommodation is either markedly reduced or completely absent (cycloplegia).[52] It may occur due to ciliary muscle paralysis or occulomotor nerve paralysis.[50] Parasympatholytic drugs like atropine will also cause paralysis of accommodation.[51]
Unequal accommodation
If there is amplitude of accommodation between the eyes differ 0.5 dioptre or more, it is considered as unequal.[52] Organic diseases, head trauma or functional amblyopia may be responsible for unequal accommodation.[52]
Accommodative infacility
Accommodative infacility is also known as accommodative inertia.[52] In this condition there will be difficulty in changing accommodation from one point to other. There may be difficulty in adjusting focus from distance from near.[51] It is a comparatively rare condition.
Spasm of accommodation
Spasm of accommodation also known as ciliary spasm is a condition of abnormally excessive accommodation which is out of voluntary control of the person.[50] Vision may be blurred due to induced pseudomyopia.
Accommodative excess
Accommodative excess occurs when an individual uses more than normal accommodation for performing certain near work. Modern definitions simply regard it as an inability to relax accommodation readily.[52]
Aquatic animals


Aquatic animals include some that also thrive in the air so focusing mechanisms vary more than in those that are only land based. Some whales and seals are able to focus above and below water having two areas of retina with high numbers of rods and cones[53] rather than one as in humans. Having two high resolution area of retina presumably allows two axis of vision one for above and one for below water. In reptiles and birds, the ciliary body which supports the lens via suspensory ligaments (ligamentum suspensorium) also touches the lens with a number of pads on its inner surface. These pads compress and release the lens to modify its shape while focusing on objects at different distances; the suspensory ligaments usually perform this function in mammals. With vision in fish and amphibians, the lens is fixed in shape, and focusing is instead achieved by moving the lens forwards or backwards within the eye using a muscle called the retractor lentus.[54]
In cartilaginous fish, the suspensory ligaments are replaced by a membrane, including a small muscle at the underside of the lens. This muscle pulls the lens forward from its relaxed position when focusing on nearby objects. In teleosts, by contrast, a muscle (retractor lentis) projects from a vascular structure in the floor of the eye, called the falciform process, and serves to pull the lens backwards from the relaxed position to focus on distant objects. The muscle is antagonistic to the suspensory ligaments. While amphibians move the lens forward, as do cartilaginous fish, the muscles involved are not similar in either type of animal. In frogs, there are two muscles, one above and one below the lens, while other amphibians have only the lower muscle.[54]
In the simplest vertebrates, the lampreys and hagfish, the lens is not attached to the outer surface of the eyeball at all. There is no aqueous humor in these fish, and the vitreous body simply presses the lens against the surface of the cornea. To focus its eyes, a lamprey flattens the cornea using muscles outside of the eye and pushes the lens backwards.[54]
While not vertebrate, brief mention is made here of the convergent evolution of vertebrate and Molluscan eyes. The most complex Molluscan eye is the Cephalopod eye which is superficially similar structure and function to a vertebrate eye, including accommodation, while differing in basic ways such as having a two part lens and no cornea.[55][56] The fundamental requirements of optics must be filled by all eyes with lenses using the tissues at their disposal so superficially eyes all tend to look similar. It is the way optical requirements are met using different cell types and structural mechanisms that varies among animals.
Remove ads
See also
Disorders of and relating to accommodation
Other
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
