ActivityPub
Decentralized social networking protocol From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
ActivityPub is a protocol and open standard for decentralized social networking. It provides a client-to-server (C2S) API for creating and modifying content, as well as a federated server-to-server (S2S) protocol for delivering notifications and content to other servers.[2] ActivityPub has become the main standard used in the fediverse, a popular network used for social networking that consists of software such as Mastodon, Pixelfed and PeerTube.[3]
| Communication protocol | |
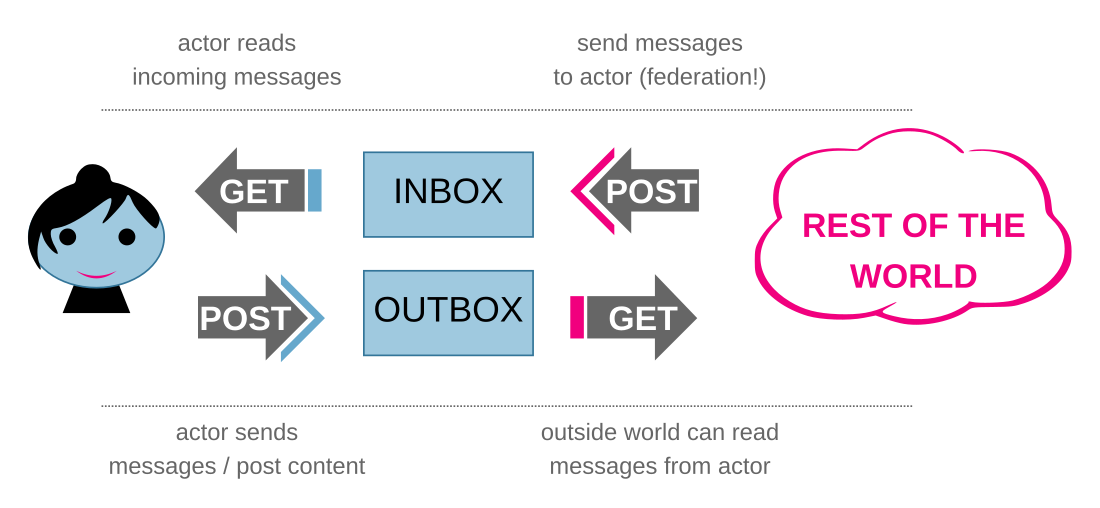
 An infographic of the core functionality of ActivityPub | |
| Abbreviation | AP |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Decentralized social networking |
| Developer(s) | World Wide Web Consortium, Christine Lemmer-Webber, Evan Prodromou, et al. |
| Introduction | January 23, 2018 |
| Based on | ActivityStreams, JSON-LD |
| Influenced | AT Protocol[1] |
| Website | activitypub |
ActivityPub is considered to be an update to the ActivityPump protocol used in pump.io, and the official W3C repository for ActivityPub is identified as a fork of ActivityPump.[4][5] The creation of a new standard for decentralized social networking was prompted by the complexity of OStatus, the most commonly used protocol at the time. OStatus was built using a multitude of technologies (such as Atom, Salmon, WebSub and WebFinger), a product of the infrastructure used in GNU social (the originator and largest user of the OStatus protocol), which made it difficult to implement the protocol into new software. OStatus was also only designed to work with microblogging services, with little flexibility to the types of data that it could hold.
The standard was first published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as a W3C Recommendation in January 2018 by the Social Web Working Group (SocialWG), a working group chartered to build the protocols and vocabularies needed to create a standard for social functionality.[6] Shortly after, further development was moved to the Social Web Community Group (SocialCG), the successor to the SocialWG.
Design
Summarize
Perspective
ActivityPub uses the ActivityStreams 2.0 format for building its content, which itself uses JSON-LD. The three main data types used in ActivityPub are Objects, Activities and Actors. Objects are the most common data type, and can be images, videos, or more abstract items such as locations or events. Activities are actions that create and modify objects, for example a Create activity creates an object. Actors are representative of an individual, a group, an application or a service, and are the owners of objects.
Every actor type contains an inbox and outbox stream, which sends and receives activities for a user. In order to publish data (for example liking an article), a user creates an activity that declares that they liked an Article object and publishes it to their outbox, where it is then delivered by the ActivityPub server via a POST request to the inboxes listed in the activity's to, bto, cc and bcc fields. The receiving servers then account for the newly received activity and update the article by adding the like action to it.
Lead author Christine Lemmer-Webber notes that the team predominantly identified as queer, which led to features that help users and administrators protect against "undesired interaction". She also notes that the team authoring ActivityPub had no corporate participation.[7]
Example data
An example actor object that represents a user account:[8]
{
"@context": ["https://www.w3.org/ns/activitystreams",
{"@language": "ja"}],
"type": "Person",
"id": "https://kenzoishii.example.com/",
"following": "https://kenzoishii.example.com/following.json",
"followers": "https://kenzoishii.example.com/followers.json",
"liked": "https://kenzoishii.example.com/liked.json",
"inbox": "https://kenzoishii.example.com/inbox.json",
"outbox": "https://kenzoishii.example.com/feed.json",
"preferredUsername": "kenzoishii",
"name": "石井健蔵",
"summary": "この方はただの例です",
"icon": [
"https://kenzoishii.example.com/image/165987aklre4"
]
}
An example activity that likes an article object:
{
"@context": ["https://www.w3.org/ns/activitystreams",
{"@language": "en"}],
"type": "Like",
"actor": "https://dustycloud.org/christine/",
"summary": "Christine liked 'Minimal ActivityPub update client'",
"object": "https://rhiaro.co.uk/2016/05/minimal-activitypub",
"to": ["https://rhiaro.co.uk/#amy",
"https://dustycloud.org/followers",
"https://rhiaro.co.uk/followers/"],
"cc": "https://e14n.com/evan"
}
An example article object:
{
"@context": ["https://www.w3.org/ns/activitystreams",
{"@language": "en-GB"}],
"id": "https://rhiaro.co.uk/2016/05/minimal-activitypub",
"type": "Article",
"name": "Minimal ActivityPub update client",
"content": "Today I finished morph, a client for posting ActivityStreams2...",
"attributedTo": "https://rhiaro.co.uk/#amy",
"to": "https://rhiaro.co.uk/followers/",
"cc": "https://e14n.com/evan"
}
Project status
The SocialCG previously organized a yearly free conference called ActivityPub Conf about the future of ActivityPub.[9][10] Triages are held regularly to review issues pertaining to the ActivityPub and ActivityStreams 2.0 specifications as part of the SocialCG.[11]
In 2023, Germany's Sovereign Tech Fund donated €152,000 to socialweb.coop with the goal of building a new suite for testing various ActivityPub implementations and their compliance with the specification.[12]
Adoption
The initial wave of adoption for ActivityPub (circa 2016-2018) came from software that was already using OStatus as their federation protocol, such as Mastodon, GNU social and Pleroma.[13] Following the acquisition of Twitter by Elon Musk in 2022, many groups of users that were critical of the acquisition migrated to Mastodon, bringing new attention to the ActivityPub protocol with it.[14] Various major social media platforms and corporations have since pledged to implement ActivityPub support, including Tumblr,[15] Flipboard[16] and Meta Platforms' Threads.[17]
Criticism
Summarize
Perspective
Accidental denial-of-service attacks
Poorly optimized ActivityPub implementations can cause unintentional distributed denial-of-service (DDOS) attacks on other websites and servers, due to the decentralized nature of the network.[citation needed] An example would be Mastodon's implementation of OpenGraph link previews, wherein every instance that receives a post that contains a link with OpenGraph metadata will download the associated data, such as a thumbnail, in a very short timeframe, which can slow down or crash servers as a result of the sudden burst of requests.[18][19]
Account migration
ActivityPub has been criticized for not natively supporting moving accounts from one server to another, forcing implementations to build their own solutions.[20] While there has been work on building a standardized system for migrating accounts using the Move activity via the Fediverse Enhancement Proposal organization, the current proposal only allows for basic follower migration, with all other data remaining linked to the original account.[21]
Missing content and data
ActivityPub implementations have been criticized for missing replies and parts of reply threads from remote posts, and presenting outdated statistics (e.g. likes and reposts) about remote posts.[22][23] However, this isn't a problem with the ActivityPub protocol itself, but with implementations not refreshing their content for updated data when needed.[24][25][citation needed]
Software using ActivityPub
| Software name | Total users[26][27] | Initial ActivityPub-compatible release | Type of software | Fork of |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akkoma | 18,108 | 2022[28] | Blogging | Pleroma |
| BookWyrm[29] | 34,351 | 2021[30] | Book cataloging | |
| Castopod | ? | 2020[31] | Audio hosting | |
| dokieli | ? | 2018[32] | Authoring system, Blogging, Notification system, Semantic publishing, Web annotation | |
| Epicyon | 3 | 2019[33] | Blogging | |
| Firefish | 19,695 | 2022[34] | Blogging | Misskey |
| Flipboard[35] | 145,000,000[36] | 2023[37][38] | Social news | |
| Friendica[39] | 20,069 | 2019 | Blogging, event management, groups, image gallery | |
| Funkwhale | 11,448 | 2018[40] | Audio hosting | |
| Gancio[41] | 1,273 | 2020[42] | Calendar, event planner | |
| GNU social | 368 | 2018[43] | Blogging | |
| Guppe[44] | ? | 2021[45] | Groups | |
| GoToSocial | 1,919 | 2021[46] | Blogging | |
| Hollo | 48 | 2024[47] | Blogging | |
| Honk | 7 | 2019[48] | Blogging | |
| Hubzilla[49] | 5,748 | 2017 | Blogging, event planner, file hosting, image gallery, wiki | |
| Inventaire.io[50] | ? | 2021 | Book cataloging | |
| kbin[51] | 66,320 | 2023 | Social news | |
| Lemmy[52] | 392,074 | 2019 | Social news | |
| Libervia[53] | ? | 2022 (in beta) | Blogging, event management, file sharing, instant messaging | |
| lotide[54] | 457 | 2020[55] | Social news | |
| Mastodon | 9,630,383 | 2017[56] | Blogging | |
| Mobilizon | 45,503 | 2020 | Event management, groups | |
| mbin[57] | 5,490 | 2023 | Social news | kbin |
| Micro.blog | 168,418 | 2021[58] | Microblogging | |
| microblog.pub | 66 | 2022[59] | Blogging | |
| Misskey | 849,930 | 2018[60] | Blogging | |
| Nextcloud Social | 50 (approx.) | 2018[61] | Blogging | |
| NodeBB | ? | 2025[62] | Internet forum | |
| Owncast[63] | 240 | 2022 | Live streaming | |
| PeerTube[64] | 351,142 | 2018 | Video sharing | |
| Pixelfed[65] | 18,733 | 2018 | Image sharing | |
| Pleroma | 138,294 | 2018[66] | Blogging | |
| Plume[67] | 25,290 | 2018[68] | Blogging | |
| Postmarks[69] | 29 | 2023[70] | Social bookmarking | |
| Sharkey[71] | 20,807 | 2023 | Blogging | Misskey |
| Snac[72] | 176 | 2022[73] | Blogging | |
| Socialhome | 2,325 | 2016[74] | Blogging | |
| Streams[75] | ? | 2022[76] | Blogging, image sharing, wiki | |
| Takahē | 278 | 2022[77] | Blogging | |
| Threads | 130,000,000[78] | 2023[79] | Blogging | |
| Wafrn[80] | 891 | 2023 | Blogging | |
| WordPress[81][82] | 6,000+ blogs[83] | 2023[84] | Blogging | |
| WriteFreely | 160,761 | 2018[85] | Blogging | |
| Zap[86] | 22 | 2019[87] | Blogging, file hosting, image gallery |
Future implementations
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.