Acetylenediol
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
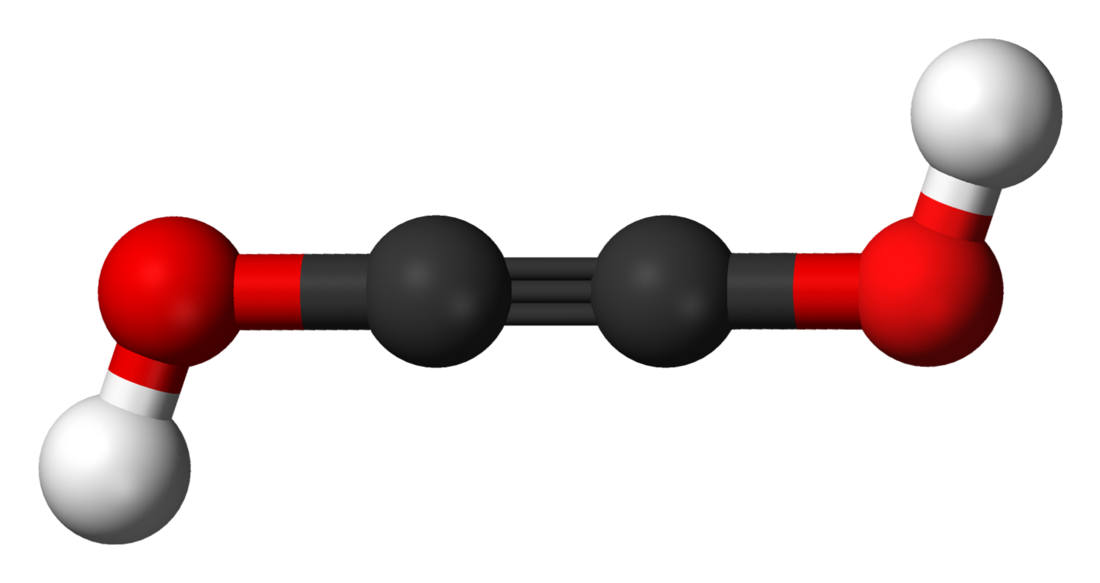
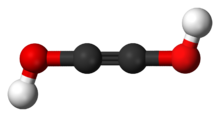
Acetylenediol, or ethynediol, is a chemical substance with formula HO−C≡C−OH (an ynol). It is the diol of acetylene. Acetylenediol is unstable in the condensed phase, although its tautomer glyoxal (CHO)2 is well known.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethynediol | |
| Other names
Dihydroxyacetylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 58.07 g/mol |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Detection
Acetylenediol was first observed in the gas-phase by mass spectrometry.[1] The compound was later obtained by photolysis of squaric acid in a solid argon matrix at 10 K (−263 °C).[2] Recently, this molecule was synthesized in interstellar ice analogs composed of carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O) upon exposure to energetic electrons and detected upon sublimation by isomer-selective photoionization reflectron time-of-flight mass spectrometry.[3]
Derivatives
Summarize
Perspective
Alkoxide derivatives
Like the diol, most simple ether derivatives are labile. Di-tert-butoxyacetylene is however a distillable liquid.
Acetylenediolate salts
Salts of the acetylenediolate (ethynediolate) dianion −O−C≡C−O− are known. They are not however prepared from ethynediol, but by the reduction of carbon monoxide. Potassium acetylenediolate (K2C2O2) was first obtained by Liebig in 1834, from the reaction of carbon monoxide with metallic potassium;[4] but for a long time the product was assumed to be "potassium carbonyl" (KCO). Over the next 130 years were described the "carbonyls" of sodium (Johannis, 1893), barium (Gunz and Mentrel, 1903), strontium (Roederer, 1906), and lithium, rubidium, and caesium (Pearson, 1933).[5] The reaction was eventually shown to yield a mixture of the potassium acetylenediolate K
2C
2O
2 and potassium benzenehexolate K
6C
6O
6.[6]
The structure of these salts was clarified only in 1963 by Büchner and Weiss.[7][8]
Acetylenediolates can also be prepared by the rapid reaction of CO and a solution of the corresponding metal in liquid ammonia at low temperature.[5] Potassium acetylenediolate is a pale yellow solid that reacts explosively with air, halogens, halogenated hydrocarbons, alcohols, water, and any substance which possesses an acidic hydrogen.[9]
Coordination complexes
Acetylenediol can form coordination compounds, such as [TaH(HOC≡COH)(dmpe)2Cl]+Cl− where dmpe is bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane.[10]
Acetylenediolate and related anions such as deltate C
3O2−
3 and squarate C
4O2−
4 have been obtained from carbon monoxide under mild conditions by reductive coupling of CO ligands in organouranium complexes.[11]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.