Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Algar–Flynn–Oyamada reaction
Chemical reaction producing flavonol From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Algar–Flynn–Oyamada reaction is a chemical reaction whereby a chalcone undergoes an oxidative cyclization to form a flavonol.[1][2]
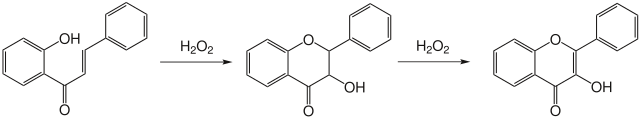
Reaction mechanism
There are several possible mechanisms to explain this reaction; however, these reaction mechanisms have not been elucidated. What is known is that a two-stage mechanism exists. First, dihydroflavonol is formed, which then subsequently oxidizes to form a flavonol.
Proposed mechanisms involving epoxidation of the alkene have been disproven.[3]
The probable mechanisms are thus two possibilities:
- The phenoxide attacks the enone at the beta position, and the alkene directly attacks hydrogen peroxide from the alpha position, forming the dihydroflavonol.
- The phenoxide attacks the enone at the beta position, closing the six-membered ring and forming an enolate intermediate. The enolate then attacks hydrogen peroxide, forming the dihydroflavonol.

Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads